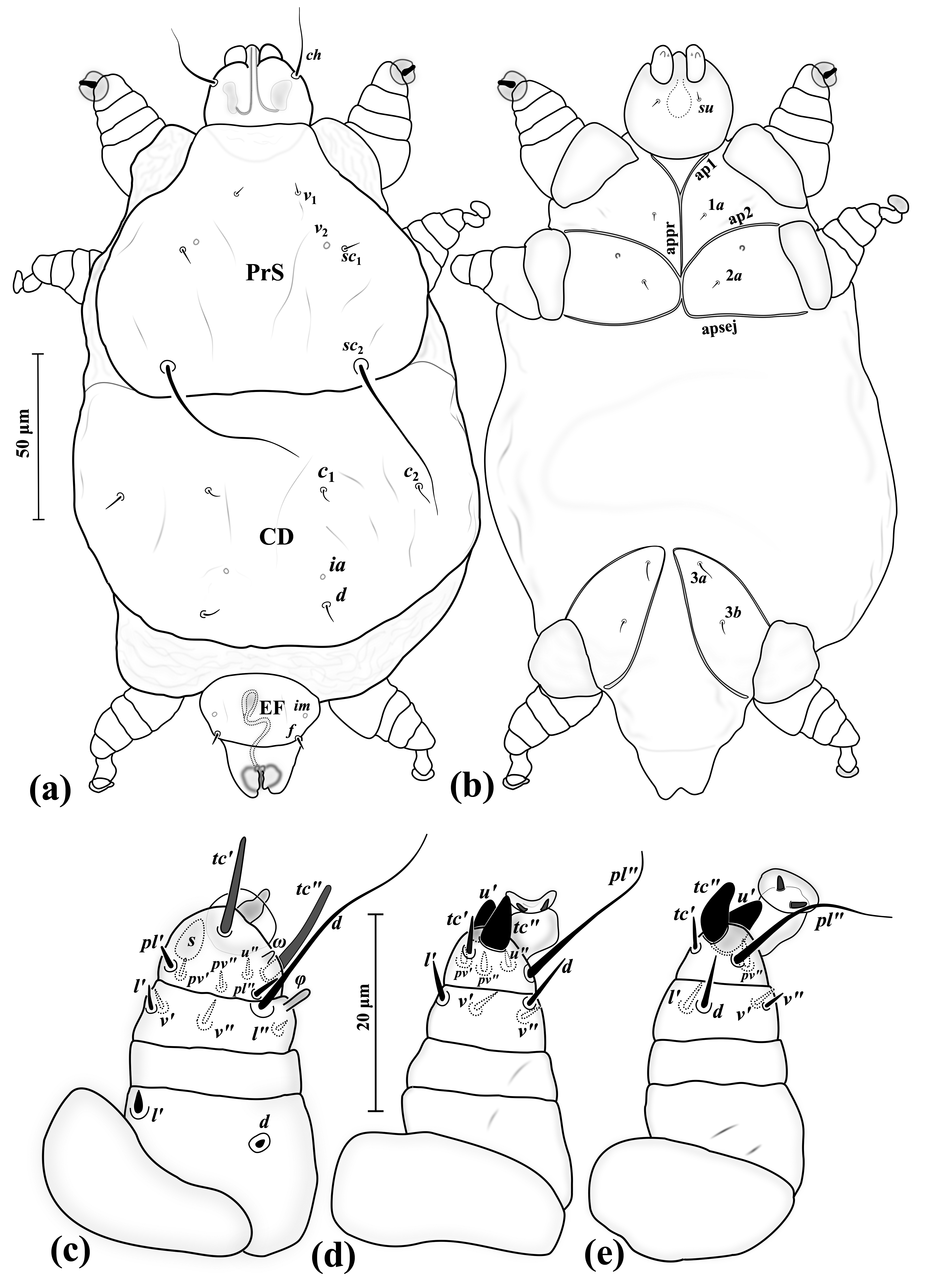
|
Neophyllobius
''Neophyllobius'' is a genus of mites. References * Ahaniazad, M. et al. 2013: A new species of Neophyllobius from Iran, re-description of Stigmaeus echinopus Summers and a key to the Iranian species of Neophyllobius (Acari: Trombidiformes: Prostigmata). International journal of acarology, 39(4), pages 341–346, * Bolland, H.R. 1991: Review of the systematics of the family Camerobiidae. II. The genus Neophyllobius Berlese, 1886 (Acari: Raphignathoidea). Genus, 2, pages 59–226 * Bolland, H.R.; Swift, S.F. 2000: Hawaiian Raphignathoidea: family Camerobiidae (Acariformes: Prostigmata), with descriptions of three new species. International journal of acarology, 26(4), pages 347–356, * Fan, Q.-H.; Zhang, Z.-Q. 2005: Raphignathoidea (Acari: Prostigmata). Fauna of New Zealand, (52) * Khanjani, M.; Fayaz, B.A.; Ghanbalani, G.N. 2010: Two new species of the genus Neophyllobius Berlese (Acari: Camerobiidae) from Iran. Zootaxa, 2521, pages 53–64 * Khanjani, M.; Hoseini, M.A. 2013 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raphignathoidea
Raphignathoidea is a superfamily of the Acari (mite) order Trombidiformes, comprising 1087 species in 62 genera and 12 families. Morphology Adult Raphignathoidea are generally oval or round in shape, with 2 pairs of vertical setae on the prodorsum (rarely 3), 2 pairs of scapular setae (rarely 1 or 3), and eyes and postocular bodies usually present. The second and third leg pairs are separated by a gap except in families Cryptognathidae and Raphignathidae. The legs usually bear tarsal claws at the ends. Females and males look similar except that males are often tapered posteriorly, the first and second pseudanal setae are often reduced, the genital and anal openings are fused, and an aedeagus (male reproductive organ) is present. Life cycle Most Raphignathoidea have five life stages: egg, larva, protonymph, deutonymph and adult. The species ''Agistemus exsertus'' also has a prelarval stage, while the genus ''Raphignathus'' and the family Xenocaligonellididae also have a th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acari
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods). Mites span two large orders of arachnids, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari, but genetic analysis does not show clear evidence of a close relationship. Most mites are tiny, less than in length, and have a simple, unsegmented body plan. The small size of most species makes them easily overlooked; some species live in water, many live in soil as decomposers, others live on plants, sometimes creating galls, while others again are predators or parasites. This last type includes the commercially destructive '' Varroa'' parasite of honey bees, as well as scabies mites of humans. Most species are harmless to humans, but a few are associated with allergies or may transmit diseases. The scientific discipline devoted to the study of mites is called acarology. Evolution and taxonomy The mites are not a defined taxon, but is used for two distinct groups of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arthropod cuticle, cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate. The arthropod body plan consists of segments, each with a pair of appendages. Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical and their body possesses an exoskeleton, external skeleton. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. Some species have wings. They are an extremely diverse group, with up to 10 million species. The haemocoel, an arthropod's internal cavity, through which its haemolymph – analogue of blood – circulates, accommodates its interior Organ (anatomy), organs; it has an open circulatory system. Like their exteriors, the internal or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arachnid
Arachnida () is a class of joint-legged invertebrate animals ( arthropods), in the subphylum Chelicerata. Arachnida includes, among others, spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites, pseudoscorpions, harvestmen, camel spiders, whip spiders and vinegaroons. Almost all adult arachnids have eight legs, although the front pair of legs in some species has converted to a sensory function, while in other species, different appendages can grow large enough to take on the appearance of extra pairs of legs. The term is derived from the Greek word (''aráchnē'', 'spider'), from the myth of the hubristic human weaver Arachne, who was turned into a spider. Almost all extant arachnids are terrestrial, living mainly on land. However, some inhabit freshwater environments and, with the exception of the pelagic zone, marine environments as well. They comprise over 100,000 named species, of which 47,000 are species of spiders. Morphology Almost all adult arachnids have eight legs, unli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trombidiformes
The Trombidiformes are a large, diverse order of mites. Taxonomy In 1998, Trombidiformes was divided into the Sphaerolichida and the Prostigmata. The group has few synapomorphies by which it can be defined, unlike the other major group of acariform mites, Sarcoptiformes. Its members include medically important mites (such as '' Demodex'', the chiggers, and scrub-itch mites) and many agriculturally important species, including the spider mites (Tetranychidae). The superfamily Eriophyoidea, traditionally considered members of the Trombidiformes, have been found to be basal mites in genomic analyses, sister to the clade containing Sarcoptiformes and Trombidiformes. The 2004 classification retained the two suborders, comprising around 125 families and more than 22,000 described species. In the 2011 revised classification, the order now contains 151 families, 2235 genera Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ronald Vernon Southcott
Ronald Vernon Southcott (15 May 1918 in Adelaide – 9 April 1998) was an Australian medical zoologist specializing in Acari, mites and ticks. Biography After finishing school at St Peter's College, Adelaide Southcott started working on mites, or the acari, at the age of 16 with Herbert Womersley the acarologist at the South Australian Museum. Womersley described and named the trombidiid mite, which Southcott had collected on a cycling trip in the hills near Adelaide in 1934, '' Microtrombidium southcotti'', after Southcott. Southcott considered that act by Herb Womersley, "hooked me on mites". Southcott studied medicine at the University of Adelaide where he graduated in 1941. Southcott then served in the Australian Army Medical Corps from 1942 to 1946. While he was stationed at Cairns he started working on the taxonomy and medical effects of jellyfish, the subject for which he was later to become famous. His more than 230 papers on the red mites include a classic revision of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_Lorryia_formosa_2_edit.jpg)