|
Auckland Volcanic Field
The Auckland volcanic field is an area of monogenetic volcanoes covered by much of the metropolitan area of Auckland, New Zealand's largest city, located in the North Island. The approximately 53 volcanoes in the field have produced a diverse array of maars (explosion craters), tuff rings, scoria cones, and lava flows. With the exception of Rangitoto, no volcano has erupted more than once, but the other eruptions lasted for various periods ranging from a few weeks to several years. Rangitoto erupted several times and recently twice; in an eruption that occurred about 600 years ago, followed by a second eruption approximately 50 years later. The field is fuelled entirely by basaltic magma, unlike the explosive subduction-driven volcanism in the central North Island, such as at Mount Ruapehu and Lake Taupō. Features The field ranges from Lake Pupuke and Rangitoto Island in the north to Matukutururu (Wiri Mountain) in the south, and from Mount Albert in the west to Pig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand Von Hochstetter
Christian Gottlieb Ferdinand Ritter von Hochstetter (30 April 1829 – 18 July 1884) was a Germany, German-Austrians, Austrian geologist. In 1857 he was appointed geologist on the Austrian Novara expedition to New Zealand, collecting natural history specimens and producing the first geological map of New Zealand. Career Von Hochstetter was born in Esslingen am Neckar, Esslingen, then in the kingdom of Württemberg, to Christian Ferdinand and his second wife, Sophie Orth. His father was a parson who also published on botanical and geological subjects. Having received his early education at the evangelical seminary at Maulbronn, Ferdinand proceeded to the University of Tübingen and the Tübinger Stift; there, under Friedrich August von Quenstedt, the interest he already felt in geology became permanently fixed, and he obtained his doctor's degree and a travelling scholarship. He then travelled to Vienna where in 1853, he joined the staff of the Imperial Geological Survey of Aus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
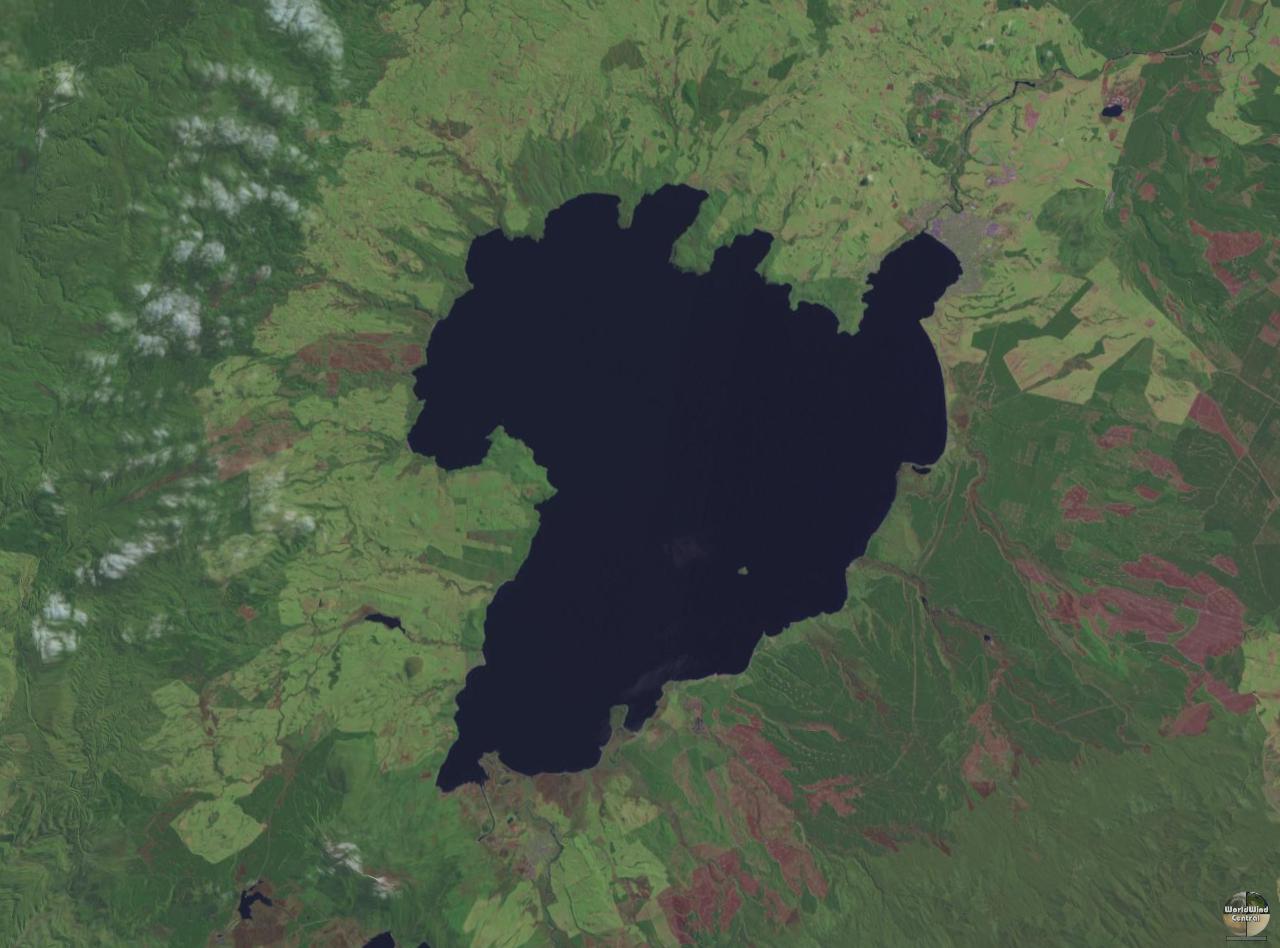
Lake Taupō
Lake Taupō (also spelled Taupo; or ) is a large crater lake in New Zealand's North Island, located in the caldera of Taupō Volcano. The lake is the namesake of the town of Taupō, which sits on a bay in the lake's northeastern shore. With a surface area of , it is the largest lake by surface area in New Zealand, and the second largest freshwater lake by surface area in geopolitical Oceania after Lake Murray in Papua New Guinea. Motutaiko Island lies in the southeastern area of the lake. Geography Lake Taupō has a perimeter of approximately and a maximum depth of . It is drained by the Waikato River (New Zealand's longest river), and its main tributaries are the Waitahanui River, the Tongariro River, and the Tauranga Taupō River. It is a noted trout fishery with stocks of introduced brown and rainbow trout. The level of the lake is controlled by Mercury Energy, the owner of the eight hydroelectric dams on the Waikato River downstream of Lake Taupō, using gates b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
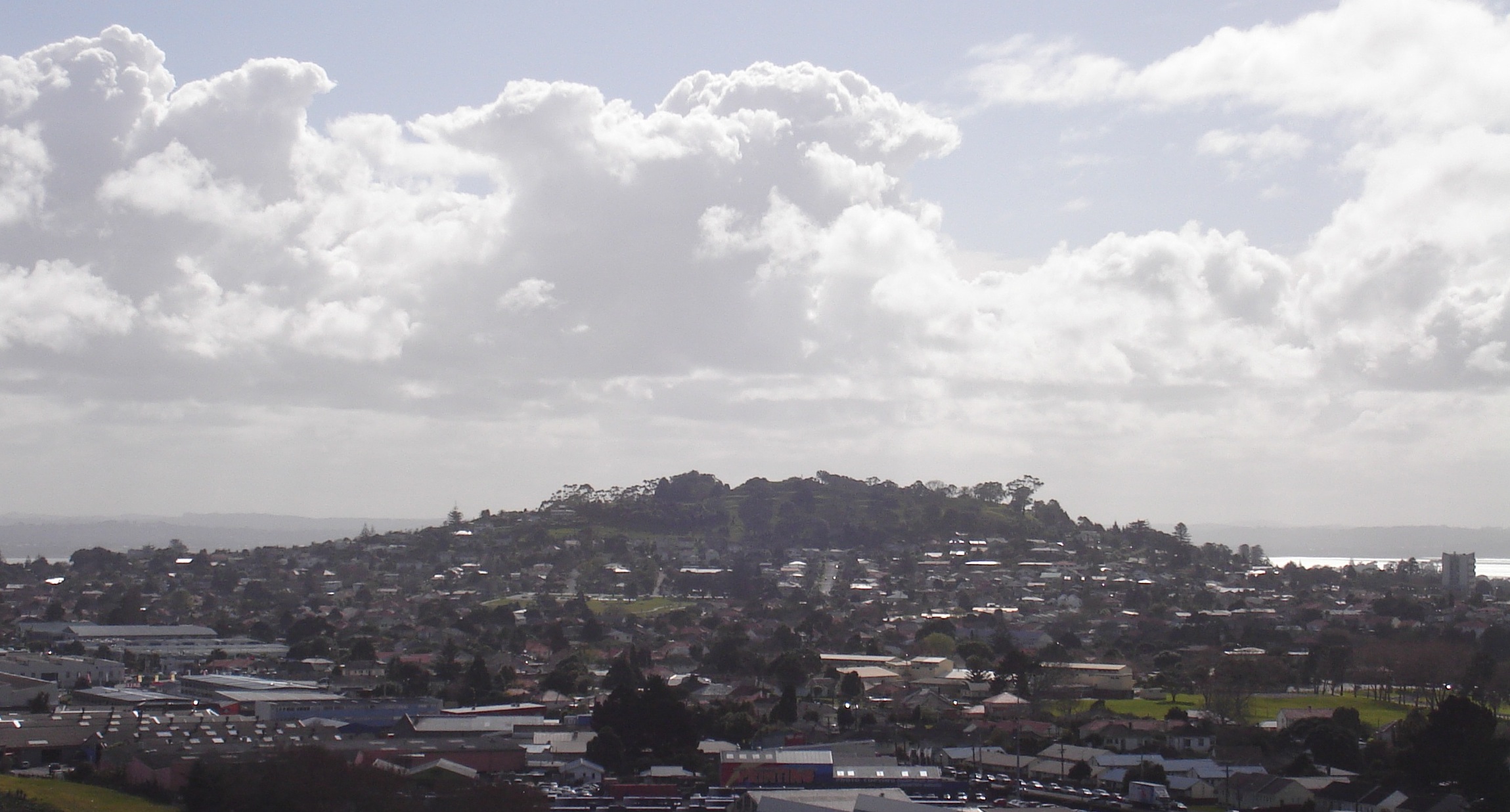
Mount Saint John, New Zealand
Mount Saint John ( or ), is a volcanic scoria cone and Tūpuna Maunga o Tāmaki Makaurau, Tūpuna Maunga (ancestral mountain) in Epsom, New Zealand, Epsom, in the Auckland volcanic field of New Zealand. Geography and geology It has a peak 126 metres above sea level and a crater around 125 m wide and 20 m deep. The age of Mount St John is currently unknown but is older than 28,500 years old as the scoria cone is mantled in ash from Te Tatua-a-Riukiuta volcano. Mount St John is now known to be the source of the long lava flow that ran west down an old stream valley and out into the Waitematā Harbour as Meola Reef. Maungawhau / Mount Eden later erupted through the lava flow. History means 'the prominent mound' and is an abbreviation of . Mount Saint John was named after Colonel J. H. H. St John, who was prominent in the New Zealand Wars. None of its three names are official. In 2014, the Tāmaki Collective agreed that both Te Kōpuke and Tītīkōpuke reflect the historical a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auckland Isthmus
The Auckland isthmus, also known as the Tāmaki isthmus, is a narrow stretch of land on the North Island of New Zealand in the Auckland Region, and the location of the central suburbs of the city of Auckland and the central business district. The isthmus is located between two rias (drowned river valleys): the Waitematā Harbour to the north, which opens to the Hauraki Gulf / Tīkapa Moana and Pacific Ocean, and the Manukau Harbour to the south, which opens to the Tasman Sea. The isthmus is the most southern section of the Northland Peninsula. The Auckland isthmus is bound on the eastern side by the Tāmaki River and by the Whau River on the west; two tidal estuaries of the Waitematā Harbour. These were used as portages by early Māori migration canoes and Tāmaki Māori to cross the isthmus (the Tāmaki River crossing known as Te Tō Waka, and the Whau River as Te Tōangawaka). Through early European settler history, canals were variously considered at either portage, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ōrākei Basin
Ōrākei Basin is a tidal basin and one of the extinct volcanoes in the Auckland volcanic field in the North Island of New Zealand. It has an explosion crater around wide, with a surrounding tuff ring. The present basin is slightly larger than the original maar crater. Sediments in the basin provided the first high-resolution palaeo-environmental reconstruction for northern New Zealand of the last 130,000 years. The basin supports recreational water sports activities for the local population. Geography Ōrākei Basin is between the suburbs of Remuera and Meadowbank, adjacent to the south shore of the Waitematā Harbour, close to the harbour entrance from the Hauraki Gulf. The western side of the basin has a road that connects the inland suburb of Remuera with the coastal suburbs and the northern side has been formed into a railway embankment which the basin drains into the sea through sluice gates at its north-east corner. The Ōrākei (Te Hori) Creek drains some of the Remuer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Takapuna
Takapuna is a suburb located on the North Shore, New Zealand, North Shore of Auckland, New Zealand. The suburb is an isthmus between Shoal Bay, New Zealand, Shoal Bay, arm of the Waitematā Harbour, and the Hauraki Gulf. Lake Pupuke, a volcanic maar and one of the oldest features of the Auckland volcanic field, is a freshwater lake located in the suburb. Takapuna was settled by Tāmaki Māori in the 13th or 14th centuries, who utilised the resources of Lake Pupuke, and a Metrosideros excelsa, pōhutukawa grove called . The grove still exists to this day and was an important location for funeral ceremonies. In 1847, the first European farmers settled at Takapuna, and New Zealand Government, the Crown gifted land at Takapuna to Ngāpuhi chief Eruera Maihi Patuone in order to create a protective barrier for Auckland. Jean-Baptiste Pompallier established St Mary's Seminary, St Mary's College at Takapuna in 1849. The area became a popular tourist destination for wealthy families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanoes
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and because most of Earth's plate boundaries are underwater, most volcanoes are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes resulting from divergent tectonic activity are usually non-explosive whereas those resulting from convergent tectonic activity cause violent eruptions."Mid-ocean ridge tectonics, volcanism and geomorphology." Geology 26, no. 455 (2001): 458. https://macdonald.faculty.geol.ucsb.edu/papers/Macdonald%20Mid-Ocean%20Ridge%20Tectonics.pdf Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shield Volcano
A shield volcano is a type of volcano named for its low profile, resembling a shield lying on the ground. It is formed by the eruption of highly fluid (low viscosity) lava, which travels farther and forms thinner flows than the more viscous lava erupted from a stratovolcano. Repeated eruptions result in the steady accumulation of broad sheets of lava, building up the shield volcano's distinctive form. Shield volcanoes are found wherever fluid, low-silica lava reaches the surface of a rocky planet. However, they are most characteristic of ocean Volcanic island, island volcanism associated with Hotspot (geology), hot spots or with Rift, continental rift volcanism. They include the largest active volcanoes on Earth, such as Mauna Loa. Giant shield volcanoes are found on other planets of the Solar System, including Olympus Mons on Mars and Sapas Mons on Venus. Etymology The term 'shield volcano' is taken from the German term ''Schildvulkan'', coined by the Austrian geologist Eduar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māori People
Māori () are the Indigenous peoples of Oceania, indigenous Polynesians, Polynesian people of mainland New Zealand. Māori originated with settlers from East Polynesia, who arrived in New Zealand in several waves of Māori migration canoes, canoe voyages between roughly 1320 and 1350. Over several centuries in isolation, these settlers developed Māori culture, a distinct culture, whose language, mythology, crafts, and performing arts evolved independently from those of other eastern Polynesian cultures. Some early Māori moved to the Chatham Islands, where their descendants became New Zealand's other indigenous Polynesian ethnic group, the Moriori. Early contact between Māori and Europeans, starting in the 18th century, ranged from beneficial trade to lethal violence; Māori actively adopted many technologies from the newcomers. With the signing of the Treaty of Waitangi, Treaty of Waitangi/Te Tiriti o Waitangi in 1840, the two cultures coexisted for a generation. Rising ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pigeon Mountain (New Zealand)
Pigeon Mountain (, officially Ōhuiarangi / Pigeon Mountain) is a high volcanic cone and Tūpuna Maunga (ancestral mountain) at Half Moon Bay, near Howick and Bucklands Beach, in Auckland, New Zealand. It is part of the Auckland volcanic field. Geography The volcano erupted around 24,000 years ago, forming a large crater and tuff ring about 500 meters wide. The prominent tuff ring is still clearly visible extending in an arc south of Sunderlands Road. Two much smaller craters were formed to the north west of the main cone. The smaller lies buried under Pigeon Mountain Road outside number 18, and the other forms Heights Park, a private reserve for the owners of 29–41 Pigeon Mountain Road and 14–36 Prince Regent Drive and 33–39 Tyrian Close. History Māori history The hill has several known traditional names in Māori. One is , shortened to Pakuranga, which refers to a legendary battle between the supernatural Tūrehu people that begun at the hill. Two other names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Albert, New Zealand
Mount Albert () is an inner suburb of Auckland, New Zealand, which is centred on Ōwairaka / Mount Albert, a local volcanic peak which dominates the landscape. By 1911, growth in the area had increased to the point where Mount Albert was declared an independent borough, which was later absorbed into Auckland. The suburb is located to the southwest of the Auckland City Centre. Geography The suburb is centred around Ōwairaka / Mount Albert, a volcano which erupted an estimated 120,000 years ago. Ōwairaka / Mount Albert is one of the older volcanoes in the Auckland volcanic field, and the westernmost volcanic feature. Approximately 28,000 years ago, Te Kōpuke / Mount Saint John erupted, causing a lava flow in northern Mount Albert, which flowed into the Waitematā Harbour and created the Meola Reef. Oakley Creek is a major stream on the Auckland isthmus, which forms the western border of the suburb. History Early history One of the earliest names Tāmaki Māori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |