|
Calcium Peroxide
Calcium peroxide or calcium dioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula CaO2. It is the peroxide (O22−) salt of Ca2+. Commercial samples can be yellowish, but the pure compound is white. It is almost insoluble in water. Structure and stability As a solid, it is relatively stable against decomposition. In contact with water however it hydrolyzes with release of oxygen. Upon treatment with an acid, it forms hydrogen peroxide. Preparation Calcium peroxide is produced by combining calcium salts and hydrogen peroxide: :Ca(OH)2 + H2O2 → CaO2 + 2 H2O The octahydrate precipitates upon the reaction of calcium hydroxide with dilute hydrogen peroxide. Upon heating it dehydrates. Applications It is mainly used as an oxidant to enhance the extraction of precious metals from their ores. In its second main application, it is used as a food additive under the E number E930 it is used as flour bleaching agent and improving agent. In agriculture it is used in the presowi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Oxide
Calcium oxide (formula: Ca O), commonly known as quicklime or burnt lime, is a widely used chemical compound. It is a white, caustic, alkaline, crystalline solid at room temperature. The broadly used term '' lime'' connotes calcium-containing inorganic compounds, in which carbonates, oxides, and hydroxides of calcium, silicon, magnesium, aluminium, and iron predominate. By contrast, ''quicklime'' specifically applies to the single compound calcium oxide. Calcium oxide that survives processing without reacting in building products, such as cement, is called free lime. Quicklime is relatively inexpensive. Both it and the chemical derivative calcium hydroxide (of which quicklime is the base anhydride) are important commodity chemicals. Preparation Calcium oxide is usually made by the thermal decomposition of materials, such as limestone or seashells, that contain calcium carbonate (CaCO3; mineral calcite) in a lime kiln. This is accomplished by heating the material to above , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flour Bleaching Agent
Flour bleaching agent is the agent added to fresh milled grains to whiten the flour by removing the yellow colour pigment called xanthophyll. It whitens the flour, which is used in the baking industry. Overview Usual flour bleaching agents are: *Organic peroxides (benzoyl peroxide) * Calcium peroxide *Chlorine *Chlorine dioxide * Azodicarbonamide *Nitrogen dioxide *Atmospheric oxygen, used during natural aging of flour Use of chlorine, bromates, and peroxides is not allowed in the European Union. Bleached flour improves the structure-forming capacity, allowing the use of dough formulas with lower proportions of flour and higher proportions of sugar . In biscuit making, use of chlorinated flour reduces the spread of the dough, and provides a "tighter" surface. The changes of functional properties of the flour proteins are likely to be caused by their oxidation. In countries where bleached flour is prohibited, microwaving plain flour produces similar chemical changes to the bleac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Additives
Food additives are substances added to food to preserve flavor or enhance taste, appearance, or other sensory qualities. Some additives, such as vinegar ( pickling), salt ( salting), smoke (smoking) and sugar (crystallization), have been used for centuries to preserve food. This allows for longer-lasting foods, such as bacon, sweets, and wines. With the advent of ultra-processed foods in the late 20th century, many additives having both natural and artificial origin were introduced. Food additives also include substances that may be introduced to food indirectly (called "indirect additives") in the manufacturing process through packaging, storage or transport. In Europe and internationally, many additives are designated with E numbers, while in the United States, additives in amounts deemed safe for human consumption are designated as GRAS. Identification To regulate these additives and inform consumers each additive is assigned a unique number called an "E number", which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Compounds
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to its heavier homologues strontium and barium. It is the fifth most abundant element in Earth's crust, and the third most abundant metal, after iron and aluminium. The most common calcium compound on Earth is calcium carbonate, found in limestone and the fossils of early sea life; gypsum, anhydrite, fluorite, and apatite are also sources of calcium. The name comes from Latin ''calx'' " lime", which was obtained from heating limestone. Some calcium compounds were known to the ancients, though their chemistry was unknown until the seventeenth century. Pure calcium was isolated in 1808 via electrolysis of its oxide by Humphry Davy, who named the element. Calcium compounds are widely used in many industries: in foods and pharmaceuticals for calc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peroxides
In chemistry, peroxides are a group of compounds with the structure , where the R's represent a radical (a portion of a complete molecule; not necessarily a free radical) and O's are single oxygen atoms. Oxygen atoms are joined to each other and to adjacent elements through single covalent bonds, denoted by dashes or lines. The group in a peroxide is often called the peroxide group, though some nomenclature discrepancies exist. This linkage is recognized as a common polyatomic ion, and exists in many molecules. General structure The characteristic structure of any regular peroxide is the oxygen–oxygen covalent single bond, which connects the two main atoms together. In the event that the molecule has no chemical substituents, the peroxide group will have a ��2 net charge. Each oxygen atom has a charge of negative one, as 5 of its valence electrons remain in the outermost orbital shell whilst one is occupied in the covalent bond. Because of the nature of the covalent bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
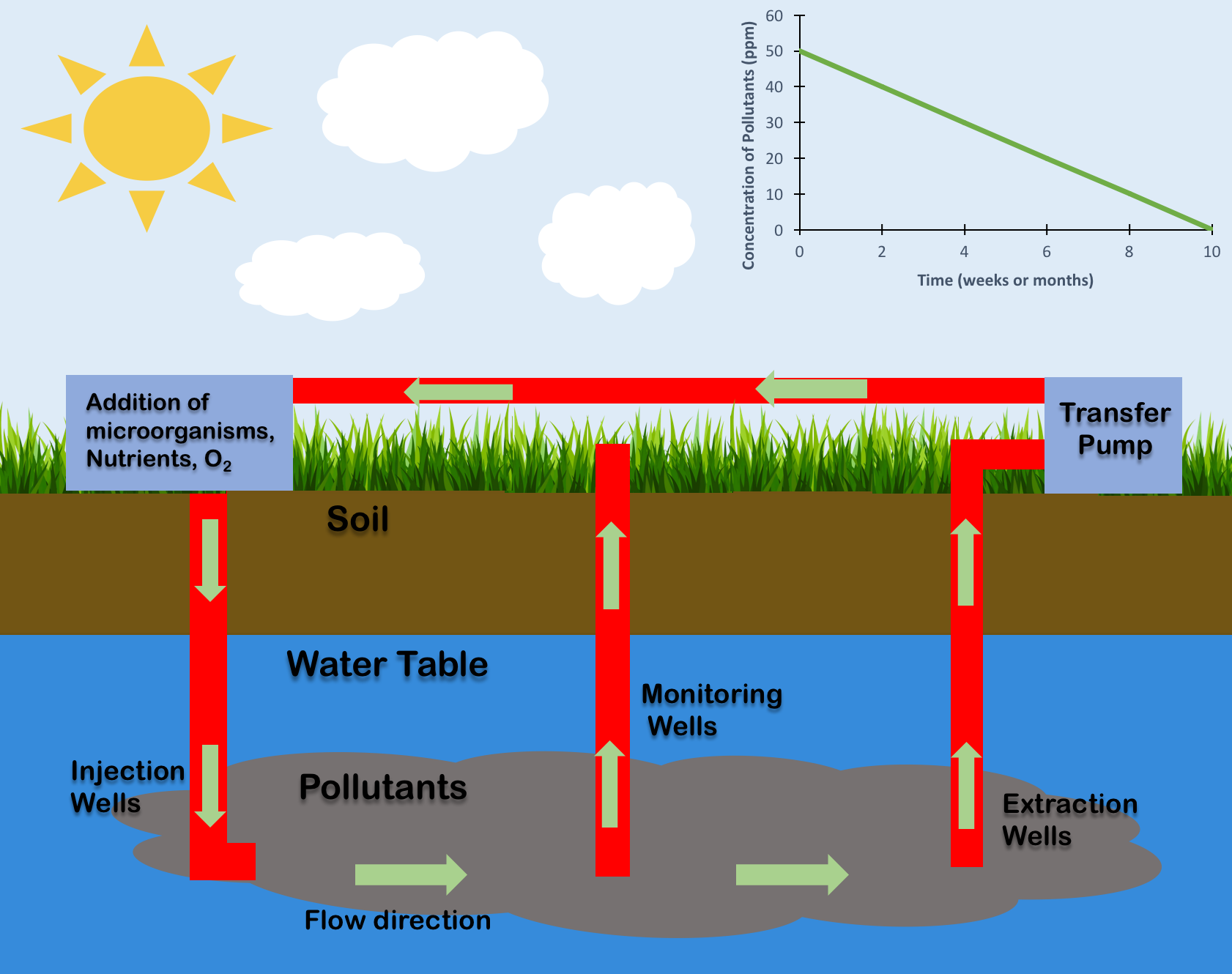
Bioremediation
Bioremediation broadly refers to any process wherein a biological system (typically bacteria, microalgae, fungi in mycoremediation, and plants in phytoremediation), living or dead, is employed for removing environmental pollutants from air, water, soil, fuel gasses, industrial effluents etc., in natural or artificial settings. The natural ability of organisms to adsorb, accumulate, and degrade common and emerging pollutants has attracted the use of biological resources in treatment of contaminated environment. In comparison to conventional physicochemical treatment methods bioremediation may offer advantages as it aims to be sustainable, eco-friendly, cheap, and scalable. This technology is rarely implemented however because it is slow or inefficient. Most bioremediation is inadvertent, involving native organisms. Research on bioremediation is heavily focused on stimulating the process by inoculation of a polluted site with organisms or supplying nutrients to promote their growt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium Peroxide
Magnesium peroxide (MgO2) is an odorless fine powder peroxide with a white to off-white color. It is similar to calcium peroxide because magnesium peroxide also releases oxygen by breaking down at a controlled rate with water. Commercially, magnesium peroxide often exists as a compound of magnesium peroxide and magnesium hydroxide. Structure O2, similarly to N2, has the ability to bind either side-on or end-on. The structure of MgO2 has been calculated as a triangular shape with the O2 molecule binding side-on to the magnesium. This arrangement is a result of the Mg+ donating charge to the oxygen and creating a Mg2+O22−. The bond between to O2 and the magnesium atom has an approximate dissociation energy of 90 kJ mol−1. In the solid state, MgO2 has a cubic pyrite-type crystal structure with 6-coordinate Mg2+ ions and O22− peroxide-groups, according to experimental data and evolutionary crystal structure prediction, the latter predicting a phase transition at the pressure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. Nelumbo nucifera, lotus). Aquaculture involves cultivating freshwater, brackish water, and saltwater populations under controlled or semi-natural conditions and can be contrasted with commercial fishing, which is the harvesting of wild fish. Aquaculture is also a practice used for restoring and rehabilitating marine and freshwater ecosystems. Mariculture, commonly known as marine farming, is aquaculture in seawater habitats and lagoons, as opposed to freshwater aquaculture. Pisciculture is a type of aquaculture that consists of fish farming to obtain Fish as food, fish products as food. Aquaculture can also be defined as the breeding, growing, and harvesting of fish and other aquatic plants, also known as farming in water. It is an environme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rice
Rice is a cereal grain and in its Domestication, domesticated form is the staple food of over half of the world's population, particularly in Asia and Africa. Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice)—or, much less commonly, ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). Asian rice was domesticated in China some 13,500 to 8,200 years ago; African rice was domesticated in Africa about 3,000 years ago. Rice has become commonplace in many cultures worldwide; in 2023, 800 million tons were produced, placing it third after sugarcane and maize. Only some 8% of rice is traded internationally. China, India, and Indonesia are the largest consumers of rice. A substantial amount of the rice produced in developing nations is lost after harvest through factors such as poor transport and storage. Rice yields can be reduced by pests including insects, rodents, and birds, as well as by weeds, and by List of rice diseases, diseases such as rice blast. Traditional rice polyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Improving Agent
A dough conditioner, flour treatment agent, improving agent or bread improver is any ingredient or chemical added to bread dough to strengthen its texture or otherwise improve it in some way. Dough conditioners may include enzymes, yeast nutrients, mineral salts, oxidants and reductants, bleaching agents and emulsifiers. They are food additives combined with flour to improve baking functionality. Flour treatment agents are used to increase the speed of dough rising and to improve the strength and workability of the dough. Examples Examples of dough conditioners include ascorbic acid, distilled monoglycerides, citrate ester of monoglycerides, diglycerides, ammonium chloride, enzymes, diacetyl tartaric acid ester of monoglycerides or DATEM, potassium bromate, potassium iodate, calcium salts such as calcium iodate, L-cystine, L-cysteine HCl, glycerol monostearate, azodicarbonamide, sodium stearoyl lactylate, sucrose palmitate or other sucrose esters, polyoxyethylene sorbitan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E Number
E numbers, short for Europe numbers, are codes for substances used as food additives, including those found naturally in many foods, such as vitamin C, for use within the European Union (EU) and European Free Trade Association (EFTA). Commonly found on food labels, their safety assessment and approval are the responsibility of the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The fact that an additive has an E number implies that its use was at one time permitted in products for sale in the European Single Market; some of these additives are no longer allowed today. Having a single unified list for food additives was first agreed upon in 1962 with food colouring. In 1964, the directives for preservatives were added, in 1970 antioxidants were added, in 1974 emulsifiers, stabilisers, thickeners and gelling agents were added as well. Numbering schemes The numbering scheme follows that of the International Numbering System for Food Additives, International Numbering System (INS) as deter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |