|
Calypso-class Corvette
The ''Calypso'' class comprised two steam corvettes (later classified as third-class cruisers) of the Royal Navy. Built for distant cruising in the heyday of the British Empire, they served with the fleet until the early twentieth century, when they became training ships. Remnants of both survive, after a fashion; in the name of the naval reserve unit the ship once served, and both in the name of a civilian charity and the more corporeal form of the hull, now awash in a cove off Newfoundland. The class exemplifies the transitional nature of the late Victorian navy. In design, materials, armament, and propulsion the ''Calypso''s show evidence of their wooden sailing antecedents, blended with characteristics of the all-metal mastless steam warships which followed. Their appearance and layout was similar to the "pure" sailing corvettes, with boiler rooms, machinery spaces, ventilators, and a flue added. Of iron and steel construction, they had coppering over timber below th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calypso Class Corvette Under Sail
Calypso refers to: * Calypso (mythology), a nymph who, famously in Homer's ''Odyssey'', kept Odysseus with her on her island of Ogygia for seven years. * Calypso (nymphs), other nymphs called Calypso. Calypso may also refer to: Books * "Calypso" (''Ulysses'' episode), an episode in James Joyce's novel ''Ulysses'' * ''Calypso'' (book), 2018 essay collection by David Sedaris * Calypso (comics), Marvel Comics character * Calypso, Camp Half-Blood Chronicles Companies and brands * Calypso (camera), an underwater camera — a precursor to the Nikonos camera * Calypso (electronic ticketing system), an electronic ticketing system for public transport * Calypso (email client), later called Courier * Calypso Park, a Canadian theme waterpark * Calypso Technology, an American financial services application software company * Ultracraft Calypso, a Belgian light aircraft design Entertainment Music * Calypso music, a genre of Trinidadian folk music * ''Calypso'' (album), by Harr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poop Deck
In naval architecture, a poop deck is a deck that forms the roof of a cabin built in the rear, or "aft", part of the superstructure of a ship. The name originates from the French word for stern, ''la poupe'', from Latin ''puppis''. Thus the poop deck is technically a stern deck, which in sailing ships was usually elevated as the roof of the stern or "after" cabin, also known as the "poop cabin". On sailing ships, the helmsman would steer the craft from the quarterdeck, immediately in front of the poop deck. At the stern, the poop deck provides an elevated position ideal for observation. On modern, motorized warships, the ship functions which were once carried out on the poop deck have been moved to the bridge A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually somethi ..., usually loca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
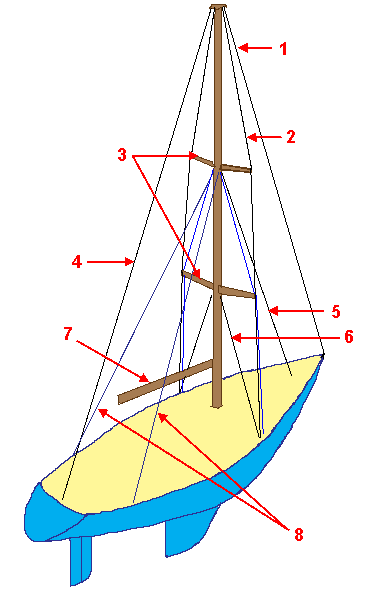
Chainplate
A chainplate is a metal plate used to fasten a shroud or stay to the hull of a sailboat. One end of the chainplate is normally fastened to a turnbuckle A turnbuckle, stretching screw or bottlescrew is a device for adjusting the tension or length of ropes, cables, tie rods, and other tensioning systems. It normally consists of two threaded eye bolts, one screwed into each end of a small meta ... which is connected to the shroud or stay, whereas the remainder of the chainplate normally has multiple holes that are bolted to the hull. This distributes the load across the hull, making it possible for a somewhat lighter hull to support the load of the shrouds and stays. References {{reflist[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shroud (sailing)
On a sailing boat, the shrouds are pieces of standing rigging which hold the mast up from side to side. There is frequently more than one shroud on each side of the boat. Usually a shroud will connect at the top of the mast, and additional shrouds might connect partway down the mast, depending on the design of the boat. Shrouds terminate at their bottom ends at the chain plates, which are tied into the hull. They are sometimes held outboard by channels, a ledge that keeps the shrouds clear of the gunwales.''The Lore of Ships,'' ed. by Bengt Kihlberg. Göteborg :Tre tryckare & New York: Holt, Rinehart & Winston, 1963. Shrouds are attached symmetrically on both the port and starboard sides. For those shrouds which attach high up the mast, a structure projecting from the mast must be used to increase the angle of the shroud at the attachment point, providing more support to the mast. On most sailing boats, such structures are called spreaders, and the shrouds they hold contin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Running Rigging
Running rigging is the rigging of a sailing vessel that is used for raising, lowering, shaping and controlling the sails on a sailing vessel—as opposed to the standing rigging, which supports the mast and bowsprit. Running rigging varies between vessels that are rigged fore and aft and those that are square-rigged. History of materials In centuries past, a ship's rigging was typically fashioned from rope. In the 19th century this was commonly referred to as Manilla, a reference to the origin of much good quality rope. Traditionally the running rigging was easily recognized since, for flexibility, it was not coated with tar and therefore of a lighter color than the standing rigging which was tarred for protection from weather and therefore darker or even black in color. On modern vessels, running rigging is likely to be made from synthetic fibers, while the standing rigging is most often fashioned from stainless steel "wire rope". Since the 1990s, several new synthetic fibe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standing Rigging
Standing rigging comprises the fixed lines, wires, or rods, which support each mast or bowsprit on a sailing vessel and reinforce those spars against wind loads transferred from the sails. This term is used in contrast to running rigging, which represents the moveable elements of rigging which adjust the position and shape of the sails. Historical development Early sailing vessels used rope of hemp or other fibers, which gave way to wire ropes of various types. Galvanized steel was common for the first half of the 20th century, continuing as an inexpensive option to its 1960s successor material—stainless steel cables and rods. In the late 20th Century, racing yachts adopted composite fiber lines for standing rigging, with the goal of reducing weight and windage aloft. Materials On modern yachts, standing rigging is often stainless steel wire, Nitronic-50 stainless steel rod or synthetic fiber. Semi-rigid stainless steel wire is by far the most common as it combines extr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem (ship)
The stem is the most forward part of a boat or ship's bow and is an extension of the keel itself. It is often found on wooden boats or ships, but not exclusively. Description The stem is the curved edge stretching from the keel below, up to the gunwale of the boat. It is part of the physical structure of a wooden boat or ship that gives it strength at the critical section of the structure, bringing together the port and starboard side planks of the hull. Plumb and raked stem There are two styles of stems: ''plumb'' and ''raked''. When the stem comes up from the water, if it is perpendicular to the waterline it is "plumb". If it is inclined at an angle to the waterline it is "raked". (For example, "The hull is single decked and characterized by a plumb stem, full bows, straight keel, moderate deadrise, and an easy turn of bilge.") Stemhead Because the stem is very sturdy, the top end of it may have something attached, either ornamental or functional in nature. On smalle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarter Gallery
A quarter gallery is an architectural feature of the stern of a sailing ship from around the 16th to the 19th century. Quarter galleries are a kind of balcony, typically placed on the sides of the sterncastle, the high, tower-like structure at the back of a ship that housed the officer's quarters. They functioned primarily as latrines for the ship's officers, and in inclement weather they also afforded those officers a view of the forward sails of the ship without having to go outside. On certain vessels and under certain conditions, the quarter galleries could serve as a firing platform for the ship's marines and sharpshooter A sharpshooter is one who is highly proficient at firing firearms or other projectile weapons accurately. Military units composed of sharpshooters were important factors in 19th-century combat. Along with " marksman" and "expert", "sharpshooter" ...s during boarding actions. The galleries also provided a structure that was ideally suited for attaching d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porthole
A porthole, sometimes called bull's-eye window or bull's-eye, is a generally circular window used on the hull of ships to admit light and air. Though the term is of maritime origin, it is also used to describe round windows on armored vehicles, aircraft, automobiles (the Ford Thunderbird a notable example) and even spacecraft. On a ship, the function of a porthole, when open, is to permit light and fresh air to enter the dark and often damp below- deck quarters of the vessel. It also affords below-deck occupants a limited view to the outside world. When closed, the porthole provides a strong water-tight, weather-tight and sometimes light-tight barrier. A porthole on a ship may also be called a sidescuttle or side scuttle (side hole), as officially termed in the International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea. This term is used in the U.S. Code of Federal Regulations. It is also used in related rules and regulations for the construction of ships. The use of the word "s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bowsprit
The bowsprit of a sailing vessel is a spar extending forward from the vessel's prow. The bowsprit is typically held down by a bobstay that counteracts the forces from the forestays. The word ''bowsprit'' is thought to originate from the Middle Low German word ''bōchsprēt'' – ''bōch'' meaning "bow" and ''sprēt'' meaning "pole". It is sometimes used to hold up the figurehead. References References * {{Sailing ship elements Sailboat components ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Screw Corvette
Steam frigates (including screw frigates) and the smaller steam corvettes, steam sloops, steam gunboats and steam schooners, were steam-powered warships that were not meant to stand in the line of battle. There were some exceptions like for example the French Napoléon class steam ship of the line was meant to stand in the line of battle, making it the world's first steam battleship. The first such ships were paddle steamers. Later on the invention of screw propulsion enabled construction of steam-powered versions of the traditional ships of the line, frigates, corvettes, sloops and gunboats. Evolution First steam warships The first small vessel that can be considered a steam warship was the ''Demologos'', which was launched in 1815 for the United States Navy. From the early 1820s, the British Navy began building a number of small steam warships including the armed tugs and , and by the 1830s the navies of America, Russia and France were experimenting with steam-powered w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)