|
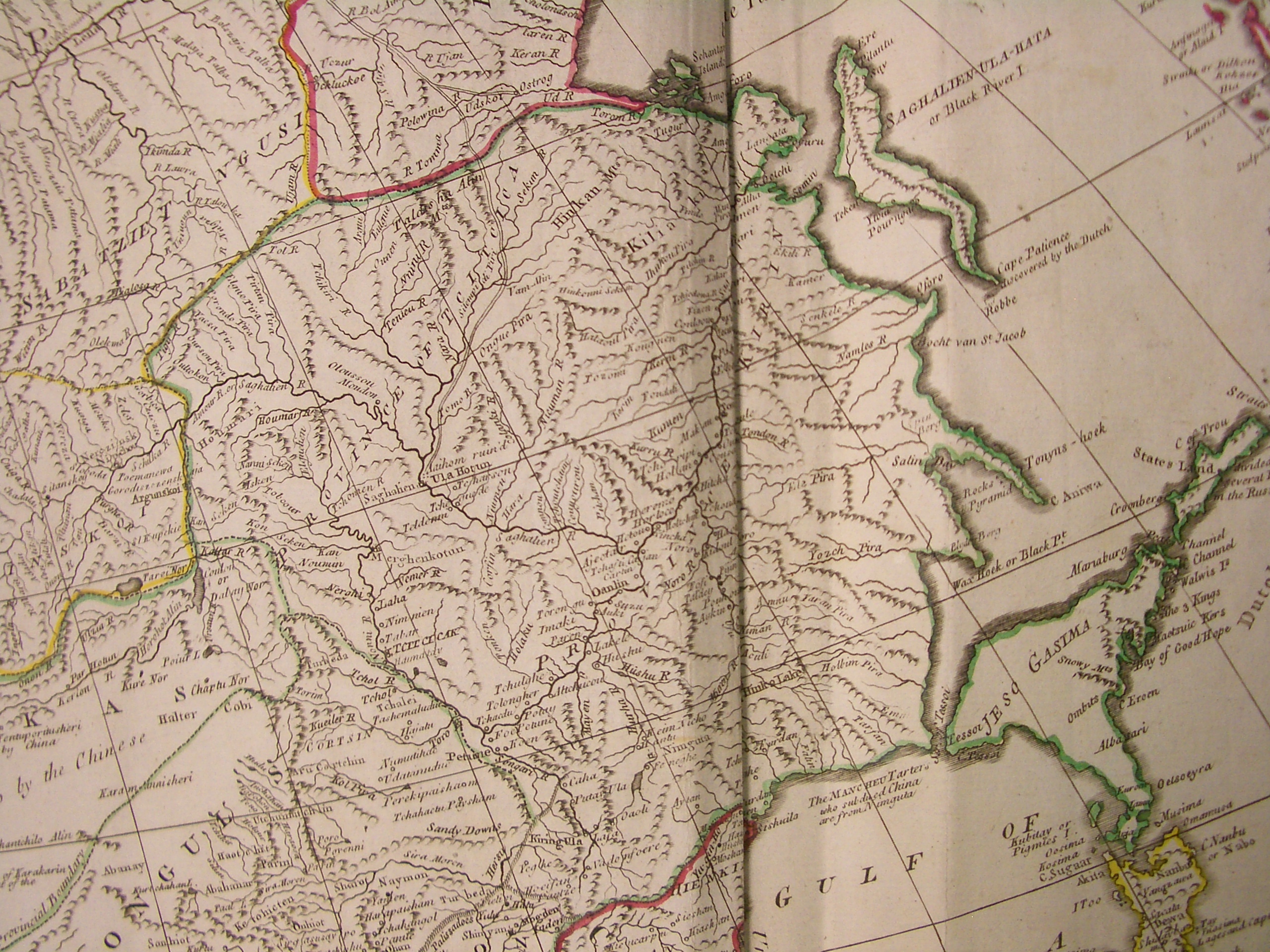
Amur Oblast (Russian Empire)
The Amur Oblast with the center in Blagoveshchensk was formed on December 20, 1858 by the Personal Decree No. 33862. By this Decree, on the proposal of the Governor–General of Eastern Siberia and the Siberian Committee, the Amur Region was made up of lands "located on the left bank of the Amur River, starting from the junction of the Shilka and Argun Rivers or the borders of the Trans–Baikal and Yakutsk Oblasts, along the entire course of the Amur, to the mouth of the river Ussuri and to the new border of the Primorsky Oblast". General characteristics The vast, little–explored area of Eastern Siberia along the left bank of the middle reaches of the Amur, mainly included the river areas of 2 large tributaries of the Amur – Zeya and Bureya. Formerly it belonged to China and was ceded to Russia in 1858 under the Aigun Treaty. *Area – 449,500 square kilometers; *Population – 62,640 people; *Main City – Blagoveshchensk (at the mouth of the Zeya). The Amur Oblast was e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oblast
An oblast ( or ) is a type of administrative division in Bulgaria and several post-Soviet states, including Belarus, Russia and Ukraine. Historically, it was used in the Russian Empire and the Soviet Union. The term ''oblast'' is often translated into English language, English as 'region' or 'province'. In some countries, oblasts are also known by cognates of the Russian term. Etymology The term ''oblast'' is Loanword, borrowed from Russian language, Russian область (), where it is inherited from Old East Slavic, in turn borrowed from Church Slavonic область ''oblastĭ'' 'power, empire', formed from the prefix (cognate with Classical Latin ''ob'' 'towards, against' and Ancient Greek ἐπί/ἔπι ''epi'' 'in power, in charge') and the stem ''vlastǐ'' 'power, rule'. In Old East Slavic, it was used alongside ''obolostǐ''—the equivalent of 'against' and 'territory, state, power' (cognate with English 'wield'; see volost). History Russian Empire In the Russia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Russian Encyclopedia
The ''Great Russian Encyclopedia'' (''GRE''; , БРЭ, transliterated as ''Bolshaya rossiyskaya entsiklopediya'' or academically as ''Bol'šaja rossijskaja ènciklopedija'') is a universal Russian encyclopedia, completed in 36 volumes, published between 2004 and 2017 by Great Russian Encyclopedia, JSC (, transliterated as ''Bolshaya rossiyskaya entsiklopediya PAO''). A successor to the ''Great Soviet Encyclopedia'', it was released under the auspices of the Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS) after President Vladimir Putin signed a presidential decree №1156 in 2002. The complete edition was released by 2017. The chief editor of the encyclopedia was Yury Osipov, the president of the RAS. The editorial board had more than 80 RAS members. The first, introductory volume, released in 2004, was dedicated to Russia. Thirty-five volumes were released between 2005 and 2017, covering the range from "A" to " Яя" (''Yaya''). The RAS plans to publish an updated version every five years, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brockhaus And Efron Encyclopedic Dictionary
The ''Brockhaus and Efron Encyclopaedic Dictionary'' (35 volumes, small; 86 volumes, large) is a comprehensive multi-volume encyclopaedia in Russian. It contains 121,240 articles, 7,800 images, and 235 maps. It was published in the Russian Empire in 1890–1907, as a joint venture of Leipzig and St Petersburg publishers. The articles were written by the prominent Russian scholars of the period, such as Dmitri Mendeleev and Vladimir Solovyov. Reprints have appeared following the dissolution of the Soviet Union. History In 1889, the owner of a printing house in St. Petersburg, , at the initiative of Semyon Afanasyevich Vengerov, entered into an agreement with the German publishing house F. A. Brockhaus for the translation into Russian of the large German encyclopaedic dictionary ''Meyers Konversations-Lexikon''. Initially, it was supposed to be limited to the translation of this publication, but only with a more detailed presentation of issues related to Russia. It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Internal Affairs Of The Russian Empire
The Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Empire () was the state executive authority of the Council of Ministers of the Russian Empire, which carried out administrative functions in the areas of state security, public security, law enforcement, leadership of local authorities, the fight against crime, protection of places of deprivation of liberty, the licensing system, and censorship in media and book publishing. The Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Empire concentrated in its hands a wide variety of tasks, both of the security police and the welfare police. History On, , the manifesto published by Alexander I named “On the establishment of ministries” was approved. Along with others ministries, the Russian Ministry of Internal Affairs was also created. The first Minister of Internal Affairs was Count Viktor Kochubey. The Deputy Minister became Count Pavel Stroganov. According to Count Speransky, the ministry should have been in charge of the country's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dmitry Putyata
Dmitry Vasilyevich Putyata () (Smolensk province, 24 February 1855 - Odessa, 3 February 1915) was a General of the Imperial Russian Army and a Russian explorer of the Pamir Mountains. In 1883 he explored Karakul (Tajikistan), Karakul Lake, Tashkurgan Town, the Bendersky Pass to the Wakhan Valley and westward along the Ghunt River. He covered more territory than any previous or subsequent expedition. Thomas Middleton and Hew Thomas, "Tajikistan and the High Pamirs", 2008 In the 1890s Putyata served on Russian General Staff as a specialist on China. In the late 1890s, Putyata as a military Attaché to Korea was sent to Korean Empire to modernize the Imperial Korean Army with some other officers as a request of Min Young-hwan, the Minister of War of Korean Empire who visited Russia before. However, he had conflicts with Min and tried to go back to Russia. According to the report of French Embassy in Korea, Putyata was unhappy about his payment in Korea and wanted to go back to Russ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanai People
The Nanai people () are a Tungusic people of East Asia who have traditionally lived along Heilongjiang (Amur), Songhuajiang (Sunggari) and Wusuli River (Ussuri) on the Middle Amur Basin. The ancestors of the Nanai were the Wild Jurchens of northernmost Manchuria, which is now the region of Outer Manchuria in Russia's Far Eastern Federal District. The Nanai language belongs to the Manchu-Tungusic family. According to the 2010 census there were 12,003 Nanai in Russia. Name Common names for these people include Nanai ( Nanai: , , , ) and Hezhen (, ; ). There are also terms formerly in use: Goldi, Golds, Goldes, and Samagir. Other self names are Qilang (, ; ), and . means 'land, earth, ground, country' or, in this context, 'native, local'; , , or means 'people' in different dialects. The Russian linguist L. I. Sem gives the name ''Hezhe nai'' () or ''Hezheni'' (, ) and explains it as the self-name of the Nanai of the lower Amur, meaning 'people who live along the low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evenks
The Evenki, also known as the Evenks and formerly as the Tungus, are a Tungusic peoples, Tungusic people of North Asia. In Russia, the Evenki are recognised as one of the Indigenous peoples of the Russian North, indigenous peoples of the Russian North, with a population of 38,396 (Russian Census (2010), 2010 census). In China, the Evenki form one of the List of Chinese ethnic groups, 56 ethnic groups officially recognised by the People's Republic of China, with a population of 30,875 (Sixth National Population Census of the People's Republic of China, 2010 census). There are 537 Evenki in Mongolia (2015 census), called ''Khamnigan'' in the Mongolian language. Origin The Evenki or Ewenki are sometimes conjectured to be connected to the Shiwei people who inhabited the Greater Khingan Range in the 5th to 9th centuries, although the native land of the majority of Evenki people is in the vast regions of Siberia between Lake Baikal and the Amur River. The Evenki language forms the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oroqen People
The Oroqen or Orochen people ( Oroqen:; ; Mongolian: ) are an ethnic group in northern China. They form one of the 56 ethnic groups officially recognized by the People's Republic of China. The Oroqen people are largely concentrated in the northern Chinese provinces of Heilongjiang and Inner Mongolia, which are home to 45.54% and 41.94% of the 8,259 Oroqen people living in China. The Oroqen Autonomous Banner is also located in Inner Mongolia. The Oroqens are mainly hunters, and customarily use animal fur and skins for clothing. Many of them have given up hunting and adhered to laws that aimed to protect wildlife in the People's Republic of China. The government has provided modern dwellings for those who have left behind the traditional way of life. The Oroqen are represented in the People's Congress by their own delegate and are a recognized ethnic minority. In the Russian Empire, various peoples in various places were called Orochen (; orthography before Soviet reform), in sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yury Osipov
Yury Sergeyevich Osipov (; born 7 July 1936) is a Soviet and Russian mathematician. He was elected a full member of the Academy of Sciences of the Soviet Union in 1987 and was a president of its successor, the Russian Academy of Sciences from 17 December 1991 to 29 May 2013. Biography Osipov was born in Tobolsk. In 1959 he graduated from the Department of Mechanics and Mathematics of the Ural State University. His teacher was Nikolay Krasovsky, scientist and founder of the Ural scientific school in mathematical theory of control and the theory of differential games. From 1961 to 1969 he worked at the Ural State University. From 1970 to 1993 he worked at the Institute of Mathematics and Mechanics of the Ural Branch of the Academy of Sciences of the Soviet Union (later, of the Russian Academy of Sciences) in Yekaterinburg (from 1986 to 1993 he was the chief of the Institute). In 1971 he defended his second thesis and received the rank of professor in 1973. In 1984 he was elected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Far Eastern Republic
The Far Eastern Republic ( rus, Дальневосточная Республика, Dal'nevostochnaya Respublika, p=dəlʲnʲɪvɐˈstotɕnəjə rʲɪsˈpublʲɪkə, links=yes; ), sometimes called the Chita Republic (, ), was a nominally independent state that existed from April 1920 to November 1922 in the easternmost part of the Russian Far East and Transbaikal. Although nominally independent, it largely came under the control of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (RSFSR), which envisaged it as a buffer state between the RSFSR and the territories occupied by Japan during the Russian Civil War of 1917–1922. The Far Eastern Republic came to an end in November 1922 when it voluntarily merged with the RSFSR, which became one of founding members of the Soviet Union the following month. Its first president was Alexander Krasnoshchyokov. The Far Eastern Republic occupied the territory of modern Zabaykalsky Krai, Amur Oblast, the Jewish Autonomous Oblast, Khabarovsk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blagoveshchensk
Blagoveshchensk ( rus, Благовещенск, p=bləɡɐˈvʲeɕːɪnsk, ) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Amur Oblast, Russia. It is located at the confluence of the Amur River, Amur and the Zeya Rivers, opposite to the Chinese city of Heihe. Population: The Amur has formed China–Russia border, Russia's border with China since the 1858 Aigun Treaty and the 1860 Treaty of Peking. The area north of the Amur belonged to the Manchu Qing dynasty by the Treaty of Nerchinsk of 1689 until it was ceded to Russia by the Aigun Treaty in 1858. History Early history of the region The early residents of both sides of the Amur in the region of today's Blagoveshchensk were the Daur people, Daurs and Duchers. An early settlement in the area of today's Blagoveshchensk was the Ducher town whose name was reported by the Russian explorer Yerofey Khabarov as Aytyun in 1652, as Aigun from 1683 to 1685, and as Aigun Old Town from 1685 until 1900 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |