|
Archosaurs
Archosauria () or archosaurs () is a clade of diapsid sauropsid tetrapods, with birds and crocodilians being the only extant taxon, extant representatives. Although broadly classified as reptiles, which traditionally exclude birds, the cladistics, cladistic sense of the term includes all living and extinct relatives of birds and crocodilians such as non-avian dinosaurs, pterosaurs, phytosaurs, aetosaurs and rauisuchians as well as many marine reptile#Extinct groups, Mesozoic marine reptiles. Modern paleontologists define Archosauria as a crown group that includes the most recent common ancestor of living birds and crocodilians, and all of its descendants. The base of Archosauria splits into two clades: Pseudosuchia, which includes crocodilians and their extinct relatives; and Avemetatarsalia, which includes birds and their extinct relatives (such as non-avian dinosaurs and pterosaurs). Older definitions of the group Archosauria rely on shared morphology (biology), morphological ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudosuchia
Pseudosuchia, from Ancient Greek ψεύδος (''pseúdos)'', meaning "false", and σούχος (''soúkhos''), meaning "crocodile" is one of two major divisions of Archosauria, including living crocodilians and all archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds. Pseudosuchians are also informally known as "crocodilian-line archosaurs", in contrast to the "bird-line archosaurs" or Avemetatarsalia. Despite Pseudosuchia meaning "false crocodiles", the name is a misnomer as true crocodilians are now defined as a subset of the group. The clade Pseudosuchia is potentially equivalent to another term, Crurotarsi, even though the latter has a different, Node-based taxon, node-based definition: "all taxa the least inclusive clade containing ''Rutiodon carolinensis'' (Emmons, 1856), and ''Crocodylus niloticus'' (Laurenti, 1768)." Many paleontologists of the late 20th century took this proposal for granted, using Crurotarsi as the term for crocodilian ancestors. In 2011, a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytosauria
Phytosaurs (Φυτόσαυροι in greek language, Greek, meaning 'plant lizard') are an extinct group of large, mostly semiaquatic Late Triassic archosauriform or Basal (phylogenetics), basal archosaurian reptiles. Phytosaurs belong to the order (biology), order Phytosauria and are sometimes referred to as parasuchians. Phytosauria, Parasuchia, Parasuchidae, and Phytosauridae have often been considered equivalent groupings containing the same species. Some recent studies have offered a more nuanced approach, defining Parasuchidae and Phytosauridae as nested clades within Phytosauria as a whole. The clade Phytosauria was defined by Paul Sereno in 2005 as ''Rutiodon, Rutiodon carolinensis'' and all taxa more closely related to it than to ''Aetosaurus ferratus'', ''Rauisuchus, Rauisuchus tiradentes'', ''Prestosuchus chiniquensis'', ''Ornithosuchus, Ornithosuchus woodwardi'', or ''Crocodylus niloticus'' (the Nile crocodile). Phytosaurs were long-snouted and heavily armoured, bearin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avemetatarsalia
Avemetatarsalia (meaning "bird metatarsals") is a clade of diapsid Reptile, reptiles containing all archosaurs more closely related to birds than to crocodilians. The two most successful groups of avemetatarsalians were the dinosaurs and pterosaurs. Dinosaur, Dinosaurs were the largest terrestrial animals for much of the Mesozoic era, Mesozoic Era, and one group of small feathered dinosaurs (Aves, i.e. birds) has survived up to the present day. Pterosaur, Pterosaurs were the first flying vertebrates and persisted through the Mesozoic before dying out at the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) extinction event. Both dinosaurs and pterosaurs appeared in the Triassic period, Triassic Period, shortly after avemetatarsalians as a whole. The name Avemetatarsalia was first established by British palaeontologist Michael J. Benton, Michael Benton in 1999. An alternate name is Pan-Aves, or "all birds", in reference to its definition containing all animals, li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
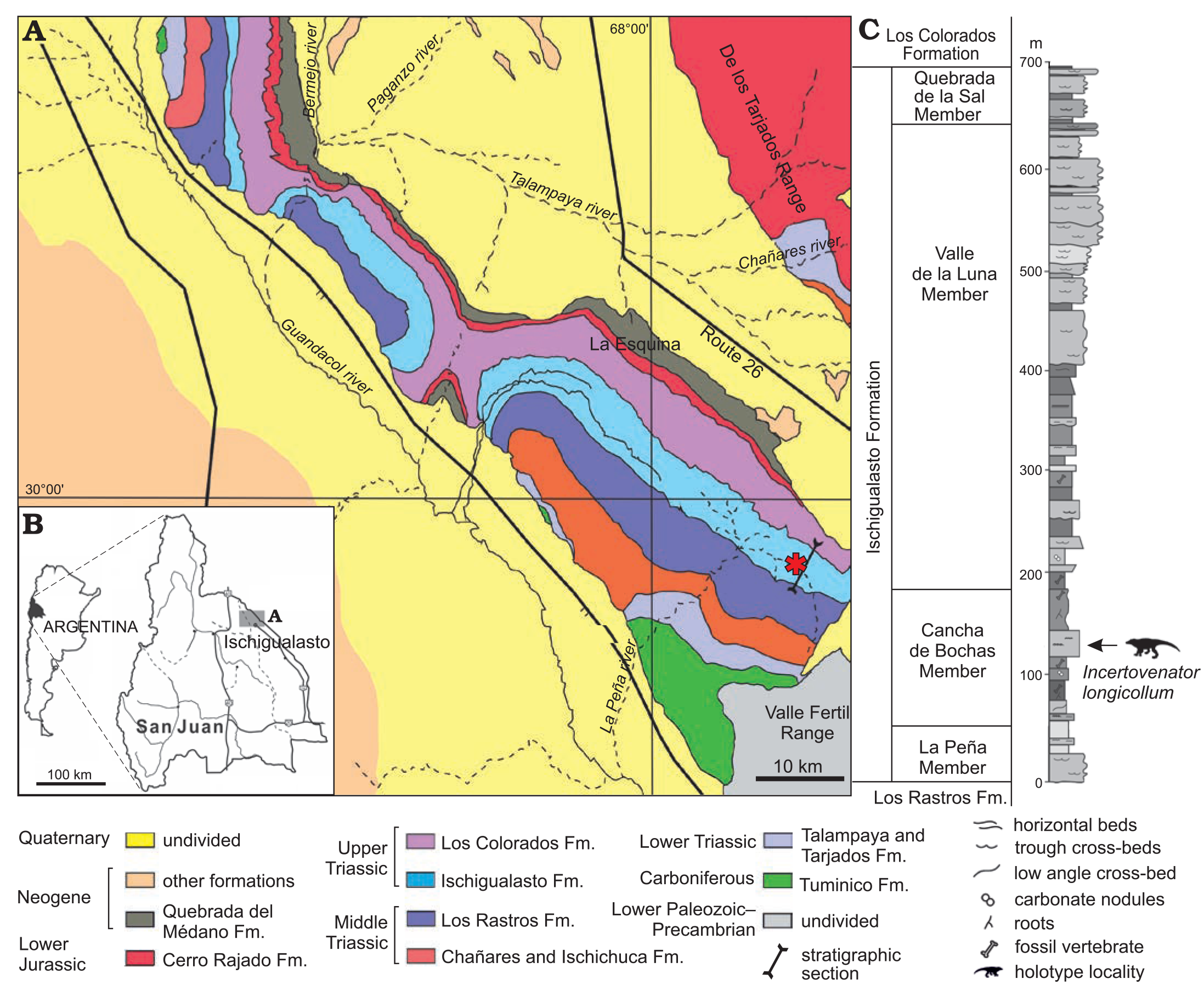
Incertovenator
''Incertovenator'' (meaning "uncertain hunter") is an extinct genus of archosauriform reptile, likely an archosaur, of uncertain affinities. Its unstable position is a result of possessing a number features found in both the bird-line avemetatarsalian archosaurs and the crocodylian-line pseudosuchians. The Type species, type and only known species is ''I. longicollum'', which is known from single specimen discovered in the Late Triassic (Carnian aged) Ischigualasto Formation of Argentina. ''Incertovenator'' is known almost entirely by its vertebral column. This indicates that it had a relatively long neck, leading to its uncertain classification due to the convergent evolution of elongated neck vertebrae in both avemetatarsalian and pseudosuchian archosaurs. Discovery and naming The Type specimen, type and only known specimen of ''Incertovenator'', PVSJ 397, was discovered in the Cancha de Bochas Stratigraphic unit#Member, member of the Ischigualasto Formation. The specimen was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smok (archosaur)
''Smok'' (meaning "dragon" in Polish language, Polish) is an extinct genus of large carnivorous archosaur. It lived during the Late Triassic, latest Triassic period (geology), period (latest Norian to early Rhaetian stage, between 208.5–205 mya (unit), Ma). Its remains have been found in Lisowice, Silesian Voivodeship, Lisowice, southern Poland. The Monotypic taxon, only species is ''Smok wawelski'' (after the Wawel Dragon, a dragon from Polish folklore) and was named in 2012 in paleontology, 2012. It is larger than any other known predatory archosaur from the Late Triassic or Early Jurassic of central Europe. The relation of ''Smok'' to other archosaurs has not yet been thoroughly studied; it may be a rauisuchidae, rauisuchid, prestosuchidae, prestosuchid, an ornithosuchid pseudosuchian (part of the crocodilian lineage of archosaurs) or a theropod dinosaur. Description At an estimated in length, ''Smok'' was the largest carnivorous archosaur in central Europe in the time it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crocodilian
Crocodilia () is an Order (biology), order of semiaquatic, predatory reptiles that are known as crocodilians. They first appeared during the Late Cretaceous and are the closest living relatives of birds. Crocodilians are a type of crocodylomorph pseudosuchian, a subset of archosaurs that appeared about 235 million years ago and were the only survivors of the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event. While other crocodylomorph groups further survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, notably sebecosuchians, only the crocodilians have survived into the Quaternary. The order includes the crocodile, true crocodiles (Family (biology), family Crocodylidae), the alligators and caimans (family Alligatoridae), and the gharial and false gharial (family Gavialidae). Although the term "crocodiles" is sometimes used to refer to all of these families, the term "crocodilians" is less ambiguous. Extant crocodilians have flat heads with long snouts and tails that are compressed on the si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crocodilia
Crocodilia () is an order of semiaquatic, predatory reptiles that are known as crocodilians. They first appeared during the Late Cretaceous and are the closest living relatives of birds. Crocodilians are a type of crocodylomorph pseudosuchian, a subset of archosaurs that appeared about 235 million years ago and were the only survivors of the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event. While other crocodylomorph groups further survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, notably sebecosuchians, only the crocodilians have survived into the Quaternary. The order includes the true crocodiles (family Crocodylidae), the alligators and caimans (family Alligatoridae), and the gharial and false gharial (family Gavialidae). Although the term "crocodiles" is sometimes used to refer to all of these families, the term "crocodilians" is less ambiguous. Extant crocodilians have flat heads with long snouts and tails that are compressed on the sides, with their eyes, ears, and n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birds
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight Bird skeleton, skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the common ostrich. There are over 11,000 living species and they are split into 44 Order (biology), orders. More than half are passerine or "perching" birds. Birds have Bird wing, wings whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the Flightless bird, loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemism, endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapod
A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek :wiktionary:τετρα-#Ancient Greek, τετρα- ''(tetra-)'' 'four' and :wiktionary:πούς#Ancient Greek, πούς ''(poús)'' 'foot') is any four-Limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animal of the clade Tetrapoda (). Tetrapods include all Neontology#Extant taxa versus extinct taxa, extant and Extinction, extinct amphibians and amniotes, with the latter in turn Evolution, evolving into two major clades, the Sauropsida, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (extinct pelycosaur, "pelycosaurs", therapsids and all extant mammals, including Homo sapiens, humans). Hox gene mutations have resulted in some tetrapods becoming Limbless vertebrate, limbless (snakes, legless lizards, and caecilians) or two-limbed (cetaceans, sirenians, Bipedidae, some lizards, kiwi (bird), kiwis, and the extinct moa and elephant birds). Nevertheless, they still qualify as tetrapods through their ancestry, and some retain a pair of ves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sikannisuchus
''Sikannisuchus'' is an extinct genus of large archosaur from upper Triassic (Norian stage) deposits of northeastern British Columbia, Canada. It is known from the holotype, TMP 94.382.3, a posterior portion of skull roof and from other fragmentary remains. It was found from four localities of the Pardonet Formation, near the community of Sikanni Chief. It was first named by Elizabeth L. Nicholls, Donald B. Brinkman, and Xiao-Chun Wu in 1998 and the type species is ''Sikannisuchus huskyi''. It would have reached about in length. Ichthyosaurs such as ''Macgowania ''Macgowania'' is an extinct genus of parvipelvian ichthyosaur known from British Columbia of Canada. It was a small ichthyosaur around in total body length. History of research The first specimen of ''Macgowania'' is the holotype ROM 419 ...'', '' Callawayia'' and possibly the giant shastasaurid '' Shonisaurus'', coelacanths '' Whiteia banffensis'' and possibly '' Garnbergia'', and various genera of mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Triassic
The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between 251.9 Ma and Ma (million years ago). Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic Series, which is a unit in chronostratigraphy. The Early Triassic is the oldest epoch of the Mesozoic Era. It is preceded by the Lopingian Epoch (late Permian, Paleozoic Era) and followed by the Middle Triassic Epoch. The Early Triassic is divided into the Induan and Olenekian ages. The Induan is subdivided into the Griesbachian and Dienerian subages and the Olenekian is subdivided into the Smithian and Spathian subages. The Lower Triassic series is coeval with the Scythian Stage, which is today not included in the official timescales but can be found in older literature. In Europe, most of the Lower Triassic is composed of Buntsandstein, a lithostratigraphic unit of continental red beds. The Early Triassic and partly also the Middle Trias ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |