|
Archaeological Sites In Cambodia
This is a list of notable archaeological sites sorted by country and territories. Afghanistan * Aï Khānum *Bagram *Buddhas of Bamiyan * Hadda *Haji Piyada mosque in Balkh *Mes Aynak * Minarets in Ghazni * Mousallah Complex * Surkh Kotal * Takht-i-rustam * Tillya Tepe Albania Algeria * Aïn Turk, Bouïra *Altava * Beni Hammad Fort * Bir el Ater *Cirta * Diana Veteranorum * Djémila *Fossatum Africae *Gemellae *Ghoufi *Oricum *Hammam Essalihine *Hippo Regius *Jedars *Lambaesis *Mila, Algeria *Miliana *Partenia *Qalʿat ibn Salama *Roknia *Royal Mausoleum of Mauretania *Tassili n'Ajjer *Tébessa *Timgad * Tipaza * Uzinaza Argentina *Cueva de las Manos * Piedra Museo *Pucará de Tilcara * Reserva Provincial Castillos de Pincheira *Ruins of Quilmes *Talampaya National Park * Tastil * Tolombón * Aquihuecó Armenia * Agarak *Amberd * Aramus * Areni-1 * Argištiḫinili *Artaxata * Armavir *Aruchavank * Baghaberd * Berdavan Fortress * Bjni Fortress * Carahunge * Dashtadem For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Site
An archaeological site is a place (or group of physical sites) in which evidence of past activity is preserved (either prehistoric or recorded history, historic or contemporary), and which has been, or may be, investigated using the discipline of archaeology and represents a part of the archaeological record. Sites may range from those with few or no remains visible above ground, to buildings and other structures still in use. Beyond this, the definition and geographical extent of a "site" can vary widely, depending on the period studied and the theoretical approach of the archaeologist. Geographical extent It is almost invariably difficult to delimit a site. It is sometimes taken to indicate a settlement of some sort, although the archaeologist must also define the limits of human activity around the settlement. Any episode of deposition, such as a hoard or burial, can form a site as well. Development-led archaeology undertaken as cultural resources management has the disad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
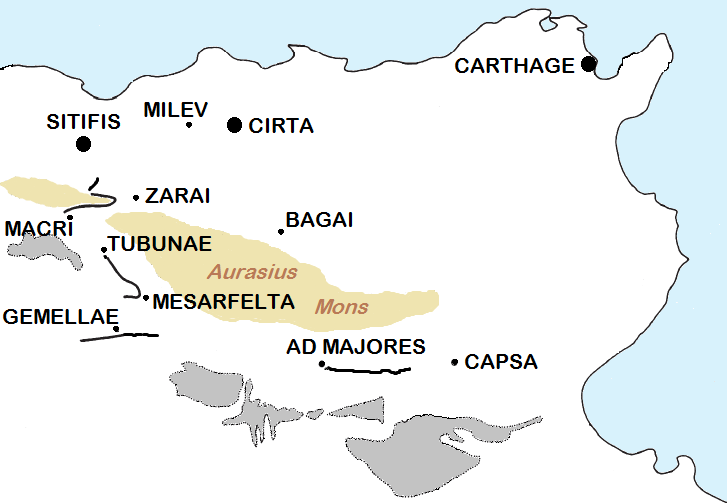
Cirta
Cirta, also known by #Names, various other names in classical antiquity, antiquity, was the ancient Berbers, Berber, Punic people, Punic and Roman Empire, Roman settlement which later became Constantine, Algeria, Constantine, Algeria. Cirta was the capital city of the Berbers, Berber kingdom of Numidia; its strategically important port city was Russicada. Although Numidia was a key ally of the ancient Roman Republic during the Punic Wars (264–146BC), Cirta was subject to Roman invasions during the 2nd and 1st centuriesBC. Eventually it fell under Roman dominion during the time of Julius Caesar. Cirta was then repopulated with Roman colonists by Caesar and Augustus and was surrounded by the autonomous territory of a "Confederation of Four Free Roman cities" (with Collo, Chullu, Russicada, and Milevum), ruled initially by Publius Sittius. The city was destroyed in the beginning of the 4thcentury and was rebuilt by the Roman emperor Constantine the Great, who gave his name to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partenia
Parthenia was a Roman–Berber town in the former Roman province of Mauretania Sitifensis, the easternmost part of ancient Mauretania. It was located in what is now northern Algeria.''Annuario Pontificio 2013'' (Libreria Editrice Vaticana, 2013, ), p. 950 History Parthenia is one of the Maghreb cities of the Roman period whose toponym recalls the cognomen of a prominent family; usually of the patrician class, in this case the family of the Parthenii. The ''Notitia Provinciarum et Civitatum Africae'', part of Victor Vitensis's ''Historia persecutionis Africanae Provinciae, temporibus Geiserici et Hunirici regum Wandalorum'', mentions Parthenia among the bishoprics of Mauretania Sitifensis. It says that the bishop Rogatus was one of those exiled by the Vandal king Huneric when he took action against the Catholic bishops in his dominions. Morcelli remarks that he could find no other mention of Parthenia in the works of the ancient geographers or other writers. A writer on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miliana
Miliana (in Berber: ⵎⵉⵍⵉⴰⵏⴰ, in Darija: مليانة) is an Algerian commune in the Aïn Defla province, serving as the capital of Miliana district approximately southwest of the Algerian capital, Algiers.r/sup>, which covers its entire northern border and reaches . There is also a smaller ridge to the south that reaches , separating Miliana from Khemis Miliana. The area around the town is well forested. To the east and south is the Chélif River Valley, and to the west is a large plateau that stretches to the Ouarsenis range. Climate Miliana has a Mediterranean climate (Köppen climate classification ''Csa''), with hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. Toponymy Miliana correspondsMiliana ville historique to the town of |
Mila, Algeria
Mila (, , ) is a city in the northeast of Algeria and the capital of Mila Province. In antiquity, it was known as Milevum (in Latin; as such still a Latin Catholic titular see) or Miraeon, ''Μιραίον'' (in Ancient Greek) and was situated in the Roman province of Numidia (Roman province), Numidia. History Ancient history In Ptolemy's ''Geography'', IV, iii, 7, the city is mentioned under the name of Mileum or Mireon. During the Roman era it was called Colonia Sarnensis Milevitana, after the River Sarnus in Campania, whence the colonists had emigrated. This name is often found in the inscriptions of the city. Together with Cirta, Collo and Rusicade, Milevum formed the confederation known as the Four Colonies, the territory of which was very extensive. In the 6th century the Byzantine Emperor Justinian had Milevum enclosed by a fortified wall, which still stands and forms a rampart for the Muslim city of Mila. It has yielded quite a number of Latin inscriptions from this city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambaesis
Lambaesis (Lambæsis), Lambaisis or Lambaesa (''Lambèse'' in colonial French), is a Roman archaeological site in Algeria, southeast of Batna and west of Timgad, located next to the modern village of Tazoult. The former bishopric is also a Latin Catholic titular bishopric. History Lambaesa was founded by the Roman military. The camp of the third legion ( Legio III ''Augusta''), to which it owes its origin, appears to have been established between AD 123–129, in the time of Roman emperor Hadrian, whose address to his soldiers was found inscribed on a pillar in a second camp to the west of the great camp still extant. However, other evidence suggests it was formed during the Punic Wars. By AD 166 mention is made of the decurions of a ''vicus'', 10 ''curiae'' of which are known by name; and the ''vicus'' became a ''municipium'' probably at the time when it was made the capital of the newly founded province of Numidia. Lambaesis was populated mainly by Romanized Ber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jedars
Jedars ( French spelling: Djeddars) are thirteen Berber mausoleums located south of Tiaret city in Algeria. The name is derived from the ''jidār'' (wall), which is used locally to refer to ancient monumental ruins. The pre-Islamic tombs date from late antiquity (4th-7th? centuries CE). Description Construction The tombs are situated on the tops of two hills in the mountainous Frenda area, around 30 km south of Tiaret. There are three sepulchres on Jabal Lakhdar (), and ten on Jabal Arawi (, also known as ''Ternaten'') 6 km south of the first group. The graves' size and commanding situation indicate that they were built for royalty. They have been systematically plundered for many centuries, and hence are in a state of ruin. The monuments were erected straight onto the substratum or with very shallow excavation. Some stone was quarried from local limestone and sandstone, some were recycled from nearby settlements and necropoli of earlier times. The materials vary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippo Regius
Hippo Regius (also known as Hippo or Hippone) is the ancient name of the modern city of Annaba, Algeria. It served as an important city for the Phoenicians, Berbers, Romans, and Vandals. Hippo was the capital city of the Vandal Kingdom from AD 435 to 439, after which it was shifted to Carthage following the Vandal capture of Carthage in 439. It was the focus of several early Christian councils and home to Augustine of Hippo, a Church Father highly important in Western Christianity. History Hippo is the latinization of (), probably related to the word ''ûbôn'', meaning "harbor". The town was first settled by Phoenicians from Tyre around the 12th centuryBC. To distinguish it from Hippo Diarrhytus (the modern Bizerte, in Tunisia), the Romans later referred to it as Hippo Regius ("the Royal Hippo") because it was one of the residences of the Numidian kings. Its nearby river was Latinized as the Ubus and the bay to its east was known as Hippo Bay (). A maritime city ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hammam Essalihine
Hammam Essalihine ( ''Ḥammām aṣ-Ṣāliḥīn'', lit. "The Bath of the Righteous"; ) is an ancient Roman bath situated in the Aurès Mountains in the El Hamma District in the Khenchela Province of Algeria. As the Latin name suggests, it dates from the time of the Flavian Dynasty. See also * List of Roman public baths This is a list of ancient Roman public baths (''thermae''). Urban baths Algeria * Timgad * Guelma (Calama) * Héliopolis, Algeria, Héliopolis * Hammam Meskoutine (Aquae Tibilitanae) * Hammam Righa (Aquae Calidae) * Hammam Essalih ... External links Compilation of images, videos, maps of articles on Hammam Essalihine {{Authority control Archaeological sites in Algeria Ancient Roman baths Former populated places in Algeria Buildings and structures in Khenchela Province Buildings and structures completed in the 1st century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghoufi
Ghoufi, also known as the Rhoufi, Balconies of Ghoufi and the Ghoufi Canyon, is a historic settlement and tourist site in the village of T'kout in Batna Province, Algeria. The canyon, located in the Aures Mountains and Abiod River Valley,was carved by the Abiod River and stretches for 3 to 4 kilometers. The site is remarkable for the Balconies of Ghoufi, which overlook an oasis. The Ghoufi balcony ruins include troglodyte homes or domesticated cave dwellings. The homes are carved out of metamorphic and sedimentary rocks, including sandstone. The home are four centuries old and were inhabited until the 1970s. The ruins preserve traditional and indigenous construction methods. Ghoufi is included as part of the Parc des Aurès on UNESCO's Tentative List of World Heritage Sites. Geology and Geography The Abiod River (Ighzir Amellal) has cut a long canyon across the region from Tifelfel to M'Chouneche of North Africa. Along the route of the canyon, for a stretch of approxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemellae
Gemellae was a Roman fort and associated camp on the fringe of the Sahara Desert in what is today part of Algeria. It is now an archaeological site, 25 km south and 19 km west of Biskra, and 5 km southwest of the present-day village of M'Lili with which it probably shares an original Berber languages, Berber name. It was connected by military Roman road to Castellum Dimmidi and Gafsa, Capsa. History Apparently there was a fortification at Gemellae prior to the coming of the Romans. Pliny the Elder recounts that when Lucius Cornelius Balbus the Younger, Lucius Cornelius Balbus celebrated his victory over the Garamantes of the Sahara in 19 BC, one of the conquests feted in the parade through Rome was that of Milgis Gemmella, described as an ''oppidum'' (usually meaning fortified settlement). The Romans seem to have then occupied the site and made it one of the southernmost outposts, marking the ''Limes (Roman Empire), limes'' or boundary of the Roman Empire. The ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |