|
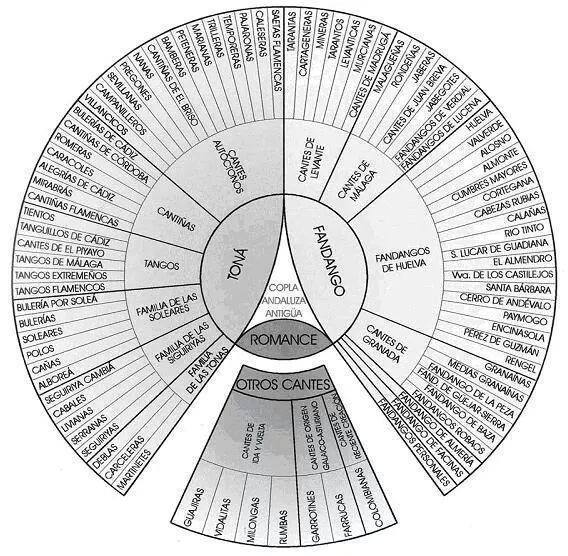
Cantes A Palo Seco
The Spanish term Cantes a palo seco refers to a category of flamenco palo (flamenco), palos (musical forms) traditionally sung a cappella or, in some cases, with some sort of percussion. The category comprises the following palos: * Tonás * Martinetes * Debla * Carceleras * Saeta (flamenco), Saetas * Trilla or ''Trilleras''. In fact, almost any ''palo'' can be sung unaccompanied, especially in private ''juergas'' (parties), where there is often no guitarist available. Even in professional settings, some palos which are normally accompanied by the guitar, like seguiriya, bulerías, or even soleá, are sometimes heard 'a palo seco'. References Flamenco styles Music of Spain Music of Andalusia Vocal music {{Music-genre-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palo (flamenco)
A ''palo'' () or cante is the name given in flamenco for the different traditional musical forms. The word ''palo'', in Spanish, has several meanings, the main one being "stick", "pole", "rod", "tree" or "branch", but in this case it has the sense of "Playing card, suit of cards" i.e. Categorization, category or classification. Identifying palos Each ''palo'' is identified by a variety of musical features such as its Rhythm, rhythmic pattern, its Musical mode, mode, its characteristic Motif (music), motifs, the type of stanza used for the lyrics, and its origin. The concept of ''palo'' is not straightforward or rigorous. It is a popular, sometimes inconsistent way of classifying songs according to similar characteristics. For example, to determine that a song belongs to the ''palo'' called Bulerías, only the rhythm is taken into consideration, no matter its mode or stanza. Fandangos, on the other hand, include a variety of forms in or , but later it developed "free" forms (t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musical Form
In music, ''form'' refers to the structure of a musical composition or musical improvisation, performance. In his book, ''Worlds of Music'', Jeff Todd Titon suggests that a number of organizational elements may determine the formal structure of a piece of music, such as "the arrangement of musical units of rhythm, melody, and/or harmony that show repetition (music), repetition or variation (music), variation, the arrangement of the instruments (as in the order of solo (music), solos in a jazz or bluegrass performance), or the way a symphonic piece is orchestration, orchestrated", among other factors. It is, "the ways in which a composition is shaped to create a meaningful musical experience for the listener."Kostka, Stefan and Payne, Dorothy (1995). ''Tonal Harmony'', p.152. McGraw-Hill. . These organizational elements may be broken into smaller units called phrases, which express a musical idea but lack sufficient weight to stand alone. Musical form unfolds over time through t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Cappella
Music performed a cappella ( , , ; ), less commonly spelled acapella in English, is music performed by a singer or a singing group without instrumental accompaniment. The term ''a cappella'' was originally intended to differentiate between Renaissance music, Renaissance polyphony and Baroque (music), Baroque concertato musical styles. In the 19th century, a renewed interest in Renaissance polyphony, coupled with an ignorance of the fact that vocal parts were often doubled by instrumentalists, led to the term coming to mean unaccompanied vocal music. The term is also used, rarely, as a synonym for ''alla breve''. Early history Research suggests that singing and vocables may have been what early humans used to communicate before the invention of language. The earliest piece of sheet music is thought to have originated from times as early as 2000 BC, while the earliest that has survived in its entirety is from the first century AD: a piece from Greece called the Seikilos epi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonás
Tonás () is a palo or type of flamenco songs. It belongs to the wider category of Cantes a palo seco, ''palos'' that are sung a cappella. Owing to this feature, they are considered by traditional flamencology to be the oldest surviving musical form of flamenco. This musical form originated in the Calé Romani subculture of Southern Spain. The first known flamenco singer, Tío Luis el de la Juliana, who lived in Jerez de la Frontera Jerez de la Frontera () or simply Jerez, also cited in old English-language sources as , is a city and Municipalities of Spain, municipality in the province of Cádiz in the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia, Sp ... in the last third of the 18th century, was said to have excelled in this ''palo''. Other ''cantes a palo seco'', such as martinetes and debla, are sometimes classified under ''tonás'', while at other times they are referred to as ''palos'' on their own. The ''tonás'' were almost in disuse by the en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martinetes
''Martinetes'' (, sing. ''martinete'') are a flamenco '' palo'' belonging to the group of the ''tonás'' or ''cantes a palo seco''. As the rest of the songs in this group, it is sung with no accompaniment. In some dance shows for the stage, though, it is accompanied by percussion played with the compás of siguiriya. The percussion instruments chosen for this are frequently a hammer and anvil, to evocate the origins of this ''palo'', attributed to Gypsy smiths. It is not probable, though, that they were real work songs: they demand too much effort and faculties to be sung while carrying out a heavy task like that of a smith. They were more probably sung in family gatherings. Although martinetes are often classified under the toná group on the grounds that they share its a cappella nature, the melody types differ strongly from the rest of tonás, so it is now generally considered to be a different ''palo''. A characteristic that differentiates them from the tonás, normally in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debla
Fazuelos, also known as fijuelas, hiuelas, deblas, and hojuelas are pastries of thin fried dough. A type of rolled pastry, their origins trace back to Spain, with references dating back to the late Spanish Middle Ages. Sephardic tradition In Sephardic Jewish tradition these pastries, reminiscent of Esther's meguillah due to their characteristic rolled form which recall the shape of Haman's ears, hold cultural significance, particularly during the celebration of Purim.Claudia Roden, (2006), ''The Book of Jewish Food: An Odyssey from Samarkand and Vilna to the Present Day'', Penguin Books, p. 592 Historically, fazuelos were mentioned in literature, notably in Francisco Delicado's ''La Lozana Andaluza'', where a Jewish woman named Aldonza reminisces about preparing the pastry while living in Andalusia, fleeing persecution from the Spanish Inquisition. Fazuelos are also made by non-Jewish communities, especially during the Christian festival of Semana Santa (Holy Week), which co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saeta (flamenco)
The ''saeta'' () is a revered form of Andalusian religious song, whose form and style have evolved over many centuries. Saetas evoke strong emotion and are sung most often during public processions. The saeta, an unaccompanied song, is also believed to stem from Jewish religious songs which are believed to date back to the 16th century. Performance The saeta is a song of Catholic Andalusia dating back many centuries. The ''saeta antigua'' ld saetaprobably arose from the recitation of psalms under the influence of liturgical music. "Saetas vary greatly in form and style, ranging from simple syllabic melodies to highly ornamented ones."Willi Apel, ''Harvard Dictionary of Music'' (Cambridge: The Belknap Press 1944, 1969) at 748. In the older tradition, solemn drums and horns might accompany the singer, or the saetero sang alone. Since the nineteenth century, however, the more favored saetas have incorporated distinct elements associated with Flamenco music, particularly the siguiriy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seguiriya
''Siguiriyas'' (; also ''seguiriyas'', ''siguerillas'', ''siguirillas'', ''seguidilla gitana'', etc.) are a form of flamenco music in the cante jondo category. This deep, expressive style is among the most important in flamenco. Unlike other palos of flamenco, siguiriyas stands out for being purely Romani (Calé) in origin. Siguiriyas are normally played in the key of A Phrygian with each measure (the compás) consisting of 12 counts with emphasis on the 1st, 3rd, 5th, 8th and 11th beats as shown here: : : '' 2 '' 4 '' 6 7 '' 9 10 1'' 12 This rhythm can be contrasted with the rhythmic pattern of the soleares, which also has 12 beats, but the accents fall differently. Taking the unusual accenting into account, it can technically be seen as a measure of 3/4 (counted in eighth notes) starting on "2", then a measure of 6/8 followed by the "1 and" of the 3/4. Every note is evenly spaced apart. For example: : : '' and '' and '' 2 3 '' 5 6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulerías
''Bulería'' (; interchangeable with the plural, ''bulerías'') is a fast flamenco rhythm made up of a 12 beat cycle with emphasis in two general forms as follows: This may be thought of as a measure of followed by a measure of (known as hemiola). For dancers, it is commonly viewed with a compas or bar of 6 counts as opposed to 12. An interesting counting method has been used by Pepe Romero, in his book ''Classical Guitar Style and Technique'', which is 2 measures of time followed by 3 measures of time. This puts the emphasis on the last beat of each measure: When performed, the ''bulería'' always starts on beat twelve of the ''compas'', so the accented beat is heard first. It is normally played at 195-240 beats per minute, most commonly in an A-Phrygian_mode, phrygian mode (por medio) with a sharpened third to make A major the root chord. A typical ''rasgueado'' pattern involves only the A and B chords, were Golpe (guitar technique), golpes are used to accen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soleá
''Soleares'' (plural of ''soleá'', ) is one of the most basic forms or '' palos'' of Flamenco music, probably originating among the Calé Romani people of Cádiz or Seville in Andalusia, the most southern region of Spain. It is usually accompanied by one guitar only, in phrygian mode "''por arriba''" (fundamental on the 6th string); "'' Bulerías por soleá''" is usually played "''por medio''" (fundamental on the 5th string). Soleares is sometimes called "mother of palos" although it is not the oldest one (e.g. siguiriyas is older than soleares) and not even related to every other palo (e.g. fandangos family is from a different origin) Lyrics When singers sing soleá, as with most palos, they normally choose different "''coplas''" (stanzas), with different melody, and combine them according to the inspiration of the moment or to a previous plan. Even if the singer has a previous plan, it is often altered on the spur of the moment. These stanzas are independent in su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flamenco Styles
Flamenco () is an art form based on the various folkloric music traditions of southern Spain, developed within the gitano subculture of the region of Andalusia, and also having historical presence in Extremadura and Murcia. In a wider sense, the term is used to refer to a variety of both contemporary and traditional musical styles typical of southern Spain. Flamenco is closely associated to the gitanos of the Romani ethnicity who have contributed significantly to its origination and professionalization. However, its style is uniquely Andalusian and flamenco artists have historically included Spaniards of both gitano and non-gitano heritage. The oldest record of flamenco music dates to 1774 in the book ''Las Cartas Marruecas'' (The Moroccan Letters) by José Cadalso. The development of flamenco over the past two centuries is well documented: "the theatre movement of sainetes (one-act plays) and tonadillas, popular song books and song sheets, customs, studies of dances, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |