|
Bogs
A bog or bogland is a wetland that accumulates peat as a deposit of dead plant materials often mosses, typically sphagnum moss. It is one of the four main Wetland#Types, types of wetlands. Other names for bogs include mire, mosses, quagmire, and muskeg; alkaline mires are called fens. A bayhead is another type of bog found in the forest of the Gulf Coast states in the United States.Watson, Geraldine Ellis (2000) ''Big Thicket Plant Ecology: An Introduction'', Third Edition (Temple Big Thicket Series #5). University of North Texas Press. Denton, Texas. 152 pp. Texas Parks and Wildlife. Ecological Mapping Systems of Texas:West Gulf Coastal Plain Seepage Swamp and Baygall. Retrieved 7 July 2020 They are often covered in Ericaceae, heath or heather shrubs rooted in the sphagnum moss and peat. The gradual accumulation of decayed plant material in a bog functions as a carbon sink. Bogs occur where the water at the ground surface is acidic and low in nutrients. A bog usually is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peat
Peat is an accumulation of partially Decomposition, decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, Moorland, moors, or muskegs. ''Sphagnum'' moss, also called peat moss, is one of the most common components in peat, although many other plants can contribute. The biological features of sphagnum mosses act to create a habitat aiding peat formation, a phenomenon termed 'habitat manipulation'. Soils consisting primarily of peat are known as histosols. Peat forms in wetland conditions, where flooding or stagnant water obstructs the flow of oxygen from the atmosphere, slowing the rate of decomposition. Peat properties such as organic matter content and saturated hydraulic conductivity can exhibit high spatial heterogeneity. Peatlands, particularly bogs, are the primary source of peat; although less common, other wetlands, including fens, pocosins and peat swamp forests, also deposit peat. Landscapes covered in peat are home to sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
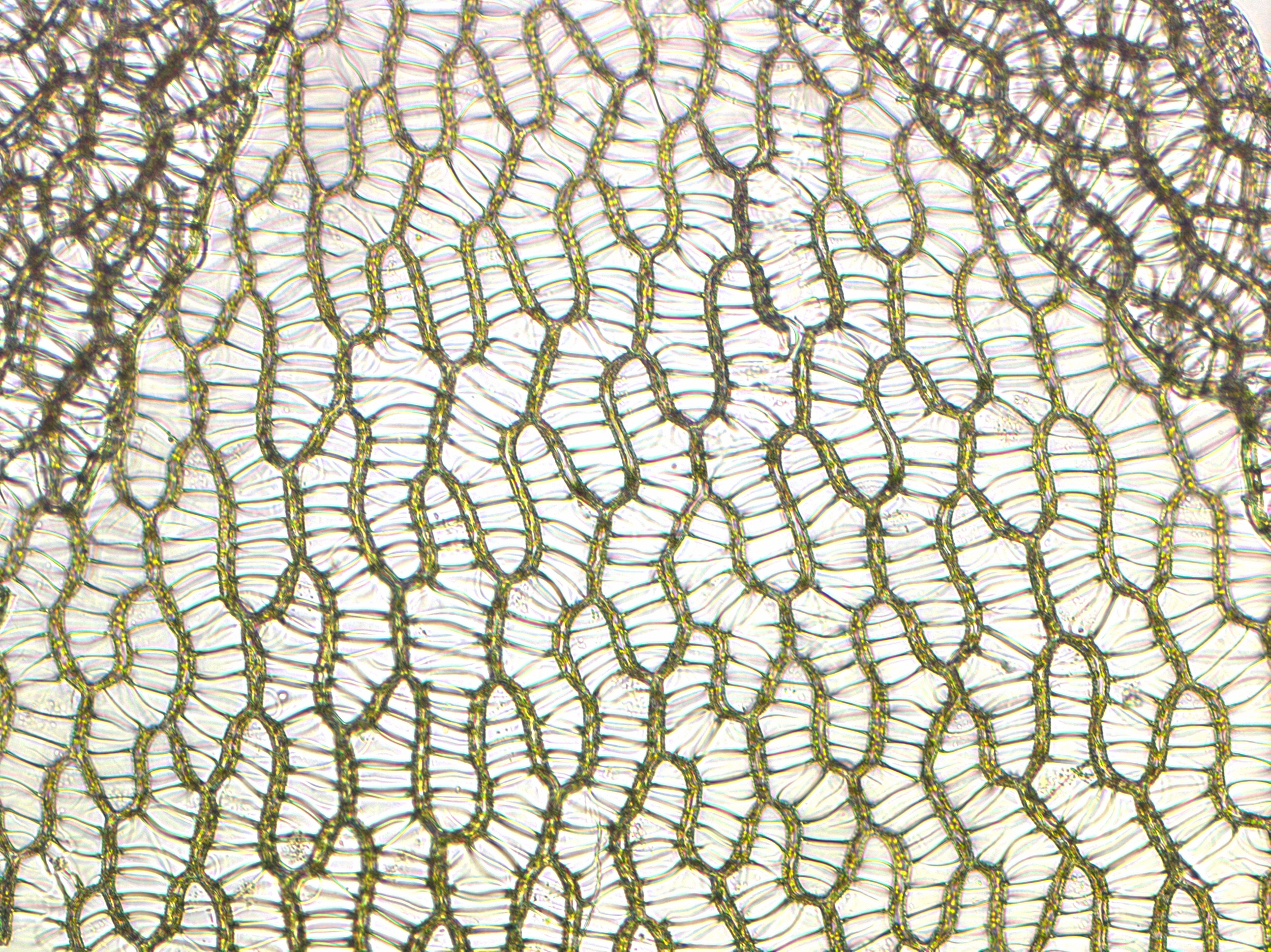
Sphagnum
''Sphagnum'' is a genus of approximately 380 accepted species of mosses, commonly known as sphagnum moss, also bog moss and quacker moss (although that term is also sometimes used for peat). Accumulations of ''Sphagnum'' can store water, since both living and dead plants can hold large quantities of water inside their cells; plants may hold 16 to 26 times as much water as their dry weight, depending on the species.Bold, H. C. 1967. Morphology of Plants. second ed. Harper and Row, New York. p. 225–229. The empty cells help retain water in drier conditions. As ''Sphagnum'' moss grows, it can slowly spread into drier conditions, forming larger mires, both raised bogs and blanket bogs. Thus, ''Sphagnum'' can influence the composition of such habitats, with some describing ''Sphagnum'' as 'habitat manipulators' or 'autogenic ecosystem engineers'. These peat accumulations then provide habitat for a wide array of peatland plants, including sedges and Calcifuge, ericaceous shrubs, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson Bay Lowland
The Hudson Bay Lowlands is a vast wetland located between the Canadian Shield and southern shores of Hudson Bay and James Bay. Most of the area lies within the province of Ontario, with smaller portions reaching into Manitoba and Quebec. Many wide and slow-moving rivers flow through this area toward the saltwater of Hudson Bay: these include the Churchill, Nelson and Hayes in Manitoba, Severn, Fawn, Winisk, Asheweig, Ekwan, Attawapiskat, and Albany in Ontario, and the Harricana, Rupert and Eastmain in Quebec. This is the largest wetland in Canada, and one of the largest in the world.Abraham, K.F. and C.J. Keddy. The Hudson Bay Lowland. Pages 118–148 in L.H. Fraser and P.A. Keddy (eds.). 2005. The World's Largest Wetlands: Ecology and Conservation. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 488 p. The region can be subdivided into three bands running roughly northwest to southeast: the Coastal Hudson Bay Lowland (a narrow band along the northern coast), Hudson Bay Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lauhanvuori Suo
Lauhanvuori National Park () is a national park in the Southern Ostrobothnia region of Finland, on the border of Kauhajoki and Isojoki. It was established in 1982 and covers . The park is characterized by its pine forestland, spring brooks, and swamps. Nature Mountain The Lauhanvuori mountain is a high moraine mountain and one of the highest points in Western Finland. The summit area was uncovered 9500 BCE when the glacier retreated, and it has never been under the water. Indeed, it was an island in the middle of the Ancylus Lake. Flora and fauna The summit of Lauhanvuori is lusher than its surroundings due to not having been under the sea and thus having retained its loose soil and nutrients. The hillsides are barren and infertile. Cranes and capercaillies can be heard in the bogs during summertime. The willow grouse also inhabits the bogs. The park also has a hectare of fen, where '' Succisa pratensis'', brown beak-sedge, carnation sedge, moor rush, Scotti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis acid. The first category of acids are the proton donors, or Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acids. In the special case of aqueous solutions, proton donors form the hydronium ion H3O+ and are known as Acid–base reaction#Arrhenius theory, Arrhenius acids. Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted, Brønsted and Martin Lowry, Lowry generalized the Arrhenius theory to include non-aqueous solvents. A Brønsted–Lowry or Arrhenius acid usually contains a hydrogen atom bonded to a chemical structure that is still energetically favorable after loss of H+. Aqueous Arrhenius acids have characteristic properties that provide a practical description of an acid. Acids form aqueous solutions with a sour taste, can turn blue litmus red, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magellanic Subpolar Forests
The Magellanic subpolar forests () are a terrestrial ecoregion of southernmost South America, covering parts of southern Chile and Argentina, and are part of the Neotropical realm. It is a temperate broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion, and contains the world's southernmost forests. Setting The Magellanic subpolar forests ecoregion lies to the west of the Andes Mountains, which run north-south for most of their length but curve eastward near the southern tip of South America, terminating at the archipelago of Tierra del Fuego. The Magellanic ecoregion was covered by glaciers during the last ice age, and the landscape is deeply dissected by fjords, with numerous islands, inlets, and channels, including the Strait of Magellan, which separates Tierra del Fuego from the South American mainland and is the route taken by Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan from the South Atlantic to the South Pacific. North of roughly 48° south latitude lies the Valdivian temperate forests eco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states since the lengthy conquest of Siberia, which began with the fall of the Khanate of Sibir in 1582 and concluded with the annexation of Chukotka in 1778. Siberia is vast and sparsely populated, covering an area of over , but home to roughly a quarter of Russia's population. Novosibirsk, Krasnoyarsk, and Omsk are the largest cities in the area. Because Siberia is a geographic and historic concept and not a political entity, there is no single precise definition of its territorial borders. Traditionally, Siberia spans the entire expanse of land from the Ural Mountains to the Pacific Ocean, with the Ural River usually forming the southernmost portion of its western boundary, and includes most of the drainage basin of the Arctic Ocean. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined by humans as being in the same celestial sphere, celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the Solar System as Earth's North Pole. Due to Earth's axial tilt of 23.439281°, there is a seasonal variation in the lengths of the day and night. There is also a seasonal variation in temperatures, which lags the variation in day and night. Conventionally, winter in the Northern Hemisphere is taken as the period from the December solstice (typically December 21 UTC) to the March equinox (typically March 20 UTC), while summer is taken as the period from the June solstice through to the September equinox (typically on 23 September UTC). The dates vary each year due to the difference between the calendar year and the Year#Astronomical years, astronomical year. Within the Northern Hemisphere, oceanic currents can change the weather patterns that aff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boreal Ecosystem
A boreal ecosystem is an ecosystem with a subarctic climate located in the Northern Hemisphere, approximately between 50° and 70°N latitude. These ecosystems are commonly known as taiga and are located in parts of North America, Europe, and Asia. The ecosystems that lie immediately to the south of boreal zones are often called hemiboreal. There are a variety of processes and species that occur in these areas as well. The Köppen symbols of boreal ecosystems are Dfc, Dwc, Dfd, and Dwd. Boreal ecosystems are some of the most vulnerable to climate change. Both loss of permafrost, reductions in cold weather and increases in summer heat cause significant changes to ecosystems, displacing cold-adapted species, increasing forest fires, and making ecosystems vulnerable to changing to other ecosystem types. These changes can cause Climate change feedback cycles, where thawing permafrost and changing ecosystems release more greenhouse gas emissions into the atmosphere causing more clima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clime
The climes (singular ''clime''; also ''clima'', plural ''climata'', from Greek κλίμα ''klima'', plural κλίματα ''klimata'', meaning "inclination" or "slope") in classical Greco-Roman geography and astronomy were the divisions of the inhabited portion of the spherical Earth by geographic latitude. Starting with Aristotle (''Meteorology'' 2.5,362a32), the Earth was divided into five zones, assuming two ''frigid'' climes (the Arctic and Antarctic) around the poles, an uninhabitable ''torrid'' clime near the equator, and two ''temperate'' climes between the frigid and the torrid ones. Different lists of climata were in use in Hellenistic and Roman time. Claudius Ptolemy was the first ancient scientist known to have devised the so-called system of seven climes (Almagest 2.12) which, due to his authority, became one of the canonical elements of late antique, medieval European and Arab geography. In Medieval Europe, the climes for 15 and 18 hours of longest daylig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |