|
Bajo De La Carpa Formation
The Bajo de la Carpa Formation is a geologic formation of the Neuquén Basin that outcrop, crops out in northern Patagonia, in the provinces of Río Negro Province, Río Negro and Neuquén Province, Neuquén, Argentina. It is the oldest of two formations belonging to the Río Colorado Subgroup within the Neuquén Group. Formerly, that subgroup was treated as a formation, and the Bajo de la Carpa Formation was known as the Bajo de la Carpa Member.Sánchez ''et al.'', 2006 At its base, this formation unconformity, conformably overlies the Plottier Formation of the older Río Neuquén Subgroup, and it is in turn overlain by the Anacleto Formation, the youngest and uppermost formation of the Neuquén Group.Fossa Mancini ''et al.'', 1938 The Bajo de la Carpa Formation can reach in thickness in some locations, and consists mainly of sandstones of various colors, all of fluvial origin, with thin layers of mudstone and siltstone in between. Geological features such as geodes, chemical no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holotype
A holotype (Latin: ''holotypus'') is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several examples, but explicitly designated as the holotype. Under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), a holotype is one of several kinds of name-bearing types. In the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and ICZN, the definitions of types are similar in intent but not identical in terminology or underlying concept. For example, the holotype for the butterfly '' Plebejus idas longinus'' is a preserved specimen of that subspecies, held by the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard University. In botany and mycology, an isotype is a duplicate of the holotype, generally pieces from the same individual plant or samples from the same genetic individual. A holotype is not necessarily "ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outcrop
An outcrop or rocky outcrop is a visible exposure of bedrock or ancient superficial deposits on the surface of the Earth and other terrestrial planets. Features Outcrops do not cover the majority of the Earth's land surface because in most places the bedrock or superficial deposits are covered by soil and vegetation and cannot be seen or examined closely. However, in places where the overlying cover is removed through erosion or tectonic uplift, the rock may be exposed, or ''crop out''. Such exposure will happen most frequently in areas where erosion is rapid and exceeds the weathering rate such as on steep hillsides, mountain ridges and tops, river banks, and tectonically active areas. In Finland, glacial erosion during the last glacial maximum (ca. 11000 BC), followed by scouring by sea waves, followed by isostatic uplift has produced many smooth coastal and littoral outcrops. Bedrock and superficial deposits may also be exposed at the Earth's surface due to human exca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
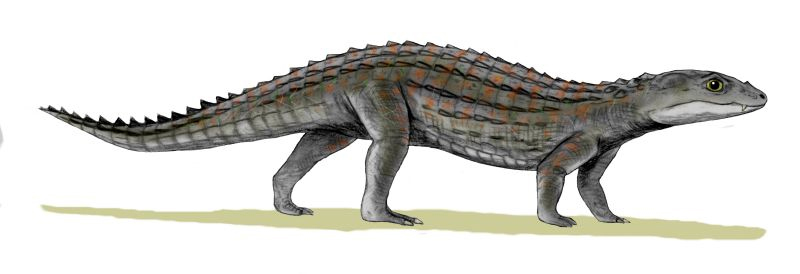
Paleochelco
''Paleochelco'' is an extinct genus of lizard, possibly a polyglyphanodontian, found in the Late Cretaceous Bajo de la Carpa Formation in Argentina Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt .... It contains a single species, ''P. occultato''. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q109535719 Squamata Prehistoric reptile genera Cretaceous Argentina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snake
Snakes are elongated limbless reptiles of the suborder Serpentes (). Cladistically squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales much like other members of the group. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more joints than their lizard ancestors and relatives, enabling them to swallow prey much larger than their heads ( cranial kinesis). To accommodate their narrow bodies, snakes' paired organs (such as kidneys) appear one in front of the other instead of side by side, and most only have one functional lung. Some species retain a pelvic girdle with a pair of vestigial claws on either side of the cloaca. Lizards have independently evolved elongate bodies without limbs or with greatly reduced limbs at least twenty-five times via convergent evolution, leading to many lineages of legless lizards. These resemble snakes, but several common groups of legless lizards have eyelids and external ears, which snakes lack, althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinilysia
''Dinilysia'' (meaning "terrible ilysia") is an extinct genus of snake from the Late Cretaceous (Coniacian) of South America. ''Dinilysia'' was a relatively large ambush predator, measuring approximately long. The skull morphology of ''Dinilysia'' is similar to Boidae, boids, suggesting that it was able to consume large prey. Living in a desert-like environment, ''Dinilysia'' is likely a terrestrial or a semi-fossorial animal. Physiology and lineage The ''Dinilysia patagonica'' is a stem snake that is very closely related to the original ancestor of the clade of crown snakes. Once the fossil of the snake was discovered, an x-ray computed tomography was used to build a digitized endocast of its inner ear. The results displayed that the ''Dinilysia patagonica'''s inner ear anatomy had three main parts. It had a large spherical vestibule, large foramen ovale, and slender semicircular canals in its inner ear. Especially significantly, the spherical vestibule is an inne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelidae
Chelidae is one of three living families of the turtle suborder Pleurodira, and are commonly called Austro-South American side-neck turtles. The family is distributed in Australia, New Guinea, parts of Indonesia, and throughout most of South America. It is a large family of turtles with a significant fossil history dating back to the Cretaceous. The family is entirely Gondwanan in origin, with no members found outside Gondwana, either in the present day or as a fossil.Georges, A. & Thomson, S. (2006). "Evolution and Zoogeography of Australian freshwater turtles". In: Merrick, J. R.; Archer, M.; Hickey, G. & Lee, M. (eds.) ''Evolution and Zoogeography of Australasian Vertebrates''. Sydney: Australia. Description Like all pleurodirous turtles, the chelids withdraw their necks sideways into their shells, differing from cryptodires that fold their necks in the vertical plane. They are all highly aquatic species with webbed feet and the capacity to stay submerged for long periods of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lomalatachelys
''Lomalatachelys neuquina'' is an extinct genus and species of chelid turtle from Argentina. The specimen was found in the Loma de La Lata zone approximately 75 km from Neuquen City in north west Patagonia, Argentina Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt .... References {{Testudines Cretaceous reptiles of South America Chelidae Fossil chelid turtles Late Cretaceous turtles Prehistoric turtle genera Bajo de la Carpa Formation Prehistoric turtles of South America Cretaceous Argentina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocephalia. About 12,000 living species of reptiles are listed in the Reptile Database. The study of the traditional reptile orders, customarily in combination with the study of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. Reptiles have been subject to several conflicting Taxonomy, taxonomic definitions. In Linnaean taxonomy, reptiles are gathered together under the Class (biology), class Reptilia ( ), which corresponds to common usage. Modern Cladistics, cladistic taxonomy regards that group as Paraphyly, paraphyletic, since Genetics, genetic and Paleontology, paleontological evidence has determined that birds (class Aves), as members of Dinosauria, are more closely related to living crocodilians than to other reptiles, and are thus nested among re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geode
A geode (; ) is a geology, geological secondary formation within sedimentary rock, sedimentary and volcanic rocks. Geodes are hollow, vaguely spherical rocks, in which masses of mineral matter (which may include crystals) are secluded. The crystals are formed by the filling of vesicular texture, vesicles in volcanic and subvolcanic rocks by minerals deposited from hydrothermal fluids; or by the solvation, dissolution of syngenetic concretions and partial filling by the same or other minerals precipitation (chemistry), precipitated from water, groundwater, or hydrothermal fluids. Formation Geodes can form in any cavity, but the term is usually reserved for more or less rounded formations in igneous and sedimentary rocks. They can form in gas bubbles in igneous rocks, such as vesicles in basaltic lava; or, as in the American Midwest, in rounded cavities in sedimentary formations. After rock around the cavity hardens, dissolved silicates and/or carbonates are deposited on the ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mudstone
Mudstone, a type of mudrock, is a fine-grained sedimentary rock whose original constituents were clays or muds. Mudstone is distinguished from ''shale'' by its lack of fissility.Blatt, H., and R.J. Tracy, 1996, ''Petrology.'' New York, New York, W. H. Freeman, 2nd ed, 529 pp. The term ''mudstone'' is also used to describe carbonate rocks (limestone or dolomite) that are composed predominantly of carbonate mud. However, in most contexts, the term refers to siliciclastic mudstone, composed mostly of silicate minerals. The NASA Curiosity rover has found deposits of mudstone on Mars that contain organic substances such as propane, benzene and toluene. Definition There is not a single definition of mudstone that has gained general acceptance,Boggs 2006, p.143 though there is wide agreement that mudstones are fine-grained sedimentary rocks, composed mostly of silicate grains with a grain size less than . Individual grains this size are too small to be distinguished without a micros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluvial
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of its course if it runs out of water, or only flow during certain seasons. Rivers are regulated by the water cycle, the processes by which water moves around the Earth. Water first enters rivers through precipitation, whether from rainfall, the runoff of water down a slope, the melting of glaciers or snow, or seepage from aquifers beneath the surface of the Earth. Rivers flow in channeled watercourses and merge in confluences to form drainage basins, or catchments, areas where surface water eventually flows to a common outlet. Rivers have a great effect on the landscape around them. They may regularly overflow their banks and flood the surrounding area, spreading nutrients to the surrounding area. Sediment or alluvium carried by rivers shapes the landscape a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks. Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar, because they are the most resistant minerals to the weathering processes at the Earth's surface. Like uncemented sand, sandstone may be imparted any color by impurities within the minerals, but the most common colors are tan, brown, yellow, red, grey, pink, white, and black. Because sandstone beds can form highly visible cliffs and other topography, topographic features, certain colors of sandstone have become strongly identified with certain regions, such as the red rock deserts of Arches National Park and other areas of the Southwestern United States, American Southwest. Rock formations composed of sandstone usually allow the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |