|
Apus
Apus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere, southern sky. It represents a bird-of-paradise, and its name means "without feet" in Greek language, Greek because the bird-of-paradise was once wrongly believed to lack feet. First depicted on a celestial globe by Petrus Plancius in 1598, it was charted on a star atlas by Johann Bayer in his 1603 ''Uranometria''. The French explorer and astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille charted and gave the brighter stars their Bayer designations in 1756. The five brightest stars are all reddish in hue. Shading the others at apparent magnitude 3.8 is Alpha Apodis, an orange giant that has around 48 times the diameter and 928 times the luminosity of the Sun. Marginally fainter is Gamma Apodis, another aging giant star. Delta Apodis is a double star, the two components of which are 103 Minute and second of arc, arcseconds apart and visible with the naked eye. Two star systems have been found to have exoplanet, planets. Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Apodis
Alpha Apodis, also named Paradys, is the brightest star in the southern circumpolar constellation of Apus (constellation), Apus. It had the Greek alpha designation as part of the constellation which Johann Bayer called Apis Indica in his 1603 ''Uranometria'' star atlas. This identifier is a Bayer designation that is Romanization of Greek, Latinied from α Apodis, and abbreviated Alpha Aps or α Aps, respectively. The star has an apparent visual magnitude of approximately 3.825, which can be viewed with the naked eye. With a declination of –79°, this is a circumpolar star for much of the southern hemisphere. It can be identified on the night sky by drawing an imaginary line through Alpha Centauri and Alpha Circini then extending it toward the south celestial pole. This is a giant star with a stellar classification of K3IIICN0.5, indicating that this star has consumed the hydrogen at its core and has stellar evolution, evolved away from the main seque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta Apodis
Delta Apodis is a double star in the southern constellation of Apus. Its identifier is a Bayer designation that is Romanization of Greek, Latinized from δ Apodis, and abbreviated Del Aps or δ Aps, respectively. Based on stellar parallax, parallax measurements, the distance to δ Apodis is approximately 620 light years, while δ Apodis is found to be around 563 light years from Earth. They may form a common proper motion pair. The brighter star, δ Apodis, has an apparent magnitude that varies from +4.66 to +4.87. It is a red giant with a stellar classification of M5 IIIb, and is classified as a semiregular variable with pulsations of multiple periods of 68.0, 94.9 and 101.7 days. δ Apodis has an apparent magnitude of +5.27 and is an orange stellar classification, K-type giant star, giant with a class of K3 III. Both stars are bright enough to be seen with the naked eye under good observing conditions. The pair have an angular separation of 103.4 arcs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Apodis
Gamma Apodis is a star in the southern circumpolar constellation of Apus. Its identifier is a Bayer designation that is Latinized from γ Apodis, and is abbreviated Gam Aps or γ Aps, respectively. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.86. From parallax measurements, the distance to this star can be estimated as . The star is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of +5.7 km/s. A stellar classification of G9 III identifies Gamma Apodis as a giant star in the later stages of its evolution. This is a red clump giant, which means it is on the horizontal branch and is generating energy through core helium fusion. The star has 2.3 times the mass of the Sun and has expanded to 10.3 times the Sun's radius. It is 2.7 billion years old and is spinning with a projected rotational velocity Stellar rotation is the angular motion of a star about its axis. The rate of rotation can be measured from the spectrum of the star, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
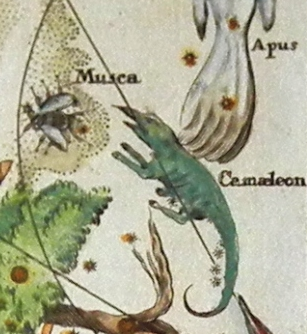
Musca
is a small constellation in the deep southern sky. It was one of 12 constellations created by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman, and it first appeared on a celestial globe in diameter published in 1597 (or 1598) in Amsterdam by Plancius and Jodocus Hondius. The first depiction of this constellation in a celestial atlas was in Johann Bayer's '' Uranometria'' of 1603. It was also known as for 200 years. Musca remains below the horizon for most Northern Hemisphere observers. Many of the constellation's brighter stars are members of the Scorpius–Centaurus association, a loose group of hot blue-white stars that appears to share a common origin and motion across the Milky Way. These include Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Zeta2 and (probably) Eta Muscae, as well as HD 100546, a blue-white Herbig Ae/Be star that is surrounded by a complex debris disk containing a large planet or brown dwarf and possible protoplanet. Two further ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangulum Australe
Triangulum Australe is a small constellation in the far Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name is Latin for "the southern triangle", which distinguishes it from Triangulum in the northern sky and is derived from the Acute triangle, acute, almost equilateral triangle, equilateral pattern of its three brightest stars. It was first depicted on a celestial globe as Triangulus Antarcticus by Petrus Plancius in 1589, and later with more accuracy and its current name by Johann Bayer in his 1603 ''Uranometria''. The French explorer and astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille charted and gave the brighter stars their Bayer designations in 1756. Alpha Trianguli Australis, known as Atria, is a apparent magnitude, second-magnitude orange bright giant, giant and the brightest star in the constellation, as well as the 42nd-brightest star in the night sky. Completing the triangle are the two A-type main sequence star, white main sequence stars Beta Trianguli Australis, Beta and Gamma Trianguli Aus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ara (constellation)
Ara (Latin for "the Altar") is a southern constellation between Scorpius, Telescopium, Triangulum Australe, and Norma. It was (as ) one of the Greek bulk (namely 48) described by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations designated by the International Astronomical Union. The orange supergiant Beta Arae, to us its brightest star measured with near-constant apparent magnitude of 2.85, is marginally brighter than blue-white Alpha Arae. Seven star systems are known to host planets. Sunlike Mu Arae hosts four known planets. Gliese 676 is a (gravity-paired) binary red dwarf system with four known planets. The Milky Way crosses the northwestern part of Ara. Within the constellation is Westerlund 1, a super star cluster that contains the red supergiant Westerlund 1-26, one of the largest stars known. History In ancient Greek mythology, Ara was identified as the altar where the gods first made offerings and formed an alliance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavo (constellation)
Pavo is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere, southern sky whose name is Latin for . Pavo first appeared on a 35-cm (14 in) diameter celestial globe published in 1598 in Amsterdam by Petrus Plancius and Jodocus Hondius and was depicted in Johann Bayer's star atlas ''Uranometria'' of 1603, and was likely conceived by Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman. French explorer and astronomer Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille gave its stars Bayer designations in 1756. The constellations Pavo, Grus (constellation), Grus, Phoenix (constellation), Phoenix and Tucana are collectively known as the "Southern Birds". The constellation's brightest member, Alpha Pavonis, is also known as Peacock and appears as a 1.91-Apparent magnitude, magnitude blue-white star, but is actually a spectroscopic binary. Delta Pavonis is a nearby Sun-like star some 19.9 light-years distant. Six of the star systems in Pavo have been found to host planets, inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circinus
Circinus is a small, faint constellation in the southern sky, first defined in 1756 by the French astronomer Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille. Its name is Latin for compass, referring to the drafting tool used for drawing circles (it should not be confused with Pyxis, a constellation that represents a mariner's compass which points north). Its brightest star is Alpha Circini, with an apparent magnitude of 3.19. Slightly variable, it is the brightest rapidly oscillating Ap star in the night sky. AX Circini is a Cepheid variable visible with the unaided eye, and BX Circini is a faint star thought to have been formed from the merger of two white dwarfs. Two sun-like stars have planetary systems: HD 134060 has two small planets, and HD 129445 has a Jupiter-like planet. Supernova SN 185 appeared in Circinus in 185 AD and was recorded by Chinese observers. Two novae have been observed more recently, in the 20th century. The Milky Way runs through the constellation, featuring prom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamaeleon
Chamaeleon () is a small constellation in the deep southern sky. It is named after the chameleon, a kind of lizard. It was first defined in the 16th century. History Chamaeleon was one of twelve constellations created by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman. It first appeared on a 35-cm diameter celestial globe published in 1597 (or 1598) in Amsterdam by Plancius and Jodocus Hondius. Johann Bayer was the first uranographer to put Chamaeleon in a celestial atlas. It was one of many constellations created by European explorers in the 15th and 16th centuries out of unfamiliar Southern Hemisphere stars. Features Stars There are four bright stars in Chamaeleon that form a compact diamond-shape approximately 10 degrees from the south celestial pole and about 15 degrees south of Acrux, along the axis formed by Acrux and Gamma Crucis. Alpha Chamaeleontis is a white-hued star of magnitude 4.1, 63 light-years from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octans
Octans is a faint constellation located in the deep southern celestial hemisphere, Southern Sky. Its name is Latin for the eighth part of a circle, but it is named after the octant (instrument), octant, a navigational instrument. Devised by kingdom of France, French astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille in 1752, Octans remains one of the IAU designated constellations, 88 modern constellations. The southern celestial pole is located within the boundaries of Octans. History and mythology Octans was one of 14 constellations created by French astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille during his expedition to the Cape of Good Hope, and was originally named ''l’Octans de Reflexion'' (“the reflecting octant”) in 1752, after he had observed and catalogued almost 10,000 southern stars during a two-year stay at the Cape of Good Hope. He devised fourteen new constellations in uncharted regions of the Southern Celestial Hemisphere not visible from Europe. All but one honoured instruments that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayer Family
Constellation families are collections of constellations sharing some defining characteristic, such as proximity on the celestial sphere, common historical origin, or common mythological theme. In the Western tradition, most of the northern constellations stem from Ptolemy's list in the ''Almagest'' (which in turn has roots that go back to Mesopotamian astronomy), and most of the far southern constellations were introduced by sailors and astronomers who traveled to the south in the 16th to 18th centuries. Separate traditions arose in India and China. Menzel's families Donald H. Menzel, director of the Harvard Observatory, gathered several traditional groups in his popular account, ''A Field Guide to the Stars and Planets'' (1975), and adjusted and regularized them so that his handful of groups covered all 88 of the modern constellations. Of these families, one (Zodiac) straddles the ecliptic which divides the sky into north and south; one (Hercules) has nearly equal porti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object. The first constellations were likely defined in prehistory. People used them to relate stories of their beliefs, experiences, creation myth, creation, and mythology. Different cultures and countries invented their own constellations, some of which lasted into the early 20th century before today's constellations were internationally recognized. The recognition of constellations has changed significantly over time. Many changed in size or shape. Some became popular, only to drop into obscurity. Some were limited to a single culture or nation. Naming constellations also helped astronomers and navigators identify stars more easily. Twelve (or thirteen) ancient constellations belong to the zodiac (straddling the ecliptic, which the Sun, Moon, and planets all traver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |