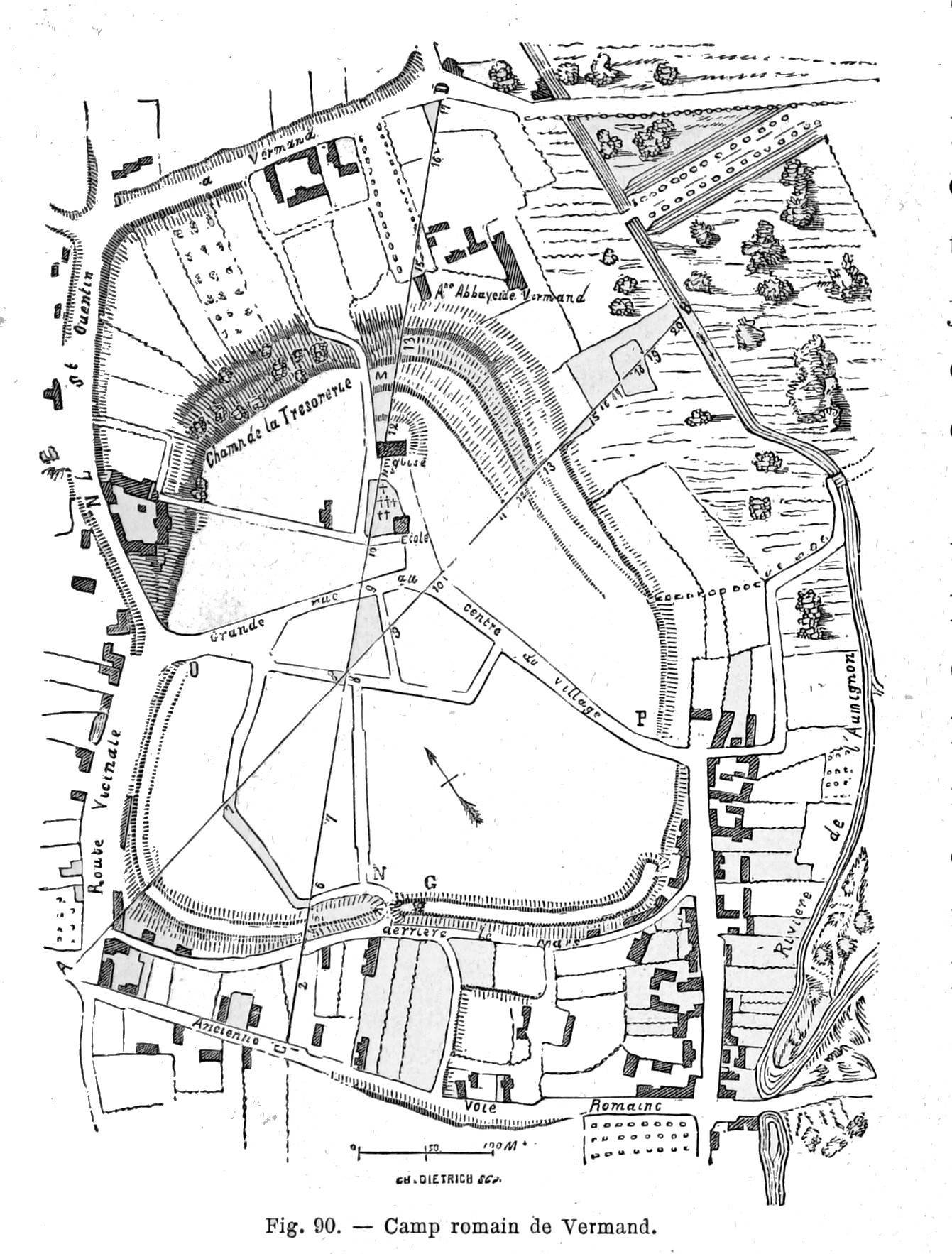
|
Belgae
The Belgae ( , ) were a large confederation of tribes living in northern Gaul, between the English Channel, the west bank of the Rhine, and the northern bank of the river Seine, from at least the third century BC. They were discussed in depth by Julius Caesar in his Commentarii de Bello Gallico, account of his wars in Gaul. Some peoples in southern Roman Britain, Britain were also called Belgae and had apparently moved from the continent. T. F. O'Rahilly believed that some had moved further west and he equated them with the Fir Bolg in Ireland. The Roman province of Gallia Belgica was named after the continental Belgae. The term continued to be used in the region until the present day and is reflected in the name of the modern country of Belgium. Etymology The consensus among linguists is that the ethnic name ''Belgae'' probably comes from the Proto-Celtic root ''*belg-'' or ''*bolg-'' meaning "to swell (particularly with anger/battle fury/etc.)", cognate with the Dutch language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaul
Gaul () was a region of Western Europe first clearly described by the Roman people, Romans, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Switzerland, the Netherlands, Germany, and Northern Italy. It covered an area of . According to Julius Caesar, who took control of the region on behalf of the Roman Republic, Gaul was divided into three parts: Gallia Celtica, Gallia Belgica, Belgica, and Gallia Aquitania, Aquitania. Archaeologically, the Gauls were bearers of the La Tène culture during the 5th to 1st centuries BC. This material culture was found throughout Gaul and as far east as modern-day southern Poland, Slovakia, and Hungary. Warbands led by the Gaul Brennus (leader of the Senones), Brennos Battle of the Allia, sacked Rome in 387 BC, becoming the only time Rome was conquered by a foreign enemy in 800 years. However, Gallia Cisalpina was conquered by the Romans in 204 BC and Gallia Narbonensis in 123 BC. Gaul was invaded after 120 BC by the Cimbri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauls
The Gauls (; , ''Galátai'') were a group of Celts, Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age Europe, Iron Age and the Roman Gaul, Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). They spoke Gaulish, a continental Celtic language. The Gauls emerged around the 5th century BC as bearers of La Tène culture north and west of the Alps. By the 4th century BC, they were spread over much of what is now France, Belgium, Switzerland, Southern Germany, Austria, and the Czech Republic, by virtue of controlling the trade routes along the river systems of the Rhône, Seine, Rhine, and Danube. They reached the peak of their power in the 3rd century BC. During the 4th and 3rd centuries BC, the Gauls expanded into Northern Italy (Cisalpine Gaul), leading to the Roman–Gallic wars, and Gallic invasion of the Balkans, into the Balkans, leading to Battle of Thermopylae (279 BC), war with the Greeks. These latter Gauls eventually settle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrebates
The Atrebates (Gaulish: *''Atrebatis'', 'dwellers, land-owners, possessors of the soil') were a Belgic tribe of the Iron Age and the Roman period, originally dwelling in the Artois region. After the tribes of Gallia Belgica were defeated by Caesar in 57 BC, 4,000 Atrebates participated in the Battle of Alesia in 53, led by their chief Commius. They revolted again in 51 BC, after which they maintained a friendly relationship with Rome, as Commius received sovereignty over the neighbouring Morini. The quality of their woollens is still mentioned in 301 AD by Diocletian's Price Edict. An offshoot of the Belgic tribe probably entered Britain before 54 BC, where it was successively ruled by kings Commius, Tincommius, Eppillus and Verica. After 43 AD, only parts of the area were still controlled by king Claudius Cogidubnus, after which they fell under Roman power. Name They are mentioned as ''Atrebates'' by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC) and Pliny (1st c. AD), ''Atrebátioi'' (Ἀ� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallia Belgica
Gallia Belgica ("Belgic Gaul") was a Roman province, province of the Roman Empire located in the north-eastern part of Roman Gaul, in what is today primarily northern France, Belgium, and Luxembourg, along with parts of the Netherlands and Germany. Before the Roman province came into existence in about 50 BC, the region was conquered by Julius Caesar during his Gallic Wars. His report, the ''Commentarii de Bello Gallico'', described Belgic Gaul as one of the three parts of Gaul (Tres Galliæ), the other two being Gallia Aquitania and Gallia Lugdunensis. Belgica stretched from the Marne River, Marne and Seine rivers, which Caesar described as a cultural boundary between the Belgae and the Celts, Celtic Gauls. In the north and east it stretched all the way to the Rhine. The official Roman province of this name was later created by emperor Augustus in 22 BC, and named after the Belgae, as the largest tribal confederation in the area. However, it also included the territories of the T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eburones
The Eburones ( Greek: ) were a Gaulish- Germanic tribe dwelling in the northeast of Gaul, who lived north of the Ardennes in the region near what is now the southern Netherlands, eastern Belgium and the German Rhineland, in the period immediately preceding the Roman conquest of the region. Though living in Gaul, they were also described as being both Belgae and Germani (for a discussion of these terms, see below). The Eburones played a major role in Julius Caesar's account of his "Gallic Wars", as the most important tribe within the ''Germani cisrhenani'' group of tribes — ''Germani'' living west of the Rhine amongst the Belgae. Caesar claimed that the name of the Eburones was wiped out after their failed revolt against his forces during the Gallic Wars, and that the tribe was largely annihilated. Whether any significant part of the population lived on in the area as Tungri, the tribal name found here later, is uncertain but considered likely. Name Attestations They are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to the south, and the North Sea to the west. Belgium covers an area of and has a population of more than 11.8 million; its population density of ranks List of countries and dependencies by population density, 22nd in the world and Area and population of European countries, sixth in Europe. The capital and Metropolitan areas in Belgium, largest metropolitan region is City of Brussels, Brussels; other major cities are Antwerp, Ghent, Charleroi, Liège, Bruges, Namur, and Leuven. Belgium is a parliamentary system, parliamentary constitutional monarchy with a complex Federation, federal system structured on regional and linguistic grounds. The country is divided into three highly autonomous Communities, regions and language areas o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veromandui
The Viromanduī or Veromanduī (Gaulish: *''Uiromanduoi'') were a Belgic tribe dwelling in the modern Vermandois region (Picardy) during the Iron Age and Roman periods. During the Gallic Wars (58–50 BC), they belonged to the Belgic coalition of 57 BC against Caesar. Name They are mentioned as ''Viromanduos'' and ''Viromanduis'' (var. ''vero''-) by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC), ''Viromanduos'' by Livy (late 1st c. BC), ''Veromandui'' (var. ''uir''-) by Pliny (1st c. AD), ''(Ou̓i)romándues'' () by Ptolemy (2nd c. AD), and as ''Veromandi'' by Orosius (early 5th c. AD). The ethnonym ''Viromanduī'' is a latinized form of Gaulish *''Uiromanduoi'' (sing. ''Uiromanduos''), which literally means 'horse-men' or 'male ponies'. It derives from the stem *''uiro-'' ('man') attached to ''mandos'' ('pony'). It should perhaps be interpreted as the 'Centaurs' or as the ' envirile in owning ponies'. Pierre-Yves Lambert has also proposed the meaning 'those who trample upon men', by comparing the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambiani
The Ambiani (Gaulish: ''Ambiāni'', 'those around') were a Belgic coastal tribe dwelling in the modern Picardy region during the Iron Age and Roman periods. They settled in the region between the 4th century and the second part of the 2nd century BC. In 113–101 BC, they took part in the fights against the Cimbri and Teutoni invaders during the Cimbrian War. In 57 and 52 BC, they participated in Gallic coalitions against Caesar, before their eventual subjugation by Rome in 51 BC. The Ambiani are known for their gold coinage, found in both northern France and Britain, which attest of extensive trading relations across the Channel. Name They are mentioned as ''Ambianos'' and ''Ambianis'' by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC), ''Ambianos'' in the summary of Livy's ''Ab Urbe Condita Libri'' (late 1st c. BC), ''Ambianoì'' (Ἀμβιανοὶ) and ''Ambianoĩs'' (Ἀμβιανοῖς) by Strabo (early 1st c. AD), ''Ambiani'' by Pliny (1st c. AD), ''Ambianoí'' (Ἀμβιανοί) by Ptolemy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bellovaci
The Bellovaci (Gaulish: ''Bellouacoi'') were a Belgic tribe dwelling in the modern Picardy region, near the present-day city of Beauvais, during the Iron Age and the Roman period. After they were defeated by Caesar in 57 BC, they gave lukewarm support to the Gallic revolt led by Vercingetorix in 52 BC. The Bellovaci nonetheless organized resistance against Rome in 51 BC. Name They are mentioned as ''Bellovacos'' and ''Bellovaci'' by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC), ''Belloákoi'' (Βελλοάκοι) by Strabo (early 1st c. AD), ''Bellovaci'' by Pliny (1st c. AD), and as ''Belloúakoi'' (Βελλούακοι) by Ptolemy (2nd c. AD). The ethnonym ''Bellovacī'' is a latinized form of Gaulish ''Bellouacoi'' (sing. ''Bellouacos''). The latter derives from the stem ''bello-'' ('strong, forceful'), but the translation of the suffix -''uaco-'' is uncertain. It could mean 'curved' (cf. Lat. ''uaccilare''), or else be related to the Irish ''fachain'' ('striving') and the Scottish Gaelic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fir Bolg
In medieval Irish myth, the Fir Bolg (also spelt Firbolg and Fir Bholg) are the fourth group of people to settle in Ireland. They are descended from the Muintir Nemid, an earlier group who abandoned Ireland and went to different parts of Europe. Those who went to Greece became the Fir Bolg and eventually return to Ireland, after it had been uninhabited for many years. After ruling it for some time and dividing the island into provinces, they are overthrown by the invading Tuatha Dé Danann. Carey, John''The Irish National Origin-Legend: Synthetic Pseudohistory''. Department of Anglo-Saxon, Norse and Celtic, University of Cambridge, 1994. pp. 1–4 Myth ''Lebor Gabála Érenn'' tells of Ireland being settled six times by six groups of people. The first three—the people of Cessair, the people of Partholón, and the people of Nemed—were wiped out or forced to abandon the island. The Fir Bolg are said to be descendants of the people of Nemed, who inhabited Ireland befo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caesar's civil war, a civil war. He subsequently became Roman dictator, dictator from 49 BC until Assassination of Julius Caesar, his assassination in 44 BC. Caesar played a critical role in Crisis of the Roman Republic, the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. In 60 BC, Caesar, Marcus Licinius Crassus, Crassus, and Pompey formed the First Triumvirate, an informal political alliance that dominated Roman politics for several years. Their attempts to amass political power were opposed by many in the Roman Senate, Senate, among them Cato the Younger with the private support of Cicero. Caesar rose to become one of the most powerful politicians in the Roman Republic through a string of military victories in the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the territory that became the Roman province of ''Britannia'' after the Roman conquest of Britain, consisting of a large part of the island of Great Britain. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. Julius Caesar invaded Britain in 55 and 54 BC as part of his Gallic Wars. According to Caesar, the Britons had been overrun or culturally assimilated by the Belgae during the British Iron Age and had been aiding Caesar's enemies. The Belgae were the only Celtic tribe to cross the sea into Britain, for to all other Celtic tribes this land was unknown. He received tribute, installed the friendly king Mandubracius over the Trinovantes, and returned to Gaul. Planned invasions under Augustus were called off in 34, 27, and 25 BC. In 40 AD, Caligula assembled 200,000 men at the Channel on the continent, only to have them gather seashells () according to Suetonius, perhaps as a symbolic gesture to proclaim Caligula's victory over th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |