|
Canadian Horse
The Canadian () is a horse breed from Canada. It is a strong, well-muscled horse, usually dark in colour. It is generally used for riding and driving. Descended from draft and light riding horses imported to Canada in the late 1600s from France, it was later crossed with other British and American breeds. During the 18th century the Canadian horse spread throughout the northeastern US, where it contributed to the development of several horse breeds. During the peak popularity of the breed, three subtypes could be distinguished, a draft horse type, a trotting type and a pacing type. Thousands of horses were exported in the 19th century, many of whom were subsequently killed while acting as cavalry horses in the American Civil War. These exports decreased the purebred Canadian population almost to the point of extinction, prompting the formation of a studbook and the passage of a law against further export. Experimental breeding programs in the early 20th century succeeded in r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, second-largest country by total area, with the List of countries by length of coastline, world's longest coastline. Its Canada–United States border, border with the United States is the world's longest international land border. The country is characterized by a wide range of both Temperature in Canada, meteorologic and Geography of Canada, geological regions. With Population of Canada, a population of over 41million people, it has widely varying population densities, with the majority residing in List of the largest population centres in Canada, urban areas and large areas of the country being sparsely populated. Canada's capital is Ottawa and List of census metropolitan areas and agglomerations in Canada, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cream Gene
The cream gene is responsible for a number of Equine coat color, horse coat colors. Horses that have the cream gene in addition to a base coat color that is chestnut (coat), chestnut will become palomino if they are heterozygous, having one copy of the cream gene, or cremello, if they are homozygous. Similarly, horses with a Bay (horse), bay base coat and the cream gene will be Buckskin (horse), buckskin or perlino. A black base coat with the cream gene becomes the not-always-recognized smoky black or a smoky cream. Cream horses, even those with blue eyes, are not white (horse), white horses. Dilution coloring is also not related to any of the Pinto horse, white spotting patterns. The cream gene (''CCr'') is an Dominance relationship, incomplete dominant allele with a distinct dosage effect. The DNA sequence responsible for the cream colors is the cream allele, which is at a specific Locus (genetics), locus on the SLC45A2, solute carrier family 45 member 2 (''SLC45A2'') ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheval Canadien Au Trot 3351 (1836–1924), French postman
Cheval may refer to: * Cheval, Florida, United States * Cheval tree, a tree native to North Agalega Island * Cheval mirror, a full-length floor-standing mirror mounted in a frame that allows it to swing freely *Cheval, loan word from French meaning horse meat People with the surname * Christophe Cheval (born 1971), French sprinter *Ferdinand Cheval Ferdinand Cheval (; 19 April 1836 – 19 August 1924), often nicknamed Facteur Cheval ("Mail Carrier Cheval") was a French mail carrier who spent 33 years building Le Palais idéal (the "Ideal Palace") in Hauterives, in southeastern France. See also * Chaval (other) {{disambiguation, surname ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microchipping
A microchip implant is an identifying integrated circuit placed under the skin of an animal. The chip, about the size of a large grain of rice, uses passive radio-frequency identification (RFID) technology, and is also known as a PIT (passive integrated transponder) tag. Standard pet microchips are typically 11–13 mm long (approximately inch) and 2 mm in diameter. Externally attached microchips such as RFID ear tags are commonly used to identify farm and ranch animals, with the exception of horses. Some external microchips can be read with the same scanner used with implanted chips. Animal shelters, animal control officers and veterinarians routinely look for microchips to return lost pets quickly to their owners, avoiding expenses for housing, food, medical care, outplacing and euthanasia. Many shelters place chips in all outplaced animals. Microchips are also used by kennels, breeders, brokers, trainers, registries, rescue groups, humane societies, clinics, fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tattoo
A tattoo is a form of body modification made by inserting tattoo ink, dyes, or pigments, either indelible or temporary, into the dermis layer of the skin to form a design. Tattoo artists create these designs using several tattooing processes and techniques, including hand-tapped traditional tattoos and modern tattoo machines. The history of tattooing goes back to Neolithic times, practiced across the globe by many cultures, and the symbolism and impact of tattoos varies in different places and cultures. Tattoos may be decorative (with no specific meaning), symbolic (with a specific meaning to the wearer), pictorial (a depiction of a specific person or item), or textual (words or pictographs from written languages). Many tattoos serve as rites of passage, marks of status and rank, symbols of religious and spiritual devotion, decorations for bravery, marks of fertility, pledges of love, amulets and talismans, protection, and as punishment, like the marks of outcasts, slaves, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foal
A foal is an equine up to one year old; this term is used mainly for horses, but can be used for donkeys. More specific terms are colt (horse), colt for a male foal and filly for a female foal, and are used until the horse is three or four. When the foal is nursing from its dam (mother), it may also be called a "suckling". After it has been weaned from its dam, it may be called a "weanling". When a mare is pregnant, she is said to be "in foal". When the mare gives birth, she is "foaling", and the impending birth is usually stated as "to foal". A newborn horse is "foaled". After a horse is one year old, it is no longer a foal, and is a "yearling (horse), yearling". There are no special age-related terms for young horses older than yearlings. When young horses reach breeding maturity, the terms change: a filly over three (four in horse racing) is called a mare, and a colt over three is called a stallion. A castrated male horse is called a gelding regardless of age; however, collo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stock Horse
A stock horse is a horse of a type that is well suited for working with livestock, particularly cattle. The related cow pony or cow horse is a historic phrase, still used colloquially today, referring to a particularly small agile cattle-herding horse; the term dates to 1874. The word "pony" in this context has little to do with the animal's size, though the traditional cow pony could be as small as and less than high. Such horses are characterized by agility, quickness, and powerful hindquarters. They are usually noted for intelligence and "cow sense," having an instinctive understanding of how to respond to the movement of cattle so as to move livestock in a desired manner with minimal or no guidance from their rider. Such horses are used both as working animals on livestock ranches or stations, and are also seen in competition where horses are evaluated on their ability to work cattle. The term may refer to any of the following: *A horse used for ranch work or for compet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trail Riding
Trail riding is riding outdoors on trails, bridle paths, and forest roads, but not on roads regularly used by motorised traffic. A trail ride can be of any length, including a long distance, multi-day trip. It originated with horse riding, and in North America, the equestrian form is usually called "trail riding", or, less often "hacking". In the UK and Europe, the practice is usually called horse, pony or donkey trekking. The modern term also encompasses mountain biking, mixed terrain cycle touring, and the use of motorcycles and other motorized all-terrain vehicles. It may be informal activities of an individual or small group, or larger events organized by a club. Some equestrian trail rides in the USA are directed by professional guides or outfitters, particularly at guest ranches, while many equestrians who own horses trail ride on their own in local, state, and national trail systems. In some parts of the world, trail riding (of whatever kind) is limited by law to reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jumping (horse)
Jumping plays a major role in many equestrian sports, such as show jumping, fox hunting, steeplechasing, and eventing. The biomechanics of jumping, the influence of the rider, and the heritability of jumping prowess have all been the focus of research. Jumping process The airborne phase of the jumping process occurs between stance phases of the fore and hind limbs and is therefore biomechanically equivalent to a highly suspended or elevated canter stride. For this reason, horses typically approach obstacles at the canter. The jumping process can be broken down into five phases: Approach The "approach" is the final canter stride before the jump, during which the horse places all four legs for the optimal take-off. The horse reaches forward and down with his neck to lower the forehand and his center of mass. The forelegs are propped or strutted out in front of the body. This relatively sudden braking action allows momentum to carry the hindlegs further under the body of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Easy Keeper
An easy keeper, easy doer, or (British English) good doer is a horse that can live on relatively little feed. The opposite of an easy keeper is a '' hard keeper'' (''poor doer''), an animal that is prone to be too thin and has difficulty maintaining adequate weight. Easy keepers tend to be found most often in breeds originally developed to survive under harsh conditions. Most pony breeds are easy keepers, and smaller, hardy horse breeds such as the Arabian or types such as the mustang have many representatives with this trait. Many draft horse breeds, such as the Percheron, are also easy keepers, as are most mules and donkeys. Though it varies from horse to horse. Things like workload, and turnout time, can influence the amount of food a horse needs. If overfed with a too rich, modern diet, the easy keeper is prone to obesity and other health problems, including laminitis and metabolic disorders. Easy keepers may be confused with a mare that is pregnant, but an easy kee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barb (horse)
The Barb horse, also known as the Barbary horse (), is a breed of riding horse with historic roots in North Africa. Known for its hardiness and stamina, it has influenced a number of modern breeds, including many in northern and western Africa. Etymology The first recorded use of the name "Barb" appears in the translation of the work Description of Africa by Hassan al-Wazzan (better known as Leo Africanus), which predates its adoption across Europe. The Barb horse breed derives its name from the Barbary Coast states, according to French historian Jean-Marie Lassère, who attributes the name to the tradition of naming animals based on their geographical origin. Jean-Louis Gouraud, on the other hand, connects the Barb to the Berbers (the European name for the '' Imazighen''), stating that "their histories and fates are inseparable". European sources also referred to this regional horse as "Berber," in reference to a region known under Roman rule as "Berberia" or "Barbaria" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
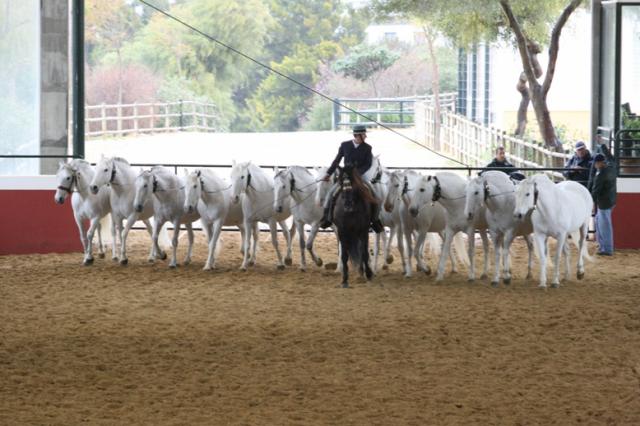
Andalusian Horse
The Andalusian, also known as the Pure Spanish Horse or PRE (Spanish language literally translates to "Spanish pure breed". This name is sometimes capitalized when used in English-language publications, but is all lower-case in Spanish, which does not capitalize adjectives derived from proper nouns.), is a horse breed from the Iberian Peninsula, where its ancestors have lived for thousands of years. The Andalusian has been recognized as a distinct breed since the 15th century, and its Equine conformation, conformation has changed very little over the centuries. Throughout its history, it has been known for its prowess as a horses in warfare, war horse, and was prized by the nobility. The breed was used as a tool of diplomacy by the Spanish government, and kings across Europe rode and owned Spanish horses. During the 19th century, warfare, disease and crossbreeding reduced herd numbers dramatically, and despite some recovery in the late 19th century, the trend continued into the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |