|
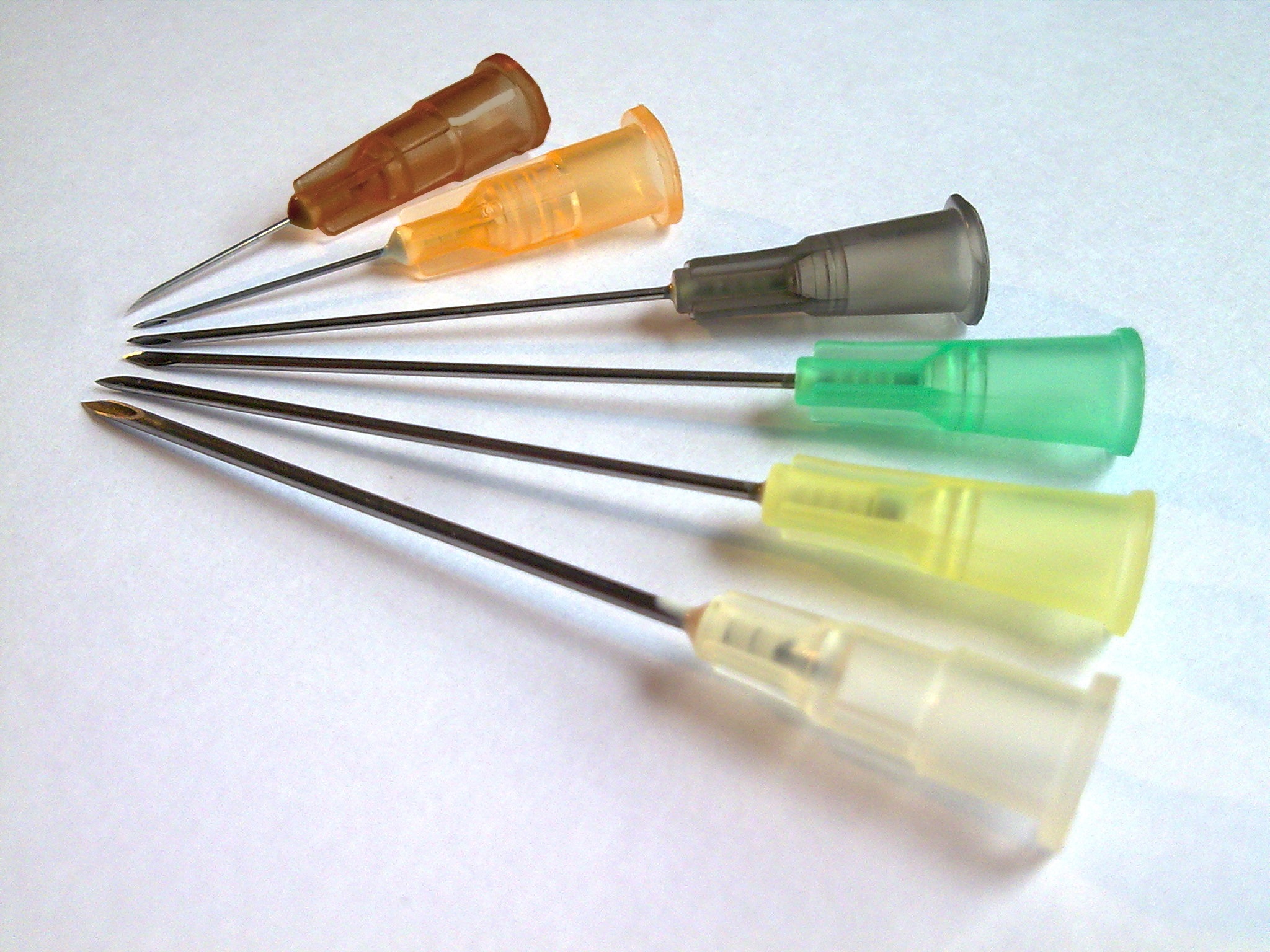
Cannula
A cannula (; Latin meaning 'little reed'; : cannulae or cannulas) is a tube that can be inserted into the body, often for the delivery or removal of fluid or for the gathering of samples. In simple terms, a cannula can surround the inner or outer surfaces of a trocar needle thus extending the effective needle length by at least half the length of the original needle. Its size mainly ranges from 14 to 26 Needle gauge comparison chart, gauge. Different-sized cannula have different colours as coded. Decannulation is the permanent removal of a cannula (intubation, extubation), especially of a tracheostomy cannula, once a physician determines it is no longer needed for breathing. Medicine Cannulas normally come with a trocar inside. The trocar is a needle, which punctures the body in order to get into the intended space. Intravenous cannulas are the most common in hospital use. A variety of cannulas are used to establish cardiopulmonary bypass in cardiac surgery. A nasal cannula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiopulmonary Bypass
Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) or heart-lung machine, also called the pump or CPB pump, is a machine that temporarily takes over the function of the heart and lungs during open-heart surgery by maintaining the circulation of blood and oxygen throughout the body. As such it is an Extracorporeal, extracorporeal device. CPB is operated by a perfusionist. The machine mechanically circulates and oxygenates blood throughout the patient's body while bypassing the heart and lungs allowing the surgeon to work in a bloodless surgical field. Uses CPB is commonly used in operations or surgical procedures involving the heart. The technique allows the surgical team to oxygenate and circulate the patient's blood, thus allowing the surgeon to operate safely on the heart. In many operations, such as Coronary artery bypass surgery, coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), the heart is Cardioplegia, arrested, due to the degree of the difficulty of operating on a beating heart. Operations requiring t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Cannula
The nasal cannula (NC) is a device used to deliver supplemental oxygen or increased airflow to a patient or person in need of respiratory help. This device consists of a lightweight tube which on one end splits into two prongs which are placed in the nostrils curving toward the sinuses behind the nose, and from which a mixture of air and oxygen flows. The other end of the tube is connected to an oxygen supply such as a portable oxygen generator, or a wall connection in a hospital via a flowmeter. The cannula is generally attached to the patient by way of the tube hooking around the patient's ears or by an elastic headband, and the prongs curve toward the paranasal sinuses Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphe .... The earliest, and most widely used form of adult nasal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water per os, by mouth. It may also be used to administer pharmaceutical drug, medications or other medical therapy such as blood transfusion, blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use. The intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body as they are introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed. For this reason, the intravenous route ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracheostomy
Tracheotomy (, ), or tracheostomy, is a surgical airway management procedure which consists of making an incision on the front of the neck to open a direct airway to the trachea. The resulting stoma (hole) can serve independently as an airway or as a site for a tracheal tube (or tracheostomy tube) to be inserted; this tube allows a person to breathe without the use of the nose or mouth. Etymology and terminology The etymology of the word ''tracheotomy'' comes from two Greek words: the root ''tom-'' (from Greek τομή ''tomḗ'') meaning "to cut", and the word ''trachea'' (from Greek τραχεία ''tracheía''). The word ''tracheostomy'', including the root ''stom-'' (from Greek στόμα ''stóma'') meaning "mouth", refers to the making of a semi-permanent or permanent opening and to the opening itself. Some sources offer different definitions of the above terms. Part of the ambiguity is due to the uncertainty of the intended permanence of the stoma (hole) at the time it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trocar
A trocar (or trochar) is a medical device, medical or veterinary medicine, veterinary device used in minimally invasive surgery. Trocars are typically made up of an Wiktionary:awl, awl (which may be metal or plastic with a pointed or tapered tip), a cannula (essentially a rigid hollow tube) and often a seal (mechanical), seal. Some trocars also include a valve mechanism to allow for insufflation (medicine), insufflation. Trocars are designed for placement through the chest and abdominal walls during thoracoscopy, thoracoscopic and laparoscopic surgery, and each trocar functions as a portal (architecture), portal for the subsequent insertion of other endoscopic instruments such as forceps, grasper, surgical scissors, scissors, surgical staple, stapler, electrocautery, suction (medicine), suction tip, etc. — hence the more commonly used colloquial jargon "port". Trocars also allow passive evacuation of excess gas or fluid from organs within the body. Etymology The word ''trocar' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arterial Catheter
An arterial line (also art-line or a-line) is a thin catheter inserted into an artery. Use Arterial lines are most commonly used in intensive care medicine and anesthesia to monitor blood pressure directly and in real-time (rather than by intermittent and indirect measurement) and to obtain samples for arterial blood gas analysis. Arterial lines are generally not used to administer medication, since many injectable drugs may lead to serious tissue damage and even require amputation of the limb if administered into an artery rather than a vein. An arterial line is usually inserted into the radial artery in the wrist, but can also be inserted into the brachial artery at the elbow, into the femoral artery in the groin, into the dorsalis pedis artery in the foot, or into the ulnar artery in the wrist. A golden rule is that there has to be collateral circulation to the area affected by the chosen artery, so that peripheral circulation is maintained by another artery even if circu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Needle Gauge Comparison Chart
The Birmingham gauge, officially the Birmingham Wire Gauge and often abbreviated as ''G'' or ''ga'', is unit or wire gauge used to measure the thickness or diameter of wires and tubing, including hypodermic needles and other medical tube products. Terminology The Birmingham gauge is also known as the Stubs Iron Wire Gauge or Birmingham Wire Gauge and is distinct from the Stubs Steel Wire Gauge and the British Standard Wire Gauge. It is commonly referred to simply as ''gauge'' (abbreviated as ''G''), but this should not be confused with the French gauge, a separate system used for measuring the outer diameter of catheters. System The Birmingham gauge ranges from 5/0 or 00000, the lowest gauge number corresponding to the largest size of , to 36, the highest gauge number corresponding to the smallest size of . The increments between gauge sizes are not linear and vary. At higher gauge numbers, the increment between the two highest gauges is , while at lower gauge numbers, the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruminal Tympany
Ruminal tympany, also known as ruminal bloat, is a disease of ruminant animals, characterized by an excessive volume of gas in the rumen. Ruminal tympany may be primary, known as frothy bloat, or secondary, known as free-gas bloat. In the rumen, food eaten by the ruminant is fermented by microbes. This fermentation process continually produces gas, the majority of which is expelled from the rumen by eructation (burping). Ruminal tympany occurs when this gas becomes trapped in the rumen. In frothy bloat (primary ruminal tympany), the gas produced by fermentation is trapped within the fermenting material in the rumen, causing a build up of foam which cannot be released by burping. In cattle, the disease may be triggered after an animal eats a large amount of easily fermenting plants, such as legumes, alfalfa, red clover, or white clover. Some legumes, such as sainfoin, birdsfoot trefoil and cicer milkvetch are not associated with causing bloat in cattle. In feedlot cattle, a di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seldinger Technique
The Seldinger technique, also known as Seldinger wire technique, is a medical procedure to obtain safe access to blood vessels and other hollow organ (anatomy), organs. It is eponym, named after Sven Ivar Seldinger (1921–1998), a Sweden, Swedish radiology, radiologist who introduced the procedure in 1953. Uses The Seldinger technique is used for angiography, insertion of chest drains and central venous catheters, insertion of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy, PEG tubes using the push technique, insertion of the leads for an artificial pacemaker or implantable cardioverter-defibrillator, and numerous other interventional medical procedures. Complications The initial puncture is with a sharp instrument, and this may lead to hemorrhage or perforation of the organ in question. Infection is a possible complication, and hence asepsis is practiced during most Seldinger procedures. Loss of the guidewire into the cavity or blood vessel is a significant and generally preventable com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |