|
Canadian Expeditionary Force
The Canadian Expeditionary Force (CEF; French: ''Corps expéditionnaire canadien'') was the expeditionary warfare, expeditionary field force of Canada during the First World War. It was formed on August 15, 1914, following United Kingdom declaration of war upon Germany (1914), Britain’s declaration of war on the German Empire, with an initial strength of one infantry Division (military), division. The division subsequently fought at Second Battle of Ypres, Ypres on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front, with a newly raised second division reinforcing the committed units to form the Canadian Corps. The CEF and corps was eventually expanded to four infantry divisions, which were all committed to the fighting in France and Belgium along the Western Front. A fifth division was partially raised in 1917, but was broken up in 1918 and used as reinforcements following heavy casualties. Personnel Recruitment The CEF was mostly volunteers; a bill allowing conscription was pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expeditionary Warfare
Expeditionary warfare is a military invasion of a foreign territory, especially away from established bases. Expeditionary forces were in part the antecedent of the modern concept of rapid deployment forces. Traditionally, expeditionary forces were essentially self-sustaining with an Organic unit, organic Military logistics, logistics capability and with a full array of supporting arms. In the ancient world The earliest examples of expeditionary warfare come from the Sea Peoples, a term used for a confederation of seafaring Raid (military), raiders of the second millennium BC who sailed into the eastern shores of the Mediterranean, caused political unrest, and attempted to enter or control Egyptian territory during the late Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt, 19th dynasty, and especially during Year 8 of Ramesses III of the Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt, 20th dynasty. The raiding tactics were expanded into the more complex expeditionary warfare operations by Alexander the Great who used C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
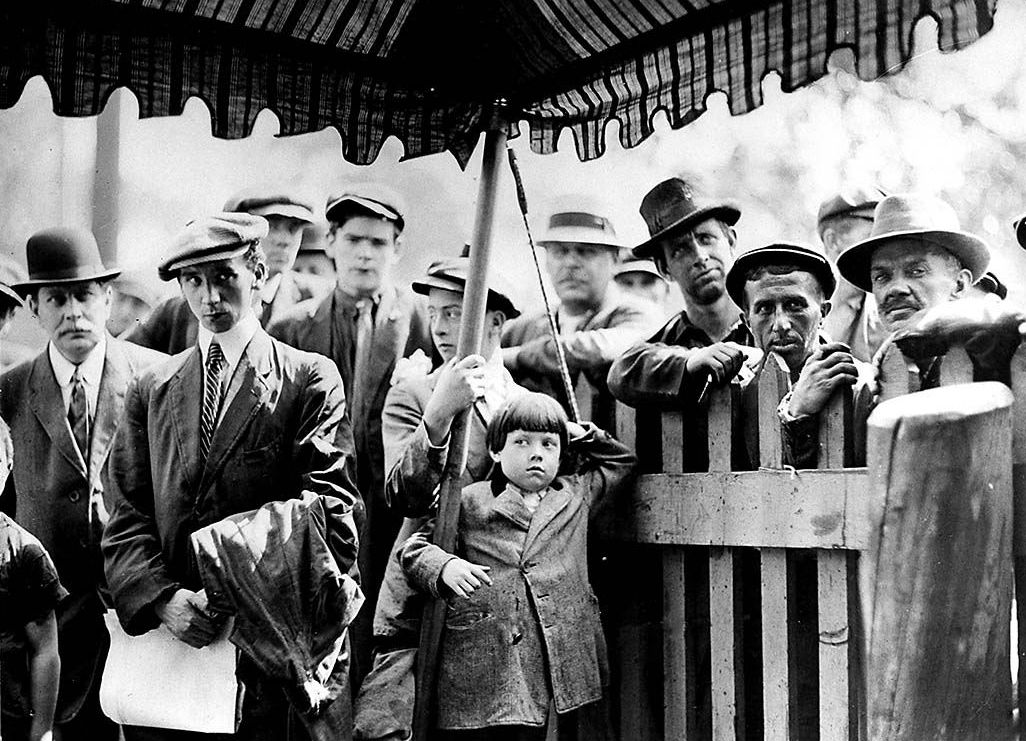
Men At The Recruiting Tent 1914
A man is an adult male human. Before adulthood, a male child or adolescent is referred to as a boy. Like most other male mammals, a man's genome usually inherits an X chromosome from the mother and a Y chromosome from the father. Sex differentiation of the male fetus is governed by the SRY gene on the Y chromosome. During puberty, hormones which stimulate androgen production result in the development of secondary sexual characteristics that result in even more differences between the sexes. These include greater muscle mass, greater height, the growth of facial hair and a lower body fat composition. Male anatomy is distinguished from female anatomy by the male reproductive system, which includes the testicles, sperm ducts, prostate gland and epididymides, and penis. Secondary sex characteristics include a narrower pelvis and hips, and smaller breasts and nipples. Throughout human history, traditional gender roles have often defined men's activities and opportunit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princess Patricia's Canadian Light Infantry
Princess Patricia's Canadian Light Infantry (PPCLI, generally referred to as the Patricias) is one of the three Regular Force infantry regiments of the Canadian Army of the Canadian Armed Forces. Formed in 1914, it is named for Princess Patricia of Connaught, daughter of the then-Governor General of Canada. The regiment is composed of three battalions, for a total of 2,000 soldiers. The PPCLI is the main lodger unit of Canadian Forces Base (CFB) Edmonton in Alberta and CFB Shilo in Manitoba, and attached to 3rd Canadian Division; as such, it serves as the "local" regular infantry regiment for much of Western Canada. The Loyal Edmonton Regiment (LER), a Reserve Force battalion, is affiliated with the PPCLI but is not formally part of it. As part of this affiliation, the LER carries the designation '4th Battalion, Princess Patricia's Canadian Light Infantry'. The PPCLI is a "British-style" Regiment which serves as the spiritual home and repository of customs and traditions for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Canadian Regiment
The Royal Canadian Regiment (RCR) is an infantry regiment of the Canadian Army. The regiment consists of four battalions, three in the Regular Force and one in the primary reserve. The RCR is ranked first in the order of precedence amongst Canadian Army infantry regiments, but in a quirk of the rules of seniority, its 4th battalion is ninth. The RCR was originally authorized as the Infantry School Corps on 21 December 1883, and established its first three Company (military unit), company stations at Fredericton, New Brunswick; St Jean, Quebec; and Toronto, Ontario. In 1887 a fourth company was authorized and the next year was established at London, Ontario. Now consisting of three Regular Force battalions and one Reserve Force battalion, the regiment's four battalions are now stationed in Ontario and New Brunswick. With many of its soldiers drawn from Ontario and the Atlantic Provinces in recent decades, the regiment maintains a general connection as the "local" infantry regiment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Strathcona's Horse
Lord Strathcona's Horse (Royal Canadians) (LdSH(RC)) is a regular armoured regiment of the Canadian Army and is Canada’s only tank regiment. Currently based in Edmonton, Alberta, the regiment is part of 3rd Canadian Division's 1 Canadian Mechanized Brigade Group. Members of the regiment are commonly called ''Strathconas'' or ''Strats'' as a short form. It was one of the last regiments in the British Empire to be created and raised by a private individual, Donald Alexander Smith, 1st Baron Strathcona and Mount Royal. The regimental motto is "Perseverance". The colonel-in-chief of the regiment is King Charles III, while the colonel of the regiment is Colonel(Ret’d) Jamie Cade. The current commanding officer is Lieutenant-Colonel D. Gray, and the regimental sergeant major is Chief Warrant Officer N. Mills. Regimental structure The regiment is composed of a regimental headquarters (RHQ), three sabre (tank) squadrons (A, B, and C Sqns), and headquarters squadron which pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Canadian Dragoons
The Royal Canadian Dragoons (RCD) is the senior armoured regiment of the Canadian Army by precedence. It is one of three armoured regiments in the Regular Force and forms part of the Royal Canadian Armoured Corps. The colonel-in-chief of the RCD is Charles III, King of Canada. The colonel of the regiment is Major-General (Retired) Dean Milner, CMM, MSC, CD. The commanding officer is Lieutenant-Colonel C. Summerfield, and the regimental sergeant major is Chief Warrant Officer J. Nickerson. The regiment is composed of Regimental Headquarters, "A", "B", "C", "D" and Headquarters Squadrons. "A", "B" and "D" Squadrons, based at CFB Petawawa, are light cavalry squadrons. "C" Squadron is based at CFB Gagetown, and the squadron consists of both Dragoons and members of 12e Régiment blindé du Canada. Headquarters Squadron, based in Petawawa, provides first-line combat service support to the regiment. Lineage The Royal Canadian Dragoons *Originated 21 December 1883 in Quebec C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permanent Active Militia
Permanent Active Militia (PAM), also known as Permanent Force (PF), was the proper name of Canada's full-time professional land forces from 1855 to 1940, when it was reorganized into the Canadian Army. PAM was in effect Canada's standing army, consisting of one regular infantry regiment and two cavalry regiments in 1914. The counterpart to PAM was the Non-Permanent Active Militia (NPAM), which referred to the reserve force of the Canadian Militia. PAM and NPAM were distinct forces from the sedentary militias raised in Canada. Both organizations were reorganized into the Canadian Army in 1940. History As the British began to withdraw soldiers from British North America in the decades after the War of 1812, the Parliament of the Province of Canada passed the Militia Act of 1855, creating the Active Militia. The Active Militia, later split off into the Permanent Active Militia (PAM), the Militia's regular armed unit (although it continued to use the label militia), and the Non-Per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Canadians
Black Canadians () are Canadians of full or partial Afro-Caribbean or sub-Saharan African descent. Black Canadian settlement and immigration patterns can be categorized into two distinct groups. The majority of Black Canadians are descendants of immigrants from the Caribbean and the African continent who arrived in Canada during significant migration waves, beginning in the post-war era of the 1950s and continuing into recent decades. A smaller yet historically significant population includes the descendants of African Americans, including fugitive slaves, Black loyalists and refugees from the War of 1812. Their descendants primarily settled in Nova Scotia and Southern Ontario, where they formed distinctive identities such as Black Ontarians and African Nova Scotians. Black Canadians have contributed to many areas of Canadian culture. Many of the first visible minorities to hold high public offices have been Black, including Michaëlle Jean, Donald Oliver, Stanley G. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Nations In Canada
''First Nations'' () is a term used to identify Indigenous peoples in Canada who are neither Inuit nor Métis. Traditionally, First Nations in Canada were peoples who lived south of the tree line, and mainly south of the Arctic Circle. There are 634 recognized List of First Nations band governments, First Nations governments or bands across Canada. Roughly half are located in the provinces of Ontario and British Columbia. Under Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms, Charter jurisprudence, First Nations are a "designated group", along with women, Visible minority, visible minorities, and people with physical or mental disabilities. First Nations are not defined as a visible minority by the criteria of Statistics Canada. North American indigenous peoples have cultures spanning thousands of years. Many of their oral traditions accurately describe historical events, such as the 1700 Cascadia earthquake, Cascadia earthquake of 1700 and the 18th-century Tseax Cone eruption. Writ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal 22e Régiment
The Royal 22nd Regiment (R22R; ) is an infantry regiment of the Canadian Army. Known colloquially in English as the Van Doos (representing an anglicized pronunciation of the French number twenty-two, ) or in French as , the mostly francophone regiment comprises three Regular Force battalions, two Primary Reserve battalions, and a band, making it the largest regiment in the Canadian Army. The headquarters () of the regiment is at the Citadelle of Quebec in Quebec City, also the site of the regimental museum, and all three of its regular battalions are stationed at Canadian Forces Base Valcartier in Saint-Gabriel-de-Valcartier, outside of Quebec City. The regiment is a "British-style" infantry regiment that is the spiritual home and repository of customs and traditions for a number of battalions that do not necessarily serve together operationally. It serves as the "local" infantry regiment for the province of Quebec, where it draws most of its recruits; it is the largest regime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
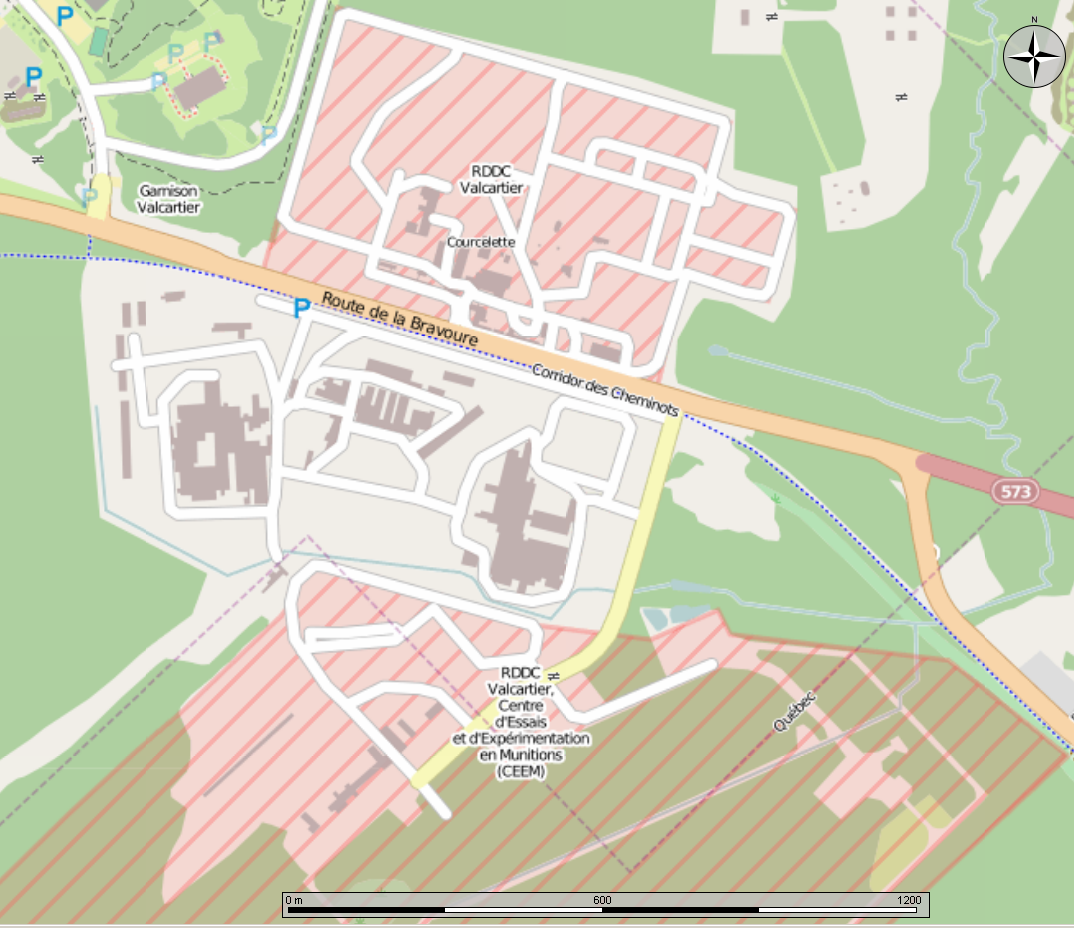
CFB Valcartier
2nd Canadian Division Support Base Valcartier (2 CDSB Valcartier), formerly known as and commonly referred to as Canadian Forces Base Valcartier (CFB Valcartier), is a Canadian Forces base located in the municipality of Saint-Gabriel-de-Valcartier, north northwest of Quebec City, Quebec, Canada. The 2nd Canadian Division is stationed at the base, comprising the 5 Canadian Mechanized Brigade Group and the 2nd Canadian Division Support Group. Origins CFB Valcartier was originally erected as a military training camp in August 1914 as part of the mobilization of the Canadian Expeditionary Force at the onset of World War I. Inaugurated by Jean Chrétien, then Prime Minister of Canada, in 1995, a high bronze figure of a World War I soldier (1995) by André Gauthier at the entrance to CFB Valcartier commemorates the training of Canadian Army volunteers for the European battlefields in World War I. The site was also used as an internment camp for "enemy aliens", mainly east ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |