|
Antifungals
An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as cryptococcal meningitis, and others. Such drugs are usually obtained by a doctor's prescription, but a few are available over the counter (OTC). The evolution of antifungal resistance is a growing threat to health globally. Routes of administration Ocular Indicated when the fungal infection is located in the eye. There is currently only one ocular antifungal available: natamycin. However, various other antifungal agents could be compounded in this formulation. Intrathecal Used occasionally when there's an infection of the central nervous system and other systemic options cannot reach the concentration required in that region for therapeutic benefit. Example(s): amphotericin B. Vaginal This may be used to treat some fungal in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphotericin B
Amphotericin B is an antifungal medication used for serious fungal infections and leishmaniasis. The fungal infections it is used to treat include mucormycosis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, and cryptococcosis. For certain infections it is given with flucytosine. It is typically given intravenously. Common side effects include a reaction with fever, chills, and headaches soon after the medication is given, as well as kidney problems. Allergic symptoms including anaphylaxis may occur. Other serious side effects include low blood potassium and myocarditis (inflammation of the heart). It appears to be relatively safe in pregnancy. There is a lipid formulation that has a lower risk of side effects. It is in the polyene class of medications and works in part by interfering with the cell membrane of the fungus. Amphotericin B was isolated from '' Streptomyces nodosus'' in 1955 at the Squibb Institute for Medical Research from cultures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terbinafine
Terbinafine, sold under the brand name Lamisil among others, is an antifungal medication used to treat pityriasis versicolor, onychomycosis, fungal nail infections, and ringworm including jock itch and athlete's foot. It is either oral administration, taken by mouth or applied to the skin as a cream or ointment. Common side effects when taken by mouth include nausea, diarrhea, headache, cough, rash, and elevated liver enzymes. Severe side effects include liver problems and allergic reactions. Liver injury is, however, unusual. Oral use during pregnancy is not typically recommended. The cream and ointment may result in itchiness but are generally well tolerated. Terbinafine is in the allylamines family of medications. It works by decreasing the ability of fungi to synthesize ergosterol. It appears to result in fungicide, fungal cell death. Terbinafine was discovered in 1991. It is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, World Health Organization's List of Essential Medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyene Antimycotic
Polyene antimycotics, sometimes referred to as polyene antibiotics, are a class of antimicrobial polyene compounds that target fungi. These polyene antimycotics are typically obtained from certain species of ''Streptomyces'' bacteria. Previously, polyenes were thought to bind to ergosterol in the fungal cell membrane, weakening it and causing leakage of K+ and Na+ ions, which could contribute to fungal cell death. However, more detailed studies of polyene molecular properties have challenged this model suggesting that polyenes instead bind and extract ergosterol directly from the cellular membrane thus disrupting the many cellular functions ergosterols perform. Amphotericin B, nystatin, and natamycin are examples of polyene antimycotics. They are a subgroup of macrolides. Structures Their chemical structures feature a large ring of atoms (in essence, a cyclic ester ring) containing multiple conjugated carbon-carbon double bonds (hence ''polyene'') on one side of the ring and mul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natamycin
Natamycin, also known as pimaricin, is an antifungal medication used to treat fungal infections around the eye. This includes infections of the eyelids, conjunctiva, and cornea. It is used as eyedrops. Natamycin is also used in the food industry as a preservative. Allergic reactions may occur. It is unclear if medical use during pregnancy or breastfeeding is safe. It is in the macrolide and polyene families of medications. It results in fungal death by altering the cell membrane. Natamycin was discovered in 1955 and approved for medical use in the United States in 1978. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is produced by fermentation of certain types of the bacterium ''Streptomyces''. Uses Medical Natamycin is used to treat fungal infections, including '' Candida'', ''Aspergillus'', '' Cephalosporium'', ''Fusarium'', and ''Penicillium''. It is applied topically as a cream, in eye drops, or (for oral infections) in a lozenge. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketoconazole
Ketoconazole, sold under the brand name Nizoral, among others, is an antiandrogen, antifungal drug, antifungal, and antiglucocorticoid medication used to treat a number of fungal infections. Applied to the skin it is used for fungal skin infections such as tinea, cutaneous candidiasis, pityriasis versicolor, dandruff, and seborrhoeic dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis. Taken oral administration, by mouth it is a less preferred option and recommended for only severe infections when other agents cannot be used. Other uses include treatment of hirsutism, excessive male-patterned hair growth in women and Cushing's syndrome. Common side effects when transdermal administration, applied to the skin include redness. Common side effects when taken by mouth include nausea, headache, and liver problems. Liver problems may result in death or the need for a liver transplantation. Other severe side effects when taken orally include QT prolongation, adrenocortical insufficiency, and anaphyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
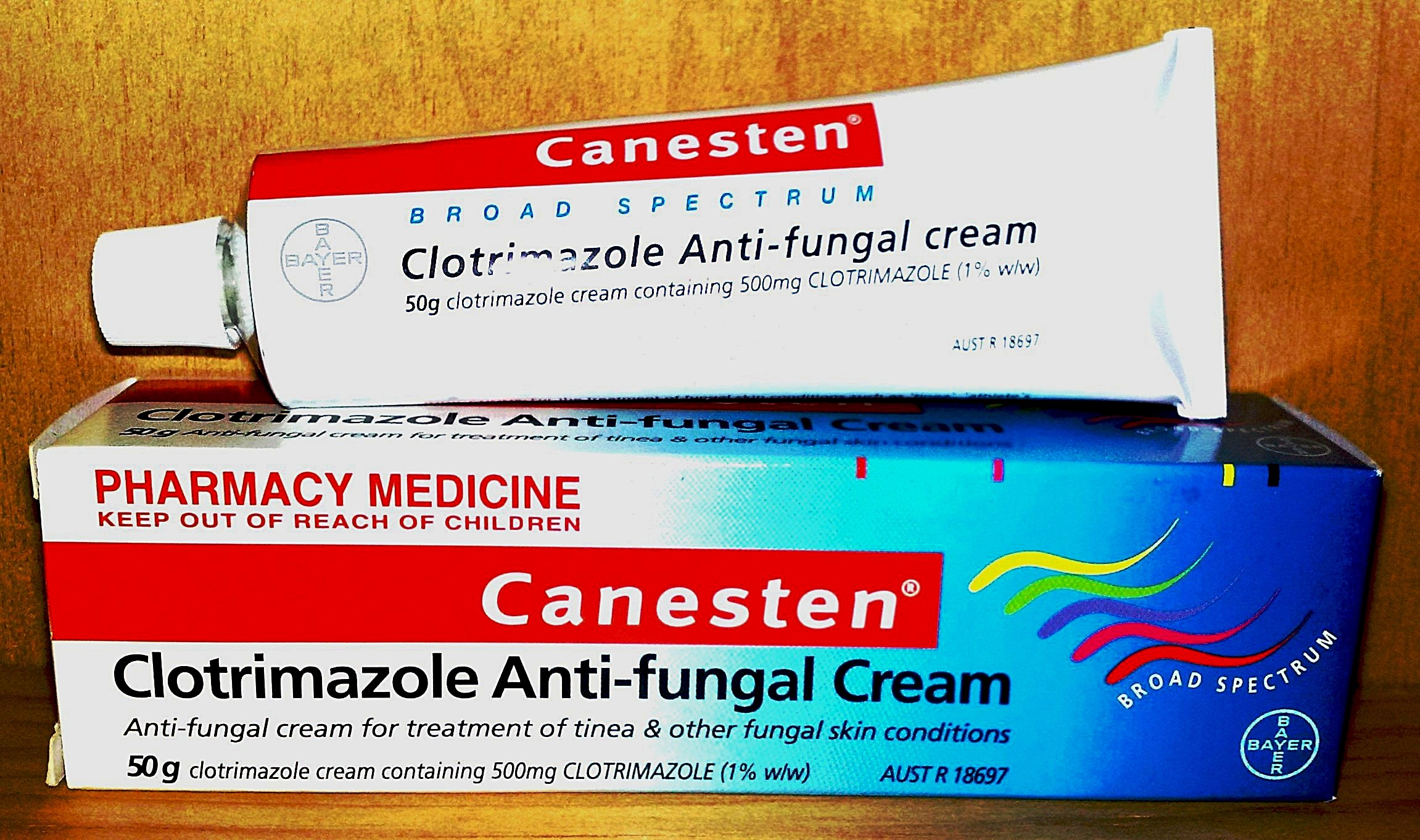
Clotrimazole
Clotrimazole, sold under the brand name Lotrimin, among others, is an antifungal medication. It is used to treat vaginal yeast infections, oral thrush, diaper rash, tinea versicolor, and types of ringworm including athlete's foot and jock itch. It can be taken by mouth or applied as a cream to the skin or in the vagina. Common side effects when taken by mouth include nausea and itchiness. When applied to the skin, common side effects include redness and a burning sensation. In pregnancy, use on the skin or in the vagina is believed to be safe. There is no evidence of harm when used by mouth during pregnancy but this has been less well studied. When used by mouth, greater care should be taken in those with liver problems. It is in the azole class of medications and works by disrupting the fungal cell membrane. Clotrimazole was discovered in 1969. It is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athlete's Foot
Athlete's foot, known medically as ''tinea pedis'', is a common skin infection of the feet caused by a fungus. Signs and symptoms often include itching, scaling, cracking and redness. In rare cases the skin may blister. Athlete's foot fungus may infect any part of the foot, but most often grows between the toes. The next most common area is the bottom of the foot. The same fungus may also affect the nails or the hands. It is a member of the group of diseases known as '' tinea''. Athlete's foot is caused by a number of different funguses, including species of '' Trichophyton'', '' Epidermophyton'', and '' Microsporum''. The condition is typically acquired by coming into contact with infected skin, or fungus in the environment. Common places where the funguses can survive are around swimming pools and in locker rooms. They may also be spread from other animals. Usually diagnosis is made based on signs and symptoms; however, it can be confirmed either by culture or seeing hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sterol
A sterol is any organic compound with a Skeletal formula, skeleton closely related to Cholestanol, cholestan-3-ol. The simplest sterol is gonan-3-ol, which has a formula of , and is derived from that of gonane by replacement of a hydrogen atom on C3 position by a hydroxyl group. It is therefore an alcohol (chemistry), alcohol of gonane. More generally, any compounds that contain the gonane structure, additional functional groups, and/or modified ring systems derived from gonane are called steroids. Therefore, sterols are a subgroup of the steroids. They occur naturally in most Eukaryote, eukaryotes, including plants, animals, and fungi, and can also be produced by some bacteria (however likely with different functions). The most familiar type of animal sterol is cholesterol, which is vital to the structure of the cell membrane, and functions as a precursor to fat-soluble vitamins and steroid hormones. While technically alcohols, sterols are classified by biochemists as lipids (f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjugated System
In physical organic chemistry, a conjugated system is a system of connected p-orbitals with delocalized electrons in a molecule, which in general lowers the overall energy of the molecule and increases Chemical stability, stability. It is Resonance (chemistry), conventionally represented as having alternating single and multiple covalent bond, bonds. Lone pairs, radical (chemistry), radicals or carbenium ions may be part of the system, which may be Cyclic molecule, cyclic, acyclic, Linear molecular geometry, linear or mixed. The term "conjugated" was coined in 1899 by the German chemist Johannes Thiele (chemist), Johannes Thiele. Conjugation is the orbital overlap, overlap of one p-orbital with another across an adjacent Sigma bond, σ bond (in transition metals, d-orbitals can be involved). A conjugated system has a region of overlapping p-orbitals, bridging the interjacent locations that simple diagrams illustrate as not having a π bond. They allow a delocalization of pi el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyene
In organic chemistry, polyenes are polyunsaturated organic compounds that contain multiple carbon–carbon double bonds (). Some sources consider dienes to be polyenes, whereas others require polyenes to contain at least three carbon–carbon double bonds. Conjugated polyenes contain a conjugated system of alternating single and double carbon–carbon bonds, with characteristic optical properties. The following polyenes are used as antimycotics for humans: amphotericin B, nystatin, candicidin, pimaricin, methyl partricin, and trichomycin. Optical properties Some polyenes are brightly colored, an otherwise rare property for a hydrocarbon. Normally alkenes absorb in the ultraviolet region of a spectrum, but the absorption energy state of polyenes with numerous conjugated double bonds can be lowered such that they enter the visible region of the spectrum, resulting in compounds which are coloured (because they contain a chromophore). Thus many natural dyes contain linear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coccidioidomycosis
Coccidioidomycosis (, ) is a mammalian mycosis, fungal disease caused by ''Coccidioides immitis'' or ''Coccidioides posadasii''. It is commonly known as cocci, Valley fever, California fever, desert rheumatism, or San Joaquin Valley fever. Coccidioidomycosis is endemic (epidemiology), endemic in certain parts of the United States in Arizona, California, Nevada, New Mexico, Texas, Utah, and northern Mexico. Description ''C. immitis'' is a Polymorphism (biology), dimorphic saprophytic fungus that grows as a mycelium in the soil and produces a spherule form in the Host (biology), host organism. It resides in the soil in certain parts of the southwestern United States, most notably in California and Arizona. It is also commonly found in northern Mexico, and parts of Central America, Central and South America. ''C. immitis'' is dormant during long dry spells, then develops as a mold with long filaments that break off into airborne spores when it rains. The spores, known as arthroc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |