|
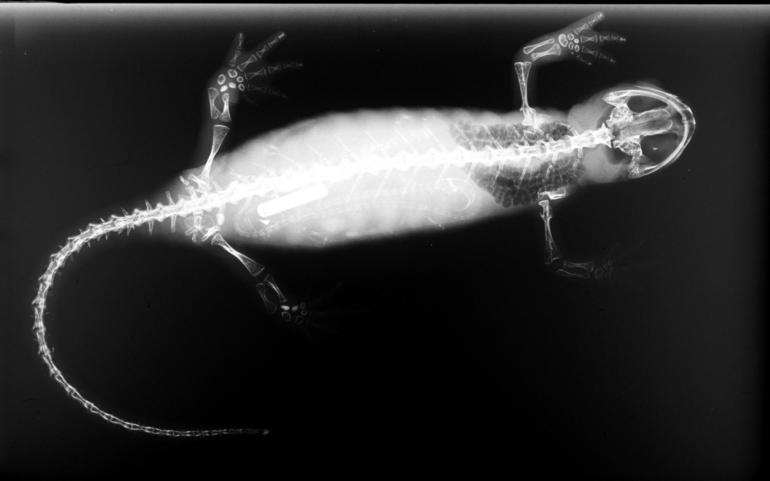
Bolitoglossa
''Bolitoglossa'' is a genus of lungless salamanders, Common name, commonly called mushroom-tongued salamanders, tropical climbing salamanders, and web-footed salamanders, in the family Plethodontidae. Their combined geographic ranges extend from northern Mexico through Central America to Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Peru, northeastern Brazil, and central Bolivia. Neotropical salamanders of the genus ''Bolitoglossa'' make up the largest genus in the order Caudata, consisting of approximately one-fifth of all known species of salamanders. Adult salamanders of the genus ''Bolitoglossa'' have a Snout–vent length, snout-to-vent length in the range of depending on the particular species. They are known for the ability to project the tongue to seize prey items. They are also known for webbed feet, having significantly more webbing than any other species outside their genus with the exception of the cave-dwelling Mexican Bolitoglossinae, bolitoglossine ''Chiropterotriton magnipes''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolitoglossa Platydactyla, Broadfoot Mushroomtongue Salamander, Tamaulipas
''Bolitoglossa'' is a genus of lungless salamanders, commonly called mushroom-tongued salamanders, tropical climbing salamanders, and web-footed salamanders, in the family Plethodontidae. Their combined geographic ranges extend from northern Mexico through Central America to Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Peru, northeastern Brazil, and central Bolivia. Neotropical salamanders of the genus ''Bolitoglossa'' make up the largest genus in the order Caudata, consisting of approximately one-fifth of all known species of salamanders. Adult salamanders of the genus ''Bolitoglossa'' have a snout-to-vent length in the range of depending on the particular species. They are known for the ability to project the tongue to seize prey items. They are also known for webbed feet, having significantly more webbing than any other species outside their genus with the exception of the cave-dwelling Mexican bolitoglossine '' Chiropterotriton magnipes''. Although webbed feet are a common characterist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberch's Salamander
Alberch's salamander (''Bolitoglossa alberchi'') is a species of salamander in the family Plethodontidae. It is endemic to mexico and known from Veracruz, extreme eastern Oaxaca, and western and central Chiapas, from near sea level to asl. Its natural habitats are tropical lowland forests. It also occurs along the edges of clearings and well-shaded plantations. It seems to be a fairly common species, although it is threatened by habitat loss Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss or habitat reduction) occurs when a natural habitat is no longer able to support its native species. The organisms once living there have either moved elsewhere, or are dead, leading to a decrease ... caused by agriculture, wood extraction, and human settlement. References Bolitoglossa Endemic amphibians of Mexico Amphibians described in 2002 Taxa named by David B. Wake Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{Plethodontidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolitoglossa Mexicana
The Mexican climbing salamander (''Bolitoglossa mexicana'') is a species of salamander in the family Plethodontidae. It is found in Belize, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, and possibly Nicaragua. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry forests, subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests, subtropical or tropical moist montane forests, plantations, and rural gardens. It is threatened by habitat loss Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss or habitat reduction) occurs when a natural habitat is no longer able to support its native species. The organisms once living there have either moved elsewhere, or are dead, leading to a decrease .... References Bolitoglossa Taxonomy articles created by Polbot Amphibians described in 1854 Taxa named by André Marie Constant Duméril {{Plethodontidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salamander
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All ten extant salamander families are grouped together under the order Urodela, the sole surviving order from the group Caudata. ''Urodela'' is a scientific Latin term based on the Ancient Greek : ourà dēlē "conspicuous tail". ''Caudata'' is the Latin for "tailed ones", from : "tail". Salamander diversity is highest in eastern North America, especially in the Appalachian Mountains; most species are found in the Holarctic realm, with some species present in the Neotropical realm. Salamanders never have more than four toes on their front legs and five on their rear legs, but some species have fewer digits and others lack hind limbs. Their permeable skin usually makes them reliant on habitats in or near water or other cool, damp places. So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter's Climbing Salamander
Peter's climbing salamander or Peter's mushroomtongue salamander (''Bolitoglossa adspersa'') is a species of salamander in the family Plethodontidae. It is endemic to Colombia. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist montane forests and subtropical or tropical high-altitude grassland. It is threatened by habitat loss Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss or habitat reduction) occurs when a natural habitat is no longer able to support its native species. The organisms once living there have either moved elsewhere, or are dead, leading to a decrease .... References adspersa Amphibians of Colombia Endemic fauna of Colombia Taxonomy articles created by Polbot Amphibians described in 1863 Taxa named by Wilhelm Peters {{Plethodontidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolitoglossinae
Bolitoglossinae is a subfamily of lungless salamander. Most of them are native to tropical areas in Central and South America, though a few such as Batrachoseps are found in temperate regions. Its sister group is the extinct genus Palaeoplethodon ''Palaeoplethodon hispaniolae'' is an extinct salamander species found in Miocene Dominican amber from the Dominican Republic. It is so far the only salamander species known to have existed in the Caribbean. Discovery and description The .... {{Taxonbar, from=Q3077933 Plethodontidae Amphibian subfamilies Taxa named by Edward Hallowell (herpetologist) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autotomy
Autotomy (from the Greek ''auto-'', "self-" and ''tome'', "severing", αὐτοτομία) or 'self-amputation', is the behaviour whereby an animal sheds or discards an appendage, usually as a self-defense mechanism to elude a predator's grasp or to distract the predator and thereby allow escape. Some animals are able to regenerate the lost body part later. Autotomy is thought to have evolved independently at least nine times. The term was coined in 1883 by Leon Fredericq. Vertebrates Reptiles and amphibians Some lizards, salamanders and tuatara when caught by the tail will shed part of it in attempting to escape. In many species the detached tail will continue to wriggle, creating a deceptive sense of continued struggle, and distracting the predator's attention from the fleeing prey animal. In addition, many species of lizards, such as '' Plestiodon fasciatus'', '' Cordylosaurus subtessellatus'', '' Holaspis guentheri'', '' Phelsuma barbouri'', and '' Ameiva wetmorei'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plethodontidae
Plethodontidae, or lungless salamanders, are a family of salamanders. With over 500 species, lungless salamanders are by far the largest family of salamanders in terms of their diversity. Most species are native to the Western Hemisphere, from British Columbia to Brazil. Only two extant genera occur in the Eastern Hemisphere: '' Speleomantes'' (native to Sardinia and mainland Europe south of the Alps) and '' Karsenia'' (native to South Korea). Biology Adult lungless salamanders have four limbs, with four toes on the fore limbs, and usually with five on the hind limbs. Within many species, mating and reproduction occur solely on land. Accordingly, many species also lack an aquatic larval stage, a phenomenon known as direct development in which the offspring hatch as fully-formed, miniature adults. Direct development is correlated with changes in the developmental characteristics of plethodontids compared to other families of salamanders including increases in egg size and durat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabriel Bibron
Gabriel Bibron (20 October 1805 – 27 March 1848) was a French zoologist and herpetologist. He was born in Paris. The son of an employee of the Museum national d'histoire naturelle, he had a good foundation in natural history and was hired to collect vertebrates in Italy and Sicily. Under the direction of Jean Baptiste Bory de Saint-Vincent (1778–1846), he took part in the Morea expedition to Peloponnese. He classified numerous reptile species A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ... with André Marie Constant Duméril (1774–1860), whom he had met in 1832. Duméril was interested mainly in the relations between genera, and he left to Bibron the task of describing the species. Working together they produced the ''Erpétologie Générale'', a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectively, in each homologous chromosome pair—the form in which chromosomes naturally exist. Somatic cells, tissues, and individual organisms can be described according to the number of sets of chromosomes present (the "ploidy level"): monoploid (1 set), diploid (2 sets), triploid (3 sets), tetraploid (4 sets), pentaploid (5 sets), hexaploid (6 sets), heptaploid or septaploid (7 sets), etc. The generic term polyploid is often used to describe cells with three or more sets of chromosomes. Virtually all sexually reproducing organisms are made up of somatic cells that are diploid or greater, but ploidy level may vary widely between different organisms, between different tissues within the same organism, and at different stages in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most important of these proteins are the histones. Aided by chaperone proteins, the histones bind to and condense the DNA molecule to maintain its integrity. These eukaryotic chromosomes display a complex three-dimensional structure that has a significant role in transcriptional regulation. Normally, chromosomes are visible under a light microscope only during the metaphase of cell division, where all chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell in their condensed form. Before this stage occurs, each chromosome is duplicated ( S phase), and the two copies are joined by a centromere—resulting in either an X-shaped structure if the centromere is located equatorially, or a two-armed structure if the centromere is located distally; the jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |