|
Biobanks
A biobank is a type of biorepository that stores biological samples (usually human) for use in research. Biobanks have become an important resource in medical research, supporting many types of contemporary research like genomics and personalized medicine. Biobanks can give researchers access to data representing a large number of people. Samples in biobanks and the data derived from those samples can often be used by multiple researchers for cross purpose research studies. For example, many diseases are associated with single-nucleotide polymorphisms. Genome-wide association studies using data from tens or hundreds of thousands of individuals can identify these genetic associations as potential disease biomarkers. Many researchers struggled to acquire sufficient samples prior to the advent of biobanks. Biobanks have provoked questions on privacy, research ethics, and medical ethics. Viewpoints on what constitutes appropriate biobank ethics diverge. However, a consensus has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biobank Ethics
Biobank ethics refers to the ethics pertaining to all aspects of biobanks. The issues examined in the field of biobank ethics are special cases of clinical research ethics. Overview of issues The following table shows many of the leading controversial issues related to biobanking. The table names an issue, then describes a point on which there is consensus and an aspect of that same point for which there is no consensus. Privacy for research participants There is broad consensus that when a person donates a specimen for research then that person has a right to privacy thereafter. To this end, researchers balance the need for specimens to be anonymous or de-identified from protected health information with the need to have access to data about the specimen so that researchers can use the sample without knowing the identity of the donor. In the United States, for example, the Office for Human Research Protections often promotes a traditional system wherein data which could ident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
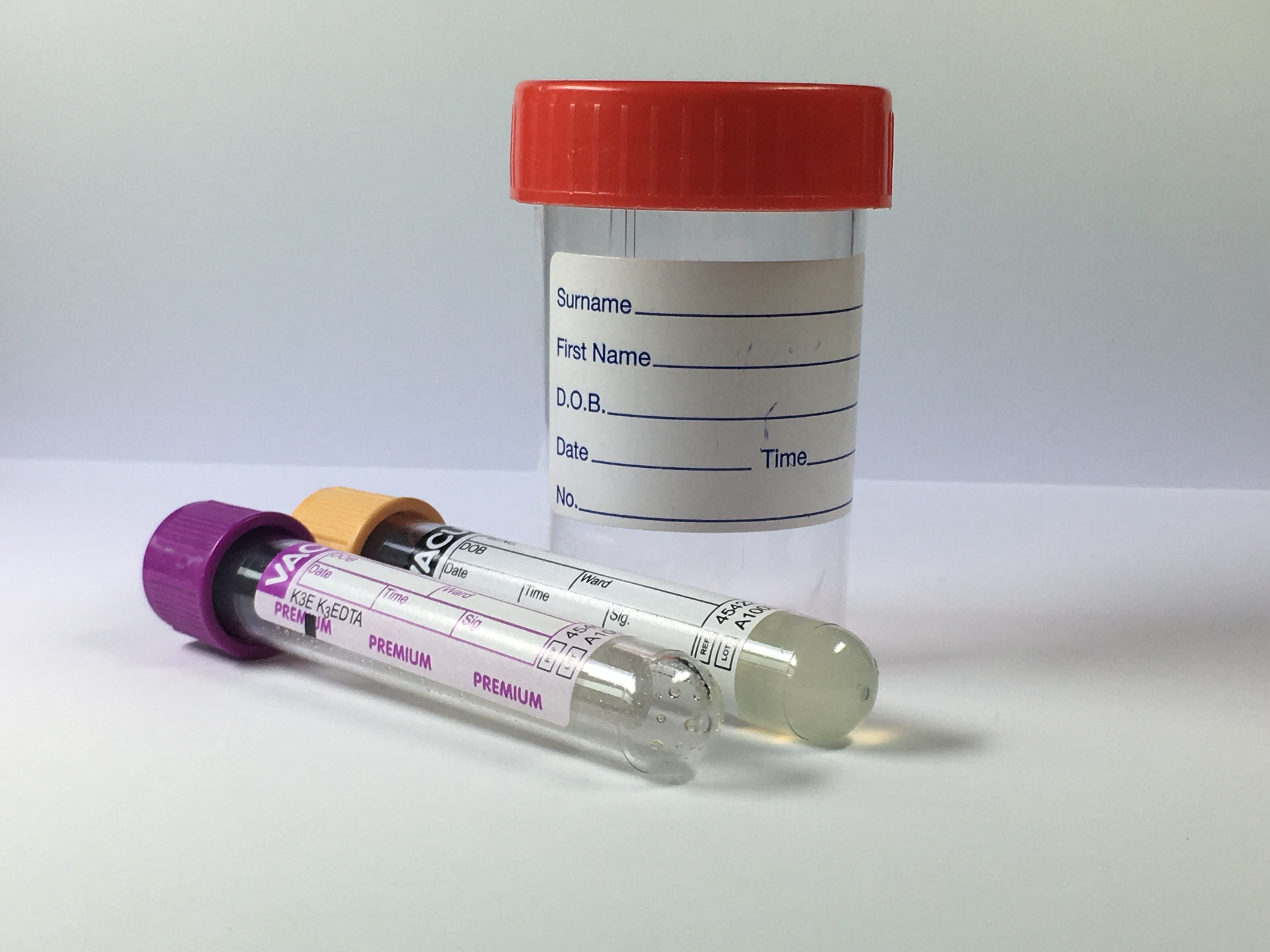
Biorepository
A biorepository is a facility that collects, catalogs, and stores samples of biological material for laboratory research. Biorepositories collect and manage specimens from animals, plants, and other living organisms. Biorepositories store many different types of specimens, including samples of blood, urine, tissue, cells, DNA, RNA, and proteins. If the samples are from people, they may be stored with medical information along with written consent to use the samples in laboratory studies. Purpose The purpose of a biorepository is to maintain biological specimens, and associated information, for future use in research. The biorepository maintains the quality of specimens in its collection and ensures that they are accessible for scientific research. Operations The four main operations of a biorepository are; (i) collection (ii) processing, (iii) storage or inventory, and (iv) distribution of biological specimens. (i) Collection or accession occurs when a specimen arrives at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tissue Bank
A tissue bank is an establishment that collects and recovers human cadaver tissue for the purposes of medical research, education and allograft transplantation. A tissue bank may also refer to a location where biomedical tissue is stored under cryogenic conditions and is generally used in a more clinical sense. The United States Navy Tissue Bank is generally accepted as the first full tissue banking service of its kind in the world although it is not the largest or only tissue bank today. Donating a body Most medical schools need donated bodies for teaching students about the anatomy and physiology of the body, as well as how to perform medical procedures. There are no upper age limits for donating your body to science. Each school has different policies and procedures for donated bodies. Act 368 of the Public Acts of Michigan 1978, Article 10, Part 101, authorizes an individual to will their body to a medical institution. Medical institutions will only accept a full body, meanin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtual Biobank
A virtual biobank is a virtual repository which provides data extracted from and characterizing samples stored at classical biobanks. Virtual biobanks are large databases and can provide high-resolution images of samples as well as other characteristic data. These virtual biobanks can be accessed via specialized software or web portals. Samples are stored in a decentralized manner. The use of virtual biobanks provides access, in the form of pre-collected data, without requiring access to the physical sample. This allows the sample's data to be more readily shared without fear of contaminating/destroying/transporting the sample. Virtual biobanks are often used in bioinformatics Bioinformatics () is an interdisciplinary field of science that develops methods and Bioinformatics software, software tools for understanding biological data, especially when the data sets are large and complex. Bioinformatics uses biology, .... List of virtual biobanks * UK Prostate Cancer Sampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (physical form and structure), its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological properties, and its behavior. An organism's phenotype results from two basic factors: the expression of an organism's genetic code (its genotype) and the influence of environmental factors. Both factors may interact, further affecting the phenotype. When two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species, the species is called polymorphic. A well-documented example of polymorphism is Labrador Retriever coloring; while the coat color depends on many genes, it is clearly seen in the environment as yellow, black, and brown. Richard Dawkins in 1978 and again in his 1982 book '' The Extended Phenotype'' suggested that one can regard bird nests and other built structures such as caddisfly larva cases and beaver dams ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing, also known as DNA testing, is used to identify changes in DNA sequence or chromosome structure. Genetic testing can also include measuring the results of genetic changes, such as RNA analysis as an output of gene expression, or through biochemical analysis to measure specific protein output. In a medical setting, genetic testing can be used to diagnose or rule out suspected genetic disorders, predict risks for specific conditions, or gain information that can be used to customize medical treatments based on an individual's genetic makeup. Genetic testing can also be used to determine biological relatives, such as a child's biological parentage (genetic mother and father) through DNA paternity testing, or be used to broadly predict an individual's ancestry. Genetic testing of plants and animals can be used for similar reasons as in humans (e.g. to assess relatedness/ancestry or predict/diagnose genetic disorders), to gain information used for selective breed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Barrier Reef
The Great Barrier Reef is the world's largest coral reef system, composed of over 2,900 individual reefs and 900 islands stretching for over over an area of approximately . The reef is located in the Coral Sea, off the coast of Queensland, Australia, separated from the coast by a channel wide in places and over deep. The Great Barrier Reef can be seen from outer space and is the world's biggest single structure made by living organisms. This reef structure is composed of and built by billions of tiny organisms, known as coral polyp (zoology), polyps. It supports a wide diversity of life and was selected as a World Heritage Site in 1981. CNN labelled it one of the Seven Wonders of the World#Seven Natural Wonders of the World, Seven Natural Wonders of the World in 1997. Australian World Heritage places included it in its list in 2007. The Queensland National Trust named it a state icon of Queensland in 2006. A large part of the reef is protected by the Great Barrier Reef Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecosystem Restoration
Ecological restoration, or ecosystem restoration, is the process of assisting the recovery of an ecosystem that has been degraded, damaged, destroyed or transformed. It is distinct from conservation in that it attempts to retroactively repair already damaged ecosystems rather than take preventative measures. Ecological restoration can help to reverse biodiversity loss, combat climate change, support the provision of ecosystem services and support local economies. The United Nations has named 2021–2030 the Decade on Ecosystem Restoration. Habitat restoration involves the deliberate rehabilitation of a specific area to reestablish a functional ecosystem. This may differ from historical baselines (the ecosystem's original condition at a particular point in time). To achieve successful habitat restoration, it is essential to understand the life cycles and interactions of species, as well as the essential elements such as food, water, nutrients, space, and shelter needed to suppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genotype
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a specific gene depends on the number of copies of each chromosome found in that species, also referred to as ploidy. In diploid species like humans, two full sets of chromosomes are present, meaning each individual has two alleles for any given gene. If both alleles are the same, the genotype is referred to as Zygosity, homozygous. If the alleles are different, the genotype is referred to as heterozygous. Genotype contributes to phenotype, the observable traits and characteristics in an individual or organism. The degree to which genotype affects phenotype depends on the trait. For example, the petal color in a pea plant is exclusively determined by genotype. The petals can be purple or white depending on the alleles present in the pea plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
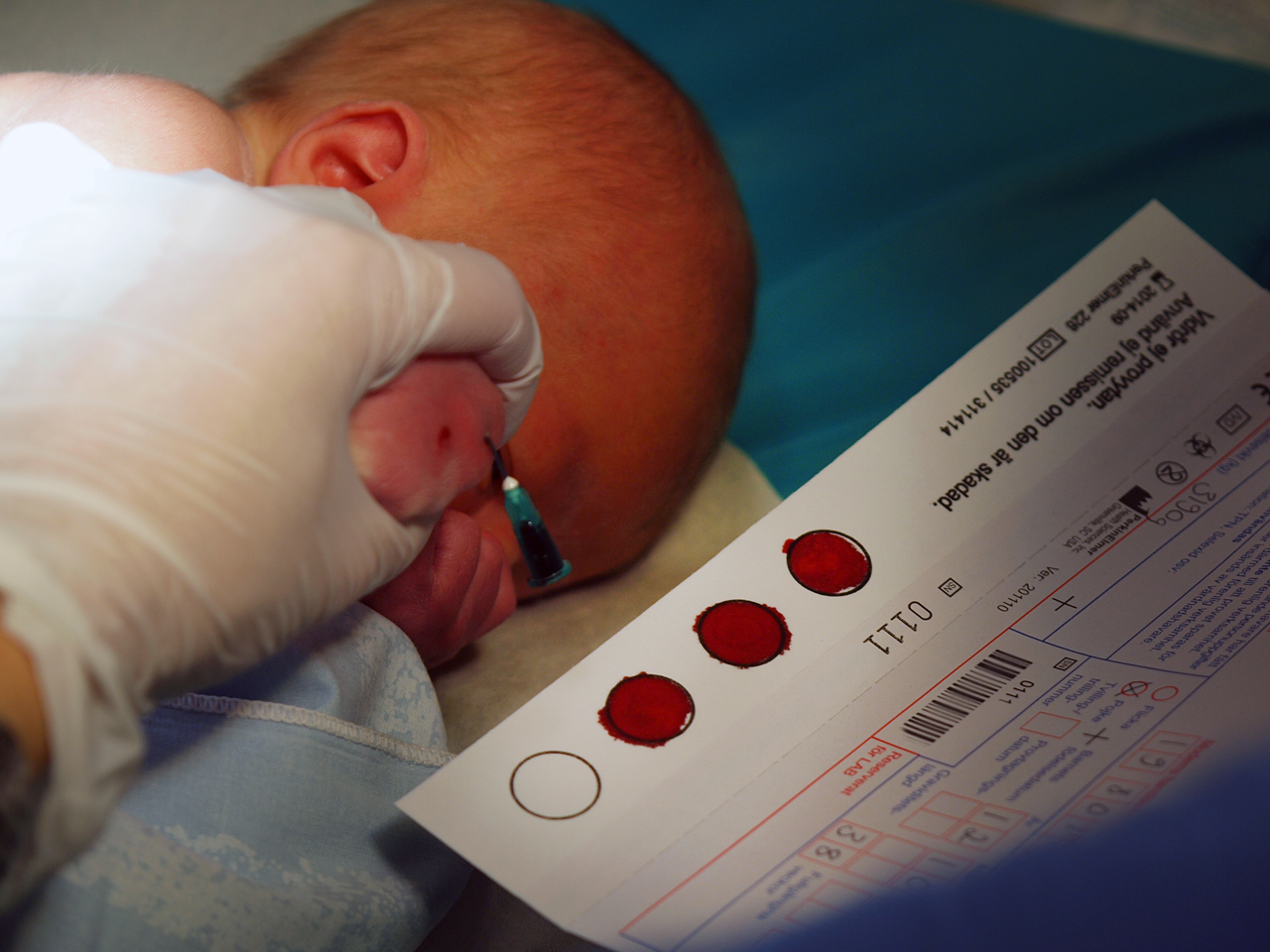
Sampling (medicine)
In medicine, sampling is gathering of matter from the body to aid in the process of a medical diagnosis and/or evaluation of an indication (medicine), indication for treatment, further medical tests or other procedures. In this sense, the sample is the gathered matter, and the sampling tool or sampler is the person or material to collect the sample. Sampling is a prerequisite for many medical tests, but generally not for medical history, physical examination and radiologic tests. By sampling technique * Obtaining excretions or materials that leave the body anyway, such as urine, Feces, stool, sputum, or vomitus, by direct collection as they exit. A sample of saliva can also be collected from the mouth. * Surgery#Types of surgery, Excision (cutting out), a surgical method for the removal of solid or soft tissue samples. * Puncture (also called ''centesis'') followed by aspiration is the main method used for sampling of many types of tissues and body fluids. Examples are thoracoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood is composed of blood cells suspended in blood plasma. Plasma, which constitutes 55% of blood fluid, is mostly water (92% by volume), and contains proteins, glucose, mineral ions, and hormones. The blood cells are mainly red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and (in mammals) platelets (thrombocytes). The most abundant cells are red blood cells. These contain hemoglobin, which facilitates oxygen transport by reversibly binding to it, increasing its solubility. Jawed vertebrates have an adaptive immune system, based largely on white blood cells. White blood cells help to resist infections and parasites. Platelets are important in the clotting of blood. Blood is circulated around the body through blood vessels by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |