|
Bamyan Province
Bamyan, also spelled Bamiyan, Bāmīān or Bāmyān (), is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan with the city of Bamyan as its center, located in central parts of Afghanistan. The terrain in Bamyan is mountainous or semi-mountainous, at the western end of the Hindu Kush mountains concurrent with the Himalayas. The province is divided into eight districts, with the town of Bamyan serving as its capital. The province has a population of about 495,557 and borders Samangan to the north, Baghlan, Parwan, and Maidan Wardak to the east, Ghazni and Daikundi to the south, and Ghor and Sar-e-Pol to the west. It is the largest province in the Central region of Afghanistan. It was a center of commerce and Buddhism in the 4th and 5th centuries. In antiquity, central Afghanistan was strategically placed to thrive from the Silk Road caravans that crisscrossed the region, trading between the Roman Empire, Han dynasty, Central Asia, and South Asia. Bamyan was a stopping-off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of Afghanistan
The provinces of Afghanistan ( ''Wilayah, wilāyat'') are the primary administrative divisions. Afghanistan is divided into 34 provinces. Each province encompasses a number of Districts of Afghanistan, districts or usually over 1,000 villages. Provincial governors played a critical role in the reconstruction of the Afghan state following the creation of the new government under Hamid Karzai. According to international security scholar Dipali Mukhopadhyay, many of the provincial governors of the western-backed government were former warlords who were incorporated into the political system. Provinces of Afghanistan Administrative The following table lists the province, capital, number of districts, UN region, region, ISO 3166-2:AF code and license plate code. Demographic The following table lists the province, population in 2024, area in square kilometers and population density. Regions of Afghanistan The following tables summarize data from the demographic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maidan Wardak Province
Wardak is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan, located in central Afghanistan. Its capital is the closest provincial city to Kabul. Wardak Have 8 District. Wardak or Wardag (Dari/Pashto: ), is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan, located in the central region of Afghanistan. It is divided into eight Districts of Afghanistan, districts and has a population of approximately 500,000. The capital of the province is Maidan Shar, Maidan Shar(Maidan City), while the most populous district in the province is Saydabad District. Wardak is known for one of its famous high peak mountain known as (Shah Foladi). In 2021, the Taliban gained control of the province during the 2021 Taliban offensive. History During the Communist Afghanistan, communist times, the people of Wardak never gave significant support to the communist government, but the people of Maidan Shahr did sympathize with them. Wardak has also threatened uprisings against the Taliban in Saydabad, numerous schooling system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zuhak, Bamyan
Shahr-e Zuhak or City of Zuhak (), also known as The Red City, is a historic city ruins in Bamyan, Afghanistan which was once home to 3,000 people. The fortress is believed to have been founded between 500 and 600 AD by the Hephthalites, around the same time as the Buddhas of Bamyan were carved into rock in the Bamiyan valley. The city lies at the easternmost point of the Bamyan valley, above the confluence of the Kunduz and Kalu Ganga rivers. The valley used to be a part of a route connecting Europe to India and China. Zuhak was fortified during the Islamic period (10th - 13th century), under the rule of the Ghaznavid and Ghorid dynasties. The fortress was later ransacked by Genghis Khan Genghis Khan (born Temüjin; August 1227), also known as Chinggis Khan, was the founder and first khan (title), khan of the Mongol Empire. After spending most of his life uniting the Mongols, Mongol tribes, he launched Mongol invasions and ... and his army during the Siege of Bamy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shahr-e-Gholghola
Shahr-e-Gholghola or Gholghola City () (also City of Screams, City of Woe, City of Sorrows) is an archaeological site located near the town of Bamyan, Afghanistan. The Siege of Bamyan took place here in 1221 during the Mongol pursuit of Jalal al-Din Mangburni, the last ruler of the Khwarazmian Empire.Dictionary of Wars, by George C. Kohn, p.55. Mutukan, eldest son of Chagatai Khan and favourite grandson of Genghis Khan, was killed in battle by an arrow from the besieged walls, which led Genghis to massacre the population of the city and its surrounding region (the origin of the city's moniker "City of Woe").Anwarul Haque Haqqi ''Chingiz Khan: The Life and Legacy of an Empire Builder'', (Primus Books, 2010), 152. See also * |
Band-e-Amir National Park
Band-e Amir National Park (; ) is located in the central Bamyan Province of Afghanistan. It was established on 22 May 2009 as Afghanistan's first national park to promote and protect the natural beauty of a series of intensely blue lakes created by natural dams high in the Hindu Kush. Band-e-Amir is a chain of six lakes in the southern mountainous desert area of the national park. The lakes formed from mineral-rich water that seeped out of faults and cracks in the rocky landscape. Over time, the water deposited layers of the mineral travertine that built up into walls that now contain the water. The Balkh River originates here and flows to Balkh Province in the north. According to CBC who conducted an interview with Mustafa Zahir, who was the head of Afghanistan's environmentalist protection agency at the time, before Band-e Amir was established as Afghanistan's first national park there were plans to utilize the area for a hydrodam project. This potential threat to the natural b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhas Of Bamiyan
The Buddhas of Bamiyan (, ) were two monumental Buddhist statues in the Bamiyan Valley of Afghanistan, built possibly around the 6th-century. Located to the northwest of Kabul, at an elevation of , carbon dating of the structural components of the Buddhas has determined that the smaller "Eastern Buddha" was built around 570 CE, and the larger "Western Buddha" was built around 618 CE, which would date both to the time when the Hephthalites ruled the region.Eastern Buddha: 549–579 CE (1 σ range, 68.2% probability) 544–595 CE (2 σ range, 95.4% probability). Western Buddha: 605–633 CE (1 σ range, 68.2%) 591–644 CE (2 σ range, 95.4% probability). In Blänsdorf et al. (2009). As a UNESCO World Heritage Site of historical Afghan Buddhism, it was a holy site for Buddhists on the Silk Road. However, in March 2001, both statues were destroyed by the Taliban following an order given on February 26, 2001, by Taliban leader Mullah Muhammad Omar, to destroy all the statues i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greco-Buddhism
Greco-Buddhism or Graeco-Buddhism was a cultural syncretism between Hellenistic culture and Buddhism developed between the 4th century BC and the 5th century AD in Gandhara, which was in present-day Pakistan and parts of north-east Afghanistan. While the Greco-Buddhist art shows clear Hellenistic influences, the majority of scholars do not assume a noticeable Greek influence on Gandharan Buddhism beyond the artistic realm. Cultural interactions between ancient Greece and Buddhism date back to Greek forays into the Indian subcontinent from the time of Alexander the Great. A few years after Alexander's death, the Easternmost fringes of the empire of his general Seleucus were lost in a war with the Mauryan Empire, under the reign of Chandragupta Maurya. The Mauryan Emperor Ashoka would convert to Buddhism and spread the religious philosophy throughout his domain, as recorded in the Edicts of Ashoka. This spread to the Greco-Bactrian kingdom, which itself seceded from the Sele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Asia
South Asia is the southern Subregion#Asia, subregion of Asia that is defined in both geographical and Ethnicity, ethnic-Culture, cultural terms. South Asia, with a population of 2.04 billion, contains a quarter (25%) of the world's population. As commonly conceptualised, the modern State (polity), states of South Asia include Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, the Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka, with Afghanistan also often included, which may otherwise be classified as part of Central Asia. South Asia borders East Asia to the northeast, Central Asia to the northwest, West Asia to the west and Southeast Asia to the east. Apart from Southeast Asia, Littoral South Asia, Maritime South Asia is the only subregion of Asia that lies partly within the Southern Hemisphere. The British Indian Ocean Territory and two out of Atolls of Maldives, 26 atolls of the Maldives in South Asia lie entirely within the Southern Hemisphere. Topographically, it is dominated by the Indian subcontinent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Persian suffix "-stan" (meaning ) in both respective native languages and most other languages. The region is bounded by the Caspian Sea to the southwest, European Russia to the northwest, China and Mongolia to the east, Afghanistan and Iran to the south, and Siberia to the north. Together, the five Central Asian countries have a total population of around million. In the pre-Islamic and early Islamic eras ( and earlier) Central Asia was inhabited predominantly by Iranian peoples, populated by Eastern Iranian-speaking Bactrians, Sogdians, Khwarezmian language, Chorasmians, and the semi-nomadic Scythians and Dahae. As the result of Turkic migration, Central Asia also became the homeland for the Kazakhs, Kyrgyzs, Volga Tatars, Tatars, Turkmens, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silk Road
The Silk Road was a network of Asian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over , it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the Eastern world, Eastern and Western worlds. The name "Silk Road" was coined in the late 19th century, but some 20th- and 21st-century historians instead prefer the term Silk Routes, on the grounds that it more accurately describes the intricate web of land and sea routes connecting Central Asia, Central, East Asia, East, South Asia, South, Southeast Asia, Southeast, and West Asia as well as East Africa and Southern Europe. The Silk Road derives its name from the highly lucrative trade of silk textiles that were History of Silk, primarily produced in China. The network began with the expansion of the Han dynasty (202 BCE220 CE) into Central Asia around 114 BCE, through the missions and explorations of the Chinese imperial env ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or 5th century Before the Common Era, BCE. It is the Major religious groups, world's fourth-largest religion, with about 500 million followers, known as Buddhists, who comprise four percent of the global population. It arose in the eastern Gangetic plain as a movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia. Buddhism has subsequently played a major role in Asian culture and spirituality, eventually spreading to Western world, the West in the 20th century. According to tradition, the Buddha instructed his followers in a path of bhavana, development which leads to Enlightenment in Buddhism, awakening and moksha, full liberation from ''Duḥkha, dukkha'' (). He regarded this path as a Middle Way between extremes su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
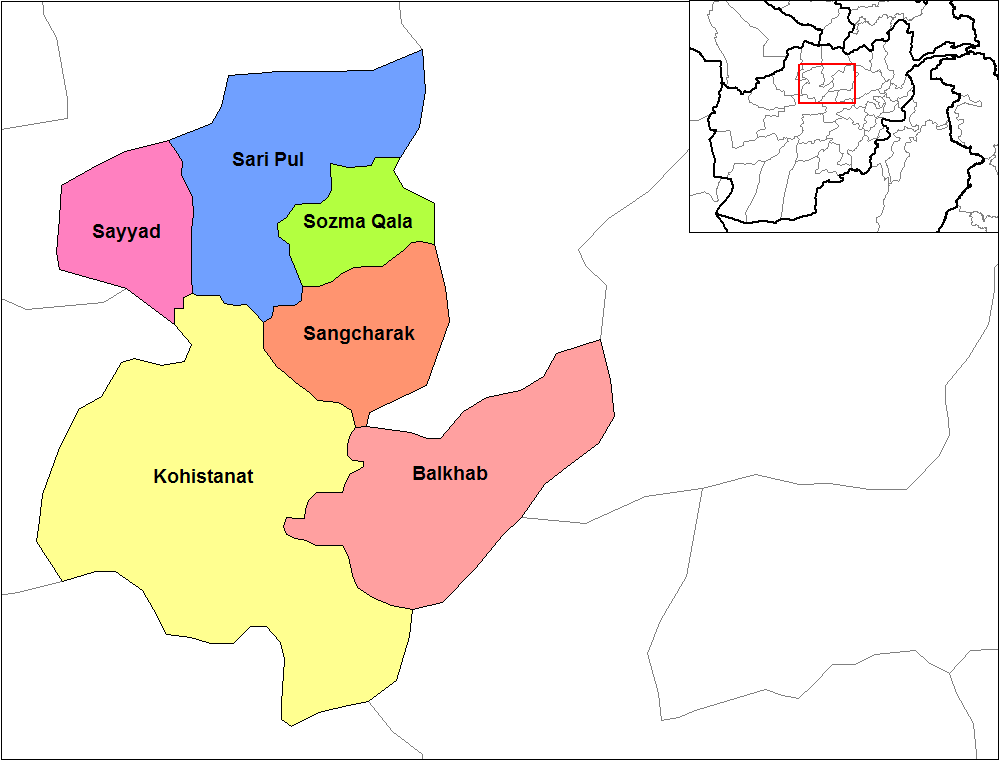
Sar-e-Pol Province
Sar-e-Pol, also spelled Sari Pul (), is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan, located in the north of the country. It borders Ghor and Bamyan to the south, Samangan to the east, Balkh and Jowzjan to the north, and Faryab to the west. The province is divided into 7 districts and contains 896 villages. It has a population of about 632,000, which is multi-ethnic and mostly a tribal society. The province was created in 1988 with the support of northern Afghan politician Sayed Nasim Mihanparast. The city of Sar-e-Pol serves as the provincial capital. In 2021, the Taliban gained control of the province during the 2021 Taliban offensive. History Between the early 16th and the mid-18th century, the territory was ruled by the Khanate of Bukhara. It was given to Ahmad Shah Durrani by Murad Beg of Bukhara after a treaty was signed in about 1750 and became part of the Durrani Empire. It was ruled by the Durranis, followed by the Barakzai dynasty. The area was untouched by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |