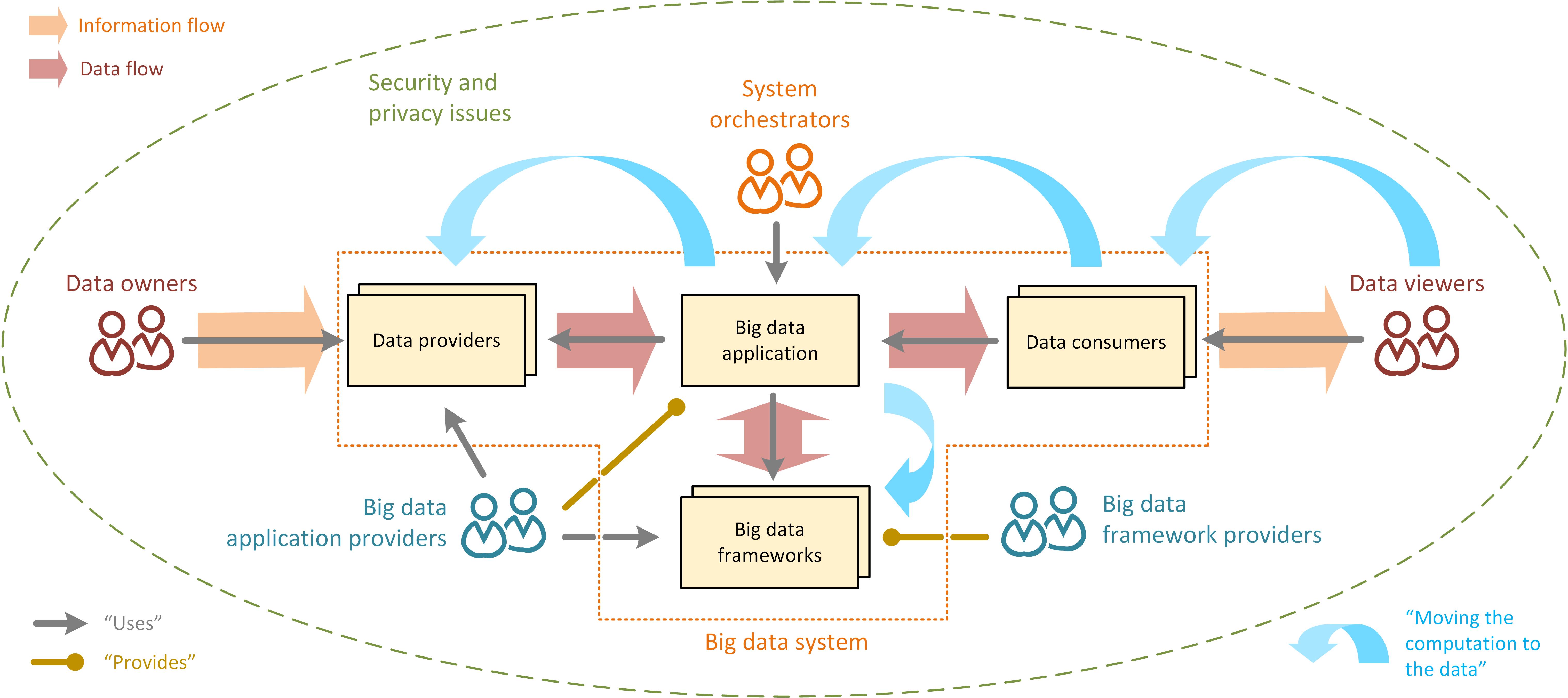
|
Big Data
Big data primarily refers to data sets that are too large or complex to be dealt with by traditional data processing, data-processing application software, software. Data with many entries (rows) offer greater statistical power, while data with higher complexity (more attributes or columns) may lead to a higher false discovery rate. Big data analysis challenges include Automatic identification and data capture, capturing data, Computer data storage, data storage, data analysis, search, Data sharing, sharing, Data transmission, transfer, Data visualization, visualization, Query language, querying, updating, information privacy, and data source. Big data was originally associated with three key concepts: ''volume'', ''variety'', and ''velocity''. The analysis of big data presents challenges in sampling, and thus previously allowing for only observations and sampling. Thus a fourth concept, ''veracity,'' refers to the quality or insightfulness of the data. Without sufficient investm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Set
A data set (or dataset) is a collection of data. In the case of tabular data, a data set corresponds to one or more table (database), database tables, where every column (database), column of a table represents a particular Variable (computer science), variable, and each row (database), row corresponds to a given Record (computer science), record of the data set in question. The data set lists values for each of the variables, such as for example height and weight of an object, for each member of the data set. Data sets can also consist of a collection of documents or files. In the open data discipline, a dataset is a unit used to measure the amount of information released in a public open data repository. The European data.europa.eu portal aggregates more than a million data sets. Properties Several characteristics define a data set's structure and properties. These include the number and types of the attributes or variables, and various statistical measures applicable to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Valuation
Data valuation is a discipline in the fields of accounting and information economics. It is concerned with methods to calculate the value of data collected, stored, analyzed and traded by organizations. This valuation depends on the type, reliability and field of data. History In the 21st century, exponential increases in computing power and data storage capabilities (in line with Moore's law) have led to a proliferation of big data, machine learning and other data analysis techniques. Businesses increasingly adapt these techniques and technologies to pursue data-driven strategies to create new business models. Traditional accounting techniques used to value organizations were developed in an era before high-volume data capture and analysis became widespread and focused on tangible assets (machinery, equipment, capital, property, materials etc.), ignoring data assets. As a result, accounting calculations often ignore data and leave its value off organizations' balance sheets. No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Camera
A digital camera, also called a digicam, is a camera that captures photographs in Digital data storage, digital memory. Most cameras produced today are digital, largely replacing those that capture images on photographic film or film stock. Digital cameras are now widely incorporated into mobile devices like smartphones with the same or more capabilities and features of dedicated cameras. High-end, high-definition dedicated cameras are still commonly used by professionals and those who desire to take higher-quality photographs. Digital and digital movie cameras share an optical system, typically using a Camera lens, lens with a variable Diaphragm (optics), diaphragm to focus light onto an image pickup device. The diaphragm and Shutter (photography), shutter admit a controlled amount of light to the image, just as with film, but the image pickup device is electronic rather than chemical. However, unlike film cameras, digital cameras can display images on a screen immediately afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remote Sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an physical object, object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring information about Earth and other planets. Remote sensing is used in numerous fields, including geophysics, geography, land surveying and most Earth science disciplines (e.g. exploration geophysics, hydrology, ecology, meteorology, oceanography, glaciology, geology). It also has military, intelligence, commercial, economic, planning, and humanitarian applications, among others. In current usage, the term ''remote sensing'' generally refers to the use of satellite- or airborne-based sensor technologies to detect and classify objects on Earth. It includes the surface and the atmosphere and oceans, based on wave propagation, propagated signals (e.g. electromagnetic radiation). It may be split into "active" remote sensing (when a signal is emitted b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Of Things
Internet of things (IoT) describes devices with sensors, processing ability, software and other technologies that connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the Internet or other communication networks. The IoT encompasses Electronic engineering, electronics, Telecommunications engineering, communication, and computer science engineering. "Internet of things" has been considered a misnomer because devices do not need to be connected to the public internet; they only need to be connected to a network and be individually addressable. The field has evolved due to the convergence of multiple technologies, including ubiquitous computing, commodity sensors, and increasingly powerful embedded systems, as well as machine learning.Hu, J.; Niu, H.; Carrasco, J.; Lennox, B.; Arvin, F.,Fault-tolerant cooperative navigation of networked UAV swarms for forest fire monitoring Aerospace Science and Technology, 2022. . Older fields of embedded systems, wireless sensor netw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobile Device
A mobile device or handheld device is a computer small enough to hold and operate in hand. Mobile devices are typically battery-powered and possess a flat-panel display and one or more built-in input devices, such as a touchscreen or keypad. Modern mobile devices often emphasize wireless networking, to both the Internet and to other devices in their vicinity, such as headsets or in-car entertainment systems, via Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular networks, or near-field communication. Characteristics Device mobility can be viewed in the context of several qualities: * Physical dimensions and weight * Whether the device is mobile or some kind of host to which it is attached is mobile * What kind of host devices it can be bound with * How devices communicate with a host * When mobility occurs Strictly speaking, many so-called mobile devices are not mobile. It is the host that is mobile, i.e., a mobile human host carries a non-mobile smartphone device. An example of a true mobile co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
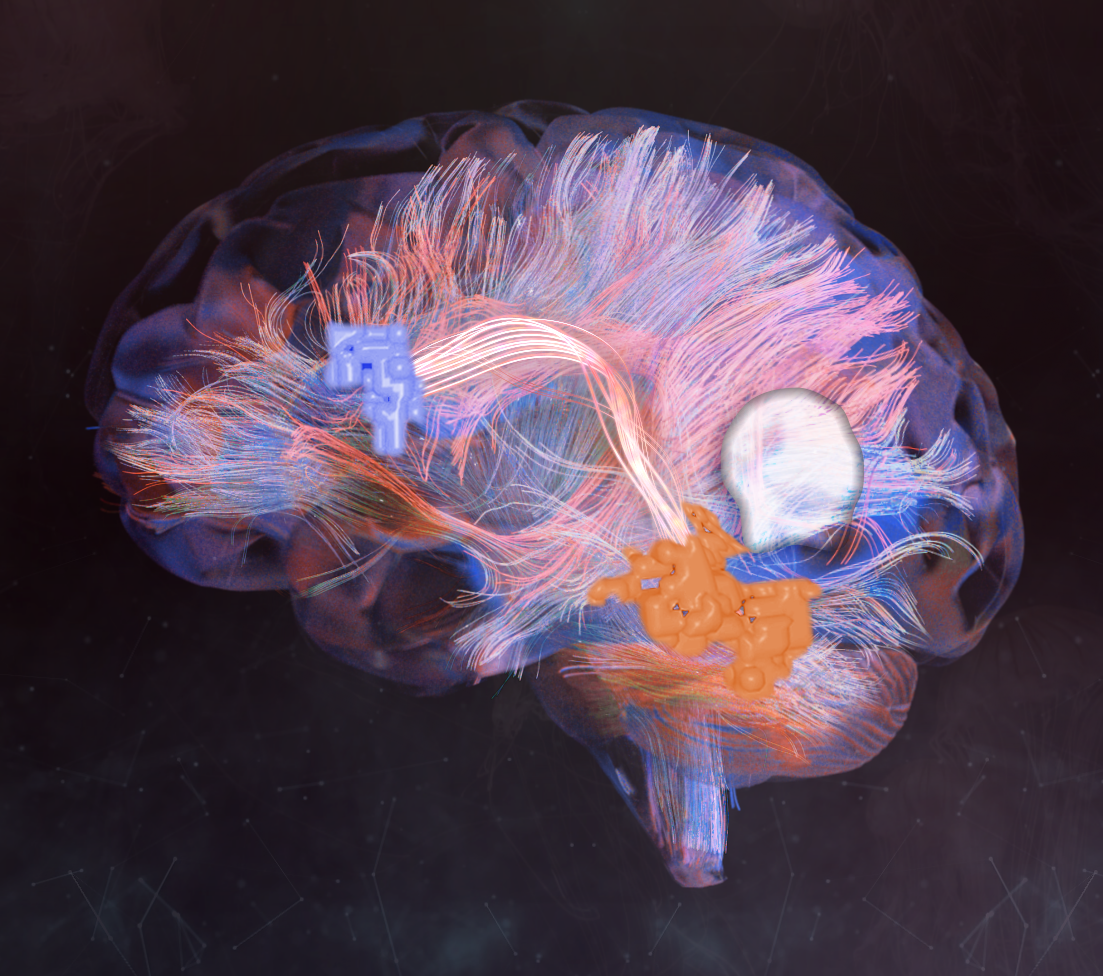
Connectomics
Connectomics is the production and study of connectomes, which are comprehensive maps of connections within an organism's nervous system. Study of neuronal wiring diagrams looks at how they contribute to the health and behavior of an organism. There are two very different types of connectomes; microscale and macroscale. Microscale connectomics maps every neuron and synapse in an organism or chunk of tissue, using electron microscopy and histology. This level of detail is only possible for small animals (flies and worms) or tiny portions (less than 1 mm on a side) of large animal brains. Macroscale connectomics, on the other hand, refers to mapping out large fiber tracts and functional gray matter areas within a much larger brain (typically human), typically using forms of MRI to map out structure and function. Somewhat confusingly, both fields simply refer to their maps as "connectomes". Macroscale connectomics typically concentrates on the human nervous system, a network ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genomics
Genomics is an interdisciplinary field of molecular biology focusing on the structure, function, evolution, mapping, and editing of genomes. A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA, including all of its genes as well as its hierarchical, three-dimensional structural configuration. In contrast to genetics, which refers to the study of ''individual'' genes and their roles in inheritance, genomics aims at the collective characterization and quantification of ''all'' of an organism's genes, their interrelations and influence on the organism. Genes may direct the production of proteins with the assistance of enzymes and messenger molecules. In turn, proteins make up body structures such as organs and tissues as well as control chemical reactions and carry signals between cells. Genomics also involves the sequencing and analysis of genomes through uses of high throughput DNA sequencing and bioinformatics to assemble and analyze the function and structure of entire genomes. Advan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |