|
Candida Antarctica
''Candida antarctica'' is a yeast species in the genus '' Candida''. ''Candida antarctica'' is a source of important industrial enzymes. Immobilized ''Candida antarctica'' lipase can be used to catalyze the regioselective acylation of flavonoid Flavonoids (or bioflavonoids; from the Latin word ''flavus'', meaning yellow, their color in nature) are a class of polyphenolic secondary metabolites found in plants, and thus commonly consumed in the diets of humans. Chemically, flavonoids ...s or the direct acetylation with phenolic acids. This species contains a lipase enzyme that is able to cleave ester bonds in PET plastic. References External links antarctica Fungi described in 1983 {{ascomycota-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Candida (fungus)
''Candida'' is a genus of yeasts and is the most common cause of fungal infections worldwide. Many species are harmless commensals or endosymbionts of hosts including humans; however, when mucosal barriers are disrupted or the immune system is compromised they can invade and cause disease, known as an opportunistic infection. Candida is located on most mucosal surfaces and mainly the gastrointestinal tract, along with the skin. ''Candida albicans'' is the most commonly isolated species and can cause infections (candidiasis or thrush) in humans and other animals. In winemaking, some species of ''Candida'' can potentially spoil wines. Many species are found in gut flora, including ''C. albicans'' in mammalian hosts, whereas others live as endosymbionts in insect hosts. Systemic infections of the bloodstream and major organs (candidemia or invasive candidiasis), particularly in patients with an impaired immune system (immunocompromised), affect over 90,000 people a year in the US. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Enzymes
Industrial enzymes are enzymes that are commercially used in a variety of industries such as pharmaceuticals, chemical production, biofuels, food & beverage, and consumer products. Due to advancements in recent years, biocatalysis through isolated enzymes is considered more economical than use of whole cells. Enzymes may be used as a unit operation within a process to generate a desired product, or may be the product of interest. Industrial biological catalysis through enzymes has experienced rapid growth in recent years due to their ability to operate at mild conditions, and exceptional chiral and positional specificity, things that traditional chemical processes lack. Isolated enzymes are typically used in hydrolytic and isomerization reactions. Whole cells are typically used when a reaction requires a co-factor. Although co-factors may be generated in vitro, it is typically more cost-effective to use metabolically active cells. Enzymes as a unit of operation Immobilization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
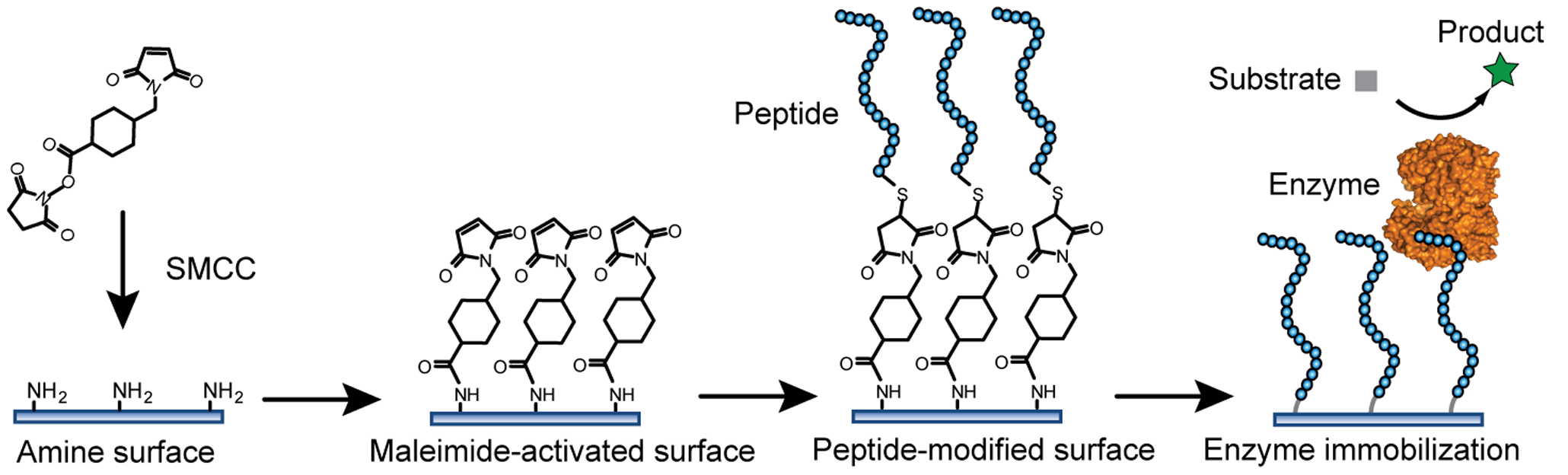
Immobilized Enzyme
An immobilized enzyme is an enzyme, with restricted mobility, attached to an inert, insoluble material—such as calcium alginate (produced by reacting a mixture of sodium alginate solution and enzyme solution with calcium chloride). This can provide increased resistance to changes in conditions such as pH or temperature. It also lets enzymes be held in place throughout the reaction, following which they are easily separated from the products and may be used again - a far more efficient process and so is widely used in industry for enzyme catalysed reactions. An alternative to enzyme immobilization is whole cell immobilization. Immobilized enzymes are easily to be handled, simply separated from their products, and can be reused. Enzymes are bio-catalysts which play an essential role in the enhancement of chemical reactions in cells without being persistently modified, wasted, nor resulting in the loss of equilibrium of chemical reactions. Although the characteristics of enzymes ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavonoid
Flavonoids (or bioflavonoids; from the Latin word ''flavus'', meaning yellow, their color in nature) are a class of polyphenolic secondary metabolites found in plants, and thus commonly consumed in the diets of humans. Chemically, flavonoids have the general structure of a 15-carbon skeleton, which consists of two phenyl rings (A and B) and a Heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic ring (C, the ring containing the embedded oxygen). This carbon structure can be abbreviated C6-C3-C6. According to the IUPAC nomenclature, they can be classified into: *flavonoids or bioflavonoids *isoflavonoids, derived from 3-phenylchromone, chromen-4-one (3-phenyl-1,4-benzopyran, benzopyrone) structure *neoflavonoids, derived from 4-phenylcoumarine (4-phenyl-1,2-benzopyran, benzopyrone) structure The three flavonoid classes above are all ketone-containing compounds and as such, anthoxanthins (flavones and flavonols). This class was the first to be termed bioflavonoids. The terms flavonoid and bioflav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenolic Acid
Phenolic acids or phenolcarboxylic acids are types of aromatic acid compounds. Included in that class are substances containing a phenolic ring and an organic carboxylic acid function (C6-C1 skeleton). Two important naturally occurring types of phenolic acids are hydroxybenzoic acids and hydroxycinnamic acids, which are derived from non-phenolic molecules of benzoic and cinnamic acid, respectively. Occurrences Phenolic acids can be found in many plant species. Their content in dried fruits can be high. Natural phenols in horse grams (''Macrotyloma uniflorum'') are mostly phenolic acids, namely 3,4-dihydroxy benzoic, ''p''-hydroxy benzoic, vanillic, caffeic, ''p''-coumaric, ferulic Ferulic acid is a hydroxycinnamic acid, an organic compound with the formula (CH3O)HOC6H3CH=CHCO2H. The name is derived from the genus ''Ferula'', referring to the giant fennel (''Ferula communis''). Classified as a phenolic phytochemical, feruli ..., syringic, and sinapinic acids. Pheno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |