|
Cannulated Bar
A cannulated bar is a bar manufactured with a central hollow that has several medical applications. A cannulated bar is differentiated from a standard medical cannula by its greater outer diameter and wall thickness. Applications Cannulated bars are used as intramedullary rod An intramedullary rod, also known as an intramedullary nail (IM nail) or inter-locking nail or Küntscher nail (without proximal or distal fixation), is a metal rod forced into the medullary cavity of a bone. IM nails have long been used to treat ...s for the fixation of long bone fractures.Ory, François & Fraysse, Jean-Luc & Veisse, Philippe. (2020). Cannulated bar technology for the orthopaedics: application and processing. MATEC Web of Conferences. The central hollow promotes marrow regrowth. In this application, a Kirschner wire may be fed through the hollow to provide fixation and traction at each end of the implant. Cannulated bars are also used as raw material, in the manufacturing of cannulated sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannula
A cannula (; Latin meaning 'little reed'; : cannulae or cannulas) is a tube that can be inserted into the body, often for the delivery or removal of fluid or for the gathering of samples. In simple terms, a cannula can surround the inner or outer surfaces of a trocar needle thus extending the effective needle length by at least half the length of the original needle. Its size mainly ranges from 14 to 26 Needle gauge comparison chart, gauge. Different-sized cannula have different colours as coded. Decannulation is the permanent removal of a cannula (intubation, extubation), especially of a tracheostomy cannula, once a physician determines it is no longer needed for breathing. Medicine Cannulas normally come with a trocar inside. The trocar is a needle, which punctures the body in order to get into the intended space. Intravenous cannulas are the most common in hospital use. A variety of cannulas are used to establish cardiopulmonary bypass in cardiac surgery. A nasal cannula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intramedullary Rod
An intramedullary rod, also known as an intramedullary nail (IM nail) or inter-locking nail or Küntscher nail (without proximal or distal fixation), is a metal rod forced into the medullary cavity of a bone. IM nails have long been used to treat fractures of long bones of the body. Gerhard Küntscher is credited with the first use of this device in 1939, during World War II, for soldiers with fractures of the femur. Prior to that, treatment of such fractures was limited to traction or plaster, both of which required long periods of inactivity. IM nails resulted in earlier return to activity for the soldiers, sometimes even within a span of a few weeks, since they share the load with the bone, rather than entirely supporting the bone. The oldest intramedullary nail was found in the left knee of a mummy named Usermontu, the remains of an Egyptian man from more than 3,500 years ago. Researchers believe the pin was inserted after the man's death, but before his burial. Design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
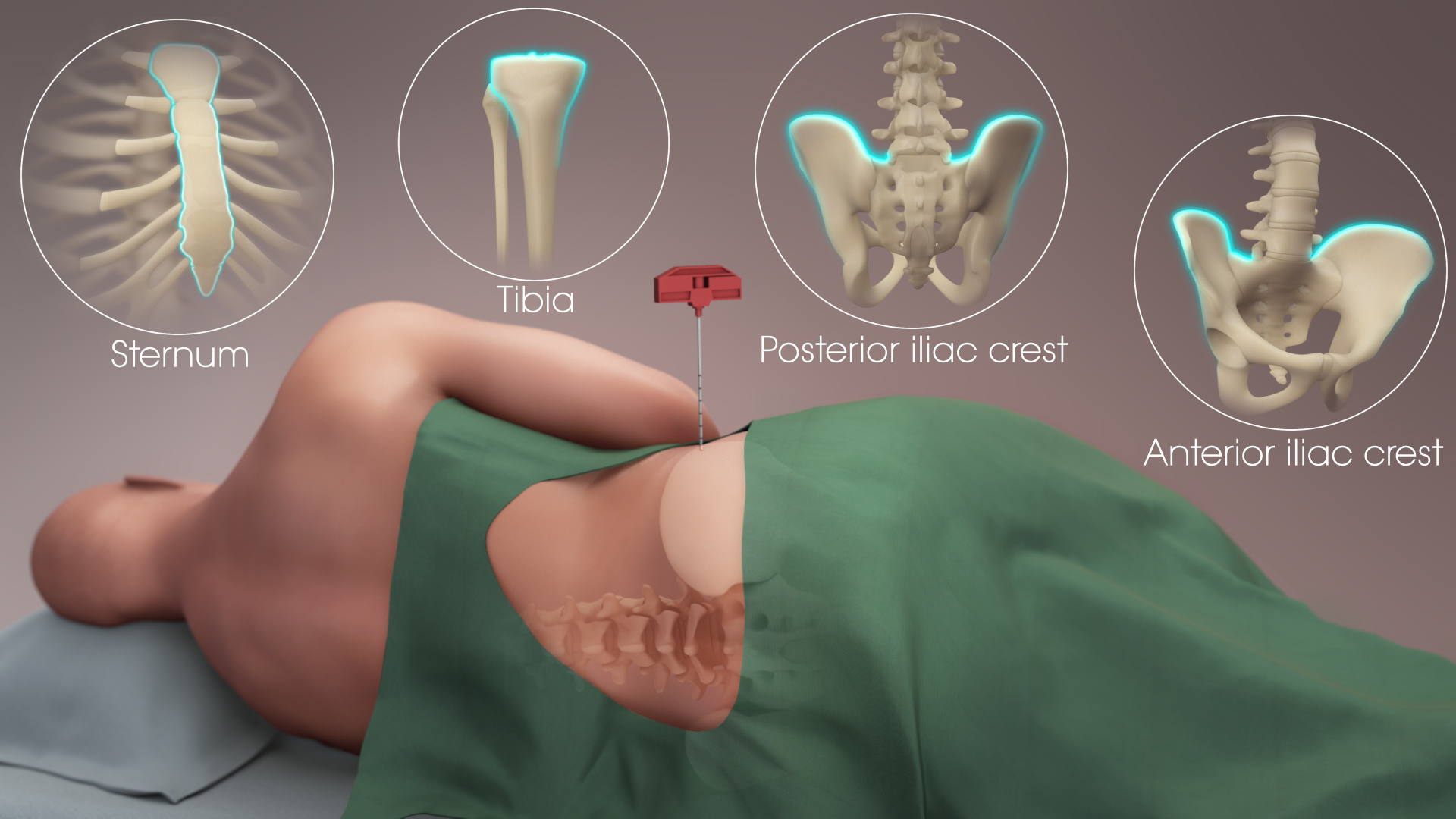
Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of Blood cell, hematopoietic cells, marrow adipose tissue, and supportive stromal cells. In adult humans, bone marrow is primarily located in the Rib cage, ribs, vertebrae, sternum, and Pelvis, bones of the pelvis. Bone marrow comprises approximately 5% of total body mass in healthy adult humans, such that a person weighing 73 kg (161 lbs) will have around 3.7 kg (8 lbs) of bone marrow. Human marrow produces approximately 500 billion blood cells per day, which join the Circulatory system, systemic circulation via permeable vasculature sinusoids within the medullary cavity. All types of Hematopoietic cell, hematopoietic cells, including both Myeloid tissue, myeloid and Lymphocyte, lymphoid lineages, are create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirschner Wire
Kirschner wires or K-wires or pins are sterilized, sharpened, smooth stainless steel pins. Introduced in 1909 by Martin Kirschner, the wires are now widely used in orthopedics and other types of medical and veterinary surgery. They come in different sizes and are used to hold bone fragments together (pin fixation) or to provide an anchor for skeletal traction. The pins are often driven into the bone through the skin (percutaneous pin fixation) using a power or hand drill. They also form part of the Ilizarov apparatus. Variations * Threaded K-wires are available. Used in situations where backing out of the pin is undesirable, they are inherently weaker than smooth K-wires. * "Denham Pins" are strong, stout wires with a threaded portion at the midpoint. They are used for skeletal traction, with the threads engaging the bone. This pin was invented in 1956 by the English orthopedic surgeon Robert Arthur Denham (born 1922). Indications * K-wires are used for temporary fixation duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |