|
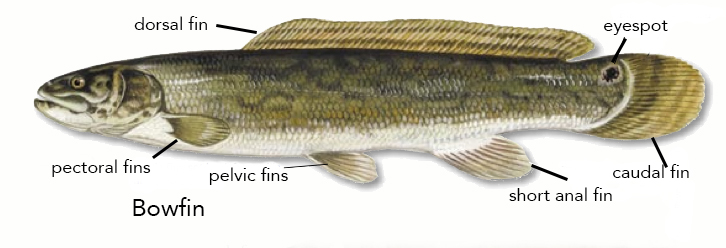
Amiiformes
The Amiiformes order (biology), order of fish has only two extant taxa, extant species, the bowfins: ''Amia calva'' and ''Amia ocellicauda'', the latter recognized as a separate species in 2022. These Amiiformes are found in the freshwater systems of North America, in the United States and parts of southern Canada. They live in freshwater streams, rivers, and swamps. The order first appeared in the Triassic, and the extinct members include both marine and freshwater species, many of which are morphologically disparate from bowfins, such as the Caturidae, caturids. Evolution and diversity The extinct species of the Amiiformes can be found as fossils in Asia and Europe, but the bowfin is the last living species in the order. Amiiformes is therefore the last surviving order (biology), order of Halecomorphi, the clade to which the bowfin and its fossil relatives belong. Other orders, such as the Parasemionotiformes, are all extinct. Halecomorphs, and its sister group Ginglymodi, be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
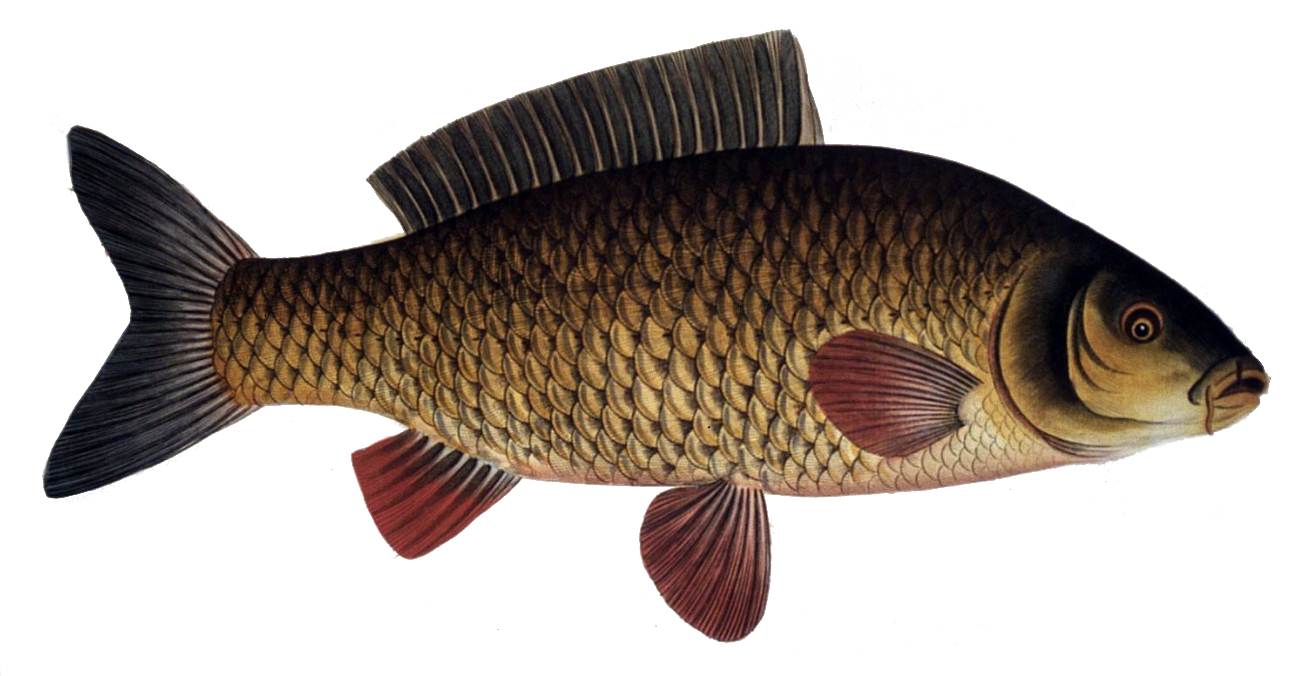
Amia Calva
The ruddy bowfin (''Amia calva'') is a ray-finned fish native to North America. Common names include mudfish, mud pike, dogfish, grindle, grinnel, swamp trout, and choupique. It is regarded as a relict species, relict, being one of only two surviving species of the Halecomorphi, a group of fish that first appeared during the Early Triassic, around 250 million years ago. The bowfin is often considered a "Evolution of fish, living fossil" because they have retained some morphological Cladistics#Terminology for character states, characteristics of their early ancestors. It is one of two species in the genus ''Amia,'' along with ''Amia ocellicauda'', the eyespot bowfin. The closest living relatives of bowfins are gars, with the two groups being united in the clade Holostei. Bowfins are Demersal fish, demersal freshwater piscivores, commonly found throughout much of the eastern United States, and in southern Ontario and Quebec. Fossil deposits indicate Amiiformes were once wides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
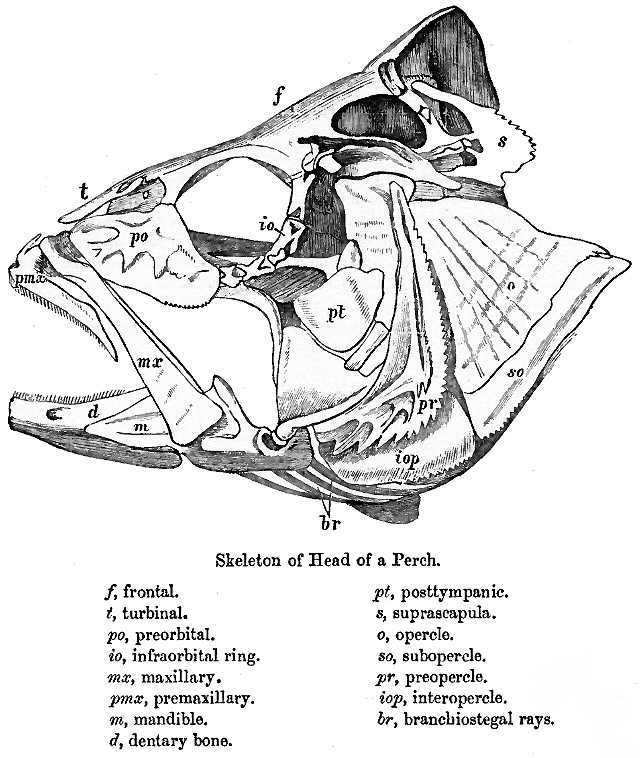
Halecomorphi
Halecomorphi is a taxon of Actinopterygii, ray-finned bony fish in the clade Neopterygii. The only extant Halecomorph species are the bowfin (''Amia calva'') and eyespot bowfin (''Amia ocellicauda''), but the group contains many extinct species in several family (biology), families (including Amiidae, Caturidae, Liodesmidae, Sinamiidae) in the order (biology), order Amiiformes, as well as the extinct orders Ionoscopiformes, Panxianichthyiformes, and Parasemionotiformes. The fossil record of halecomorphs goes back at least to the Early Triassic epoch (geology), epoch. The Halecomorphi exhibit a combination of plesiomorphy, ancestral features, such as most heavily mineralized fish scale, scales, but also by more derived or "modern" features, particularly in the structure of the skull (e.g. position and shape of preopercles). Unique derived traits (synapomorphies) of the Halecomorphi include: *Unique jaw articulation in which the Quadrate bone, quadrate and Symplectic bone, sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holostei
Holostei is a group of ray-finned bony fish. It is divided into two major clades, the Halecomorphi, represented by the single living genus, '' Amia'' with two species, the bowfins (''Amia calva'' and '' Amia ocellicauda''), as well as the Ginglymodi, the sole living representatives being the gars (Lepisosteidae), represented by seven living species in two genera ('' Atractosteus'', '' Lepisosteus''). The earliest members of the clade, which are putative " semionotiforms" such as '' Acentrophorus'' and '' Archaeolepidotus'', are known from the Middle to Late Permian and are among the earliest known neopterygians. Holostei was thought to be regarded as paraphyletic. However, a recent study provided evidence that the Holostei are the closest living relatives of the Teleostei, both within the Neopterygii. This was found from the morphology of the Holostei, for example presence of a paired vomer. Holosteans are closer to teleosts than are the chondrosteans, the other group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caturus
''Caturus'' (from , 'down' and 'tail') is an extinct genus of predatory marine fishes in the family Caturidae in the order Amiiformes, related to modern bowfin. It has been suggested that the genus is non-monophyletic with respect to other caturid genera. Fossils of this genus range from 200 to 140 mya (Early Jurassic to Early Cretaceous). Taxonomy ''Caturus'' has a confused taxonomic history. The genus was originally described by Louis Agassiz for two fossil fish (''U. pachyurus'' and ''U. gracilis'') that had been previously described in the genus ''Uraeus'', which was found to already be preoccupied by a genus of cobra of the same name (now classified as a subgenus within ''Naja''). However, neither of these species were properly described with an associated illustration or proper description, and they remain ''nomen dubia''; the specimen of ''U. pachyurus'' is lost, and the specimen of ''Caturus gracilis'' is too poorly-preserved to assign a specific taxon. Later, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caturidae
Caturidae is an extinct Family (biology), family of predatory Amiiformes, amiiform Actinopterygii, ray-finned fish, being the sister-group to the extant family Amiidae. Though their body form is very different than the modern bowfin, a number of features in the skull point towards a close relationship between the groups. Members of the family were generally larger fish that lived within more coastal marine environments along with freshwater environments near the coast. In these environments, caturids would have fed on a variety of prey items, hunting them similarly to fish like Gar, gars and Barracuda, barracudas. The earliest members of the family appeared in the early Late Triassic, reaching an apex of diversity during the Jurassic with the youngest records of the group date to the Early Cretaceous. History Caturidae was erected by Owen in 1860 though members of the family have been known since the early 19th century, with genera like ''Caturus'' being described before the fami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasemionotiformes
Parasemionotiformes is an extinct order of neopterygian ray-finned fish that existed globally during the Triassic period. It comprises the families Parasemionotidae and Promecosominidae. Many of the included genera are monotypic and most species lived during the Early Triassic epoch. Parasemionotiforms were normally small to medium-sized fishes. They were predominantly marine. Evolutionary relationships Parasemionotiformes are neopterygians, which is the clade that encompasses the vast majority of living ray-finned fishes (Actinopterygii) and about half of all living species of vertebrates. Neopterygii are divided into Teleostei and Holostei. The latter represents a depauperate group today but used to be a diverse clade especially during the Mesozoic Era. The only surviving members of the Holostei are the gars ( Ginglymodi) and the bowfin (Halecomorphi). Parasemionotiformes belong to Holostei and are one of the earliest clades of the Halecomorphi (bowfin and its extinct rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teleosteans
Teleostei (; Greek ''teleios'' "complete" + ''osteon'' "bone"), members of which are known as teleosts (), is, by far, the largest group of ray-finned fishes (class Actinopterygii), with 96% of all extant species of fish. The Teleostei, which is variously considered a division or an infraclass in different taxonomic systems, include over 26,000 species that are arranged in about 40 orders and 448 families. Teleosts range from giant oarfish measuring or more, and ocean sunfish weighing over , to the minute male anglerfish ''Photocorynus spiniceps'', just long. Including not only torpedo-shaped fish built for speed, teleosts can be flattened vertically or horizontally, be elongated cylinders or take specialised shapes as in anglerfish and seahorses. The difference between teleosts and other bony fish lies mainly in their jaw bones; teleosts have a movable premaxilla and corresponding modifications in the jaw musculature which make it possible for them to protrude their jaws ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neopterygii
Neopterygii (from Greek νέος ''neos'' 'new' and πτέρυξ ''pteryx'' 'fin') is a subclass of ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii). Neopterygii includes the Holostei and the Teleostei, of which the latter comprise the vast majority of extant fishes, and over half of all living vertebrate species. While living holosteans include only freshwater taxa, teleosts are diverse in both freshwater and marine environments. Many new species of teleosts are scientifically described each year. The potentially oldest known neopterygian is the putative " semionotiform" '' Acentrophorus varians'' from the Middle Permian of Russia; however, one study incorporating morphological data from fossils and molecular data from nuclear and mitochondrial DNA, places this divergence date at least 284 mya (million years ago), during the Artinskian stage of the Early Permian. Another study suggests an even earlier split (360 myr ago, near the Devonian-Carboniferous boundary). Evolution a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teleostei
Teleostei (; Ancient Greek, Greek ''teleios'' "complete" + ''osteon'' "bone"), members of which are known as teleosts (), is, by far, the largest group of ray-finned fishes (class Actinopterygii), with 96% of all neontology, extant species of fish. The Teleostei, which is variously considered a Division (zoology), division or an infraclass in different taxonomic systems, include over 26,000 species that are arranged in about 40 order (biology), orders and 448 family (biology), families. Teleosts range from giant oarfish measuring or more, and ocean sunfish weighing over , to the minute male anglerfish ''Photocorynus spiniceps'', just long. Including not only torpedo-shaped fish built for speed, teleosts can be flattened vertically or horizontally, be elongated cylinders or take specialised shapes as in anglerfish and seahorses. The difference between teleosts and other bony fish lies mainly in their jaw bones; teleosts have a movable premaxilla and corresponding modifications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fishes
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fins and a hard skull, but lacking limbs with digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal jawless fish and the more common jawed fish, the latter including all living cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as the extinct placoderms and acanthodians. In a break to the long tradition of grouping all fish into a single class (Pisces), modern phylogenetics views fish as a paraphyletic group. Most fish are cold-blooded, their body temperature varying with the surrounding water, though some large active swimmers like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature. Many fish can communicate acoustically with each other, such as during courtship displays. The study of fish is known as ichthyology. The earliest fish appeared during the Cambrian as small filter feeders; they continued to evolve through the Paleozoic, diversifying into many forms. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to descendants, nor does it show how much they have changed, so many differing evolutionary trees can be consistent with the same cladogram. A cladogram uses lines that branch off in different directions ending at a clade, a group of organisms with a last common ancestor. There are many shapes of cladograms but they all have lines that branch off from other lines. The lines can be traced back to where they branch off. These branching off points represent a hypothetical ancestor (not an actual entity) which can be inferred to exhibit the traits shared among the terminal taxa above it. This hypothetical ancestor might then provide clues about the order of evolution of various features, adaptation, and other e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |