|
Altenburg
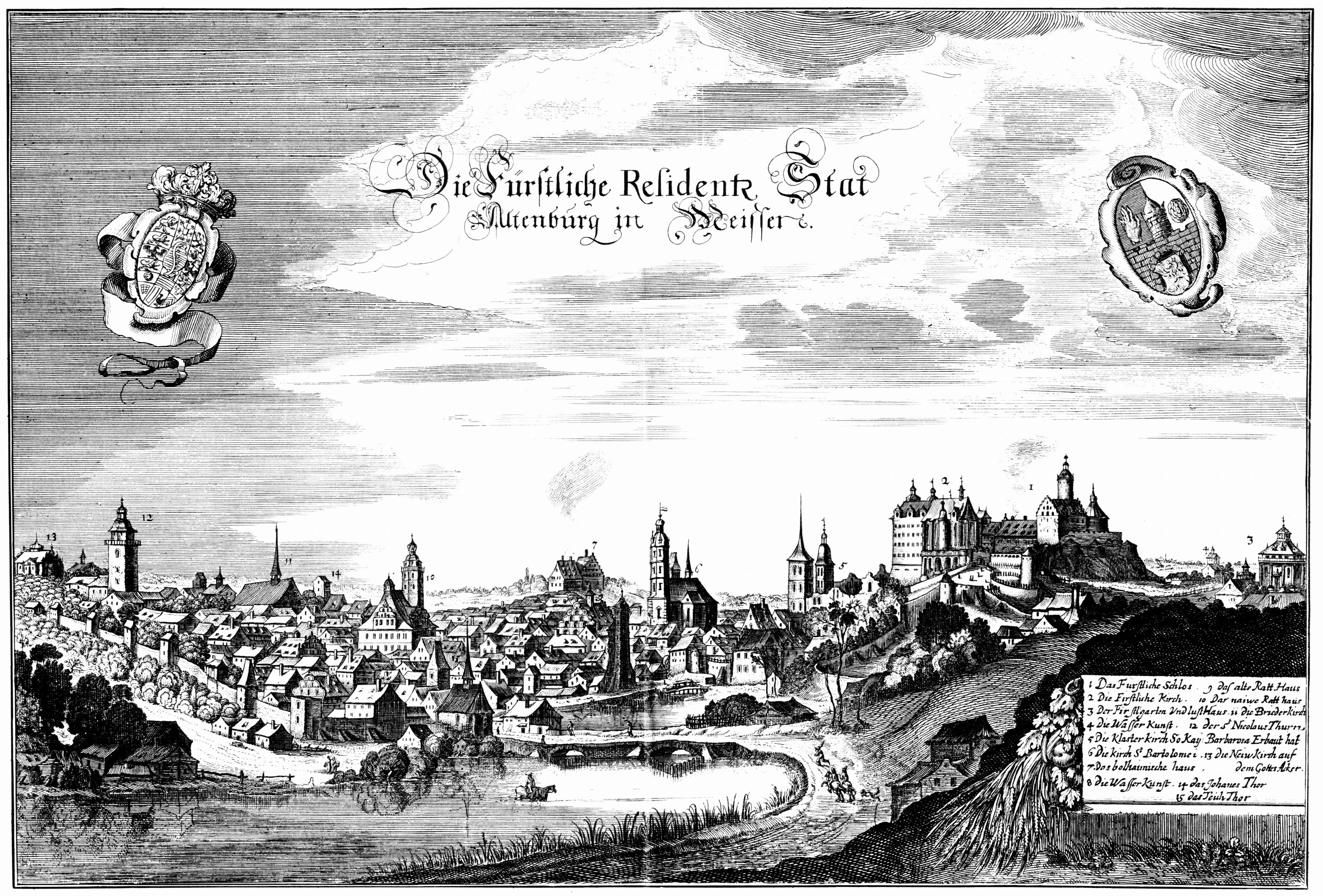
Altenburg () is a city in Thuringia, Germany, located south of Leipzig, west of Dresden and east of Erfurt. It is the capital of the Altenburger Land district and part of a polycentric old-industrial textile and metal production region between Gera, Zwickau and Chemnitz with more than 1 million inhabitants, while the city itself has a population of 33,000. Today, the city and its rural county is part of the Central German Metropolitan Region. Altenburg was first mentioned in 976 and later became one of the first German cities within former Slavic area, east of the Saale river (as part of the medieval Ostsiedlung movement). The emperor Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick Barbarossa visited Altenburg several times between 1165 and 1188, hence the town is named a Barbarossa city, Barbarossa town today. Since the 17th century, Altenburg was the residence of different House of Wettin, Ernestine duchies, of whom the Duchy of Saxe-Altenburg, Saxe-Altenburg persisted until th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
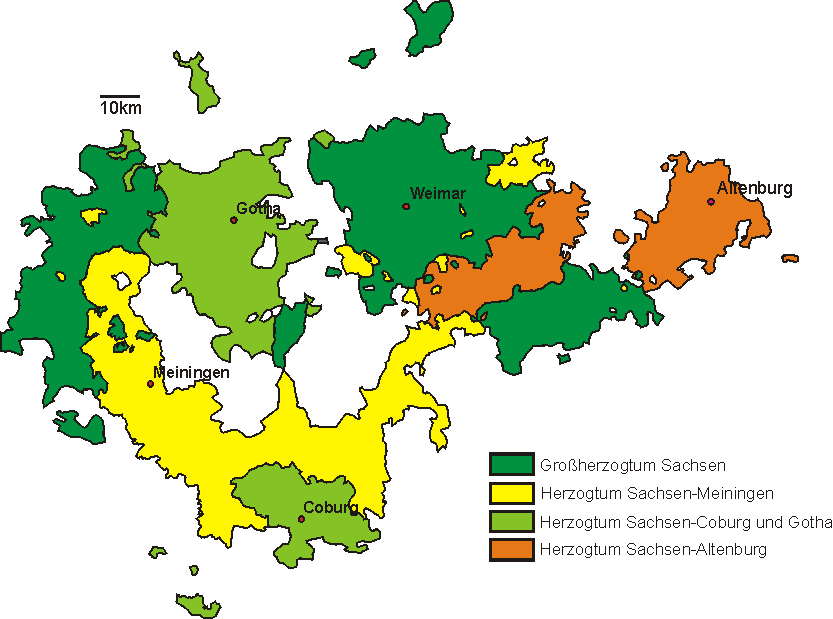
Duchy Of Saxe-Altenburg
Saxe-Altenburg () was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine duchies, Ernestine branch of the House of Wettin in present-day Thuringia. It was one of the smallest of the German states with an area of 1323 square kilometers and a population of 207,000 (1905) of whom about one fifth resided in the capital, Altenburg. The territory of the duchy consisted of two non-contiguous territories separated by land belonging to the Principality of Reuss-Gera. Its economy was based on agriculture, forestry, and small industry. The state had a constitutional monarchical form of government with a parliament composed of thirty members chosen by male taxpayers over 25 years of age. Territory Saxe-Altenburg had an area of 1,323 km2 (510 sq. mi.) and a population of 207,000 in 1905. Its capital was Altenburg. The duchy consisted of two separate areas: the Ostkreis, containing the cities of Altenburg, Schmölln, Gößnitz, Lucka und Meuselwitz (including the exclave of Mumsdorf), Gera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altenburger Land
Altenburger Land is a district in Thuringia, Germany. It is bounded by (from the west and clockwise) the district of Greiz (district), Greiz, the Burgenlandkreis (Saxony-Anhalt), and the districts Leipzig (district), Leipzig, Mittelsachsen and Zwickau (district), Zwickau in Saxony. The district is a member of the Central German Metropolitan Region. Geography Altenburger Land is the easternmost district of Thuringia. It is largely agricultural with three quarters of the total area being used for agriculture. In contrast, forests make up only around 10% of the area, especially in the south of the district there are only few forests. This can be explained by a high soil fertility with a Loess-layer of up to 3.5 meters. The main river is the Pleiße, a tributary of the White Elster, crossing the district from south to north. The hilly Osterland constituting the northernmost foothills of the Ore Mountains slopes gently away to the plains of eastern Saxony-Anhalt. History The re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thuringia
Thuringia (; officially the Free State of Thuringia, ) is one of Germany, Germany's 16 States of Germany, states. With 2.1 million people, it is 12th-largest by population, and with 16,171 square kilometers, it is 11th-largest in area. Erfurt is the capital and largest city. Other cities include Jena, Gera and Weimar. Thuringia is bordered by Bavaria, Hesse, Lower Saxony, Saxony, and Saxony-Anhalt. It has been known as "the green heart of Germany" () from the late 19th century due to its broad, dense forest. Most of Thuringia is in the Saale drainage basin, a bank (geography), left-bank tributary of the Elbe. Thuringia is home to the Rennsteig, Germany's best-known hiking, hiking trail. Its winter resort of Oberhof, Germany, Oberhof makes it a well-equipped winter sports destination – half of Germany's 136 Winter Olympics, Winter Olympic gold medals had been won by Thuringian athletes as of 2014. Thuringia was favoured by or was the birthplace of three key intellectu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Wettin
The House of Wettin () was a dynasty which included Saxon monarch, kings, Prince Elector, prince-electors, dukes, and counts, who once ruled territories in the present-day German federated states of Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia. The dynasty is one of the oldest in Europe, and its origins can be traced back to the town of Wettin, Saxony-Anhalt. The Wettins gradually rose to power within the Holy Roman Empire. Members of the family became the rulers of several Middle Ages, medieval states, starting with the Saxon Eastern March in 1030. Other states they gained were Meissen in 1089, Thuringia in 1263, and Saxony in 1423. These areas cover large parts of Central Germany (cultural area), Central Germany as a cultural area of Germany. The family divided into two ruling branches in 1485 by the Treaty of Leipzig: the Ernestine and Albertine branches. The older Ernestine branch played a key role during the Protestant Reformation. Many ruling monarchs outside Germany were later tied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lindenau-Museum
The Lindenau-Museum is an art museum in Altenburg, Thuringia, Germany. It originated as the house-museum of baron and collector Bernhard August von Lindenau. The building was completed in 1876. The museum's main attraction is its collection of Italian paintings from the late Gothic and early Renaissance age (13th–15th centuries), which are among the largest outside Italy. The artworks include Filippo Lippi's '' St. Jerome in Penance'', Sandro Botticelli's ''Portrait of Caterina Sforza'' and a predella panel by Fra Angelico. It also keeps ancient antiquities and modern works, and has a library. Additionally, there are collections of paintings primarily from the 16th to 19th centuries and asw well the 20th century, that were created in German, Italy, Netherlands and France. After 1945, collections primarily consisted of artwork created by artists from Berlin, Chemnitz, Dresden, and Leipzig. The art of the 1920s and classical modernism are emphasized in painting and graphic d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skat (card Game)
Skat (), historically Scat, is a three-player trick-taking card game of the ace–ten family, devised around 1810 in Altenburg in the Duchy of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg. It is the national game of Germany''Skat'' at www.pagat.com. Retrieved 3 Jun 2018. and, along with Doppelkopf, it is the most popular card game in Germany and Silesia and one of the most popular in the rest of Poland. A variant of 19th-century Skat was once popular in the US. John McLeod (card game researcher), John McLeod considers it one of the best and most interesting card games for three players,Keller, Thomas and Sebastian Kupferschmid, "Automatic Bidding for the Game of Skat" in ''KI 2008: Advances in Artificial Intelligence: 31st Annual German Conference on AI'', Kaiserslautern: Springer, 2008, p. 96. . and Kelbet described it as "the king of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbarossa City
"Barbarossa city" () is a nickname for German cities that the Staufer Emperor Frederick Barbarossa stayed in or near for some time. The cities usually mentioned include Sinzig, Kaiserslautern, Gelnhausen, Altenburg, Bad Frankenhausen, but Annweiler am Trifels, Bad Wimpfen, Eberbach and Waiblingen consider themselves as such as well. Sinzig Sinzig is a city on the Middle Rhine in Ahrweiler County. Celtic in its early history and settled by the Romans, the city was first mentioned in 762 as a Franconian king's court, ''sentiacum''. The city was at its height from the 12th through the 14th century as a Kaiserpfalz often visited by the German kings and emperors. Barbarossa himself stayed at Sinzig four times. Kaiserslautern The settlement history of Kaiserslautern, an industrial city and university seat at the northern edge of the Palatinate forest, begins in the 5th millennium BC. Around 1100 CE, Salian rulers built themselves a castle on the grounds of the present- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gera
Gera () is a city in the German state of Thuringia. With around 93,000 inhabitants, it is the third-largest city in Thuringia after Erfurt and Jena as well as the easternmost city of the ''Thüringer Städtekette'', an almost straight string of cities consisting of the six largest Thuringian cities from Eisenach in the west, via Gotha, Erfurt, Weimar and Jena to Gera in the east. Gera is the largest city in the Vogtland, and one of its historical capitals along with Plauen, Greiz and Weida, Thuringia, Weida. The city lies in the East Thuringian Hill Country, in the wide valley of the White Elster, between Greiz (upstream) and Leipzig (downstream). Gera is located in the Central German Metropolitan Region, approximately south of Saxony's largest city of Leipzig, east of Thuringia's capital Erfurt, west of Saxony's capital Dresden and 90 km (56 miles) north of Bavaria's city of Hof (Saale). First mentioned in 995 and developing into a city during the 13th century, Gera has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leipzig
Leipzig (, ; ; Upper Saxon: ; ) is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Saxony. The city has a population of 628,718 inhabitants as of 2023. It is the List of cities in Germany by population, eighth-largest city in Germany and is part of the Central German Metropolitan Region. The name of the city is usually interpreted as a Slavic term meaning ''place of linden trees'', in line with many other Slavic placenames in the region. Leipzig is located about southwest of Berlin, in the southernmost part of the North German Plain (the Leipzig Bay), at the confluence of the White Elster and its tributaries Pleiße and Parthe. The Leipzig Riverside Forest, Europe's largest intra-city riparian forest, has developed along these rivers. Leipzig is at the centre of Neuseenland (''new lake district''). This district has Bodies of water in Leipzig, several artificial lakes created from former lignite Open-pit_mining, open-pit mines. Leipzig has been a trade city s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zwickau
Zwickau (; ) is the fourth-largest city of Saxony, Germany, after Leipzig, Dresden and Chemnitz, with around 88,000 inhabitants,. The West Saxon city is situated in the valley of the Zwickau Mulde (German: ''Zwickauer Mulde''; progression: ), and lies in a string of cities sitting in the densely populated foreland of the Elster and Ore Mountains stretching from Plauen in the southwest via Zwickau, Chemnitz and Freiberg to Dresden in the northeast. Zwickau is the seat of the Zwickau District, the most densely populated district in the new states of Germany. Zwickau is the seat of the West Saxon University of Zwickau (German: ''Westsächsische Hochschule Zwickau'') with campuses in Zwickau, Markneukirchen, Reichenbach im Vogtland and Schneeberg (Erzgebirge). The city is the birthplace of composer Robert Schumann. Zwickau has historically been one of the centres of the German automotive industry. It is the cradle of Audi and its forerunner Horch. Horchwerke AG Zwickau wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleiße
The Pleiße () is a river of Saxony and Thuringia, Germany. It flows from south to north into the White Elster in Leipzig. Originally, its natural length was ; however, south of Leipzig, it has been straightened, which shortened it to around . The river is well accessible via the Pleiße cycle path. The name Pleiße is of old Sorbian origin and means: "the swamp-forming water". It gave its name to the Pleissnerland (Plisni) on its lower reaches, which was important in the Middle Ages. Course The Pleiße has its source southwest of Zwickau in Lichtentanne, locality Ebersbrunn. The Saxon towns of Werdau and Crimmitschau are followed by the Thuringian communities of Ponitz, Gößnitz, Nobitz and Altenburg. Behind Windischleuba, the Windischleuba dam regulates the flow to Fockendorf and Treben. After Haselbach, which is still part of the municipial association ''(Verwaltungsgemeinschaft)'' Pleißenaue in Thuringia, follow the Saxon communities of Regis-Breitingen, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Arnold Brockhaus
Friedrich Arnold Brockhaus (4 May 1772 – 20 August 1823) was a German encyclopedia publisher and editor, famed for publishing the '' Conversations-Lexikon'', which is now published as the Brockhaus encyclopedia. Biography Brockhaus was educated at the gymnasium of his native Dortmund, and from 1788 to 1793 served an apprenticeship in a mercantile house at Düsseldorf. He then devoted two years at the University of Leipzig to the study of modern languages and literature, after which he set up in Dortmund an emporium for English goods. In 1801, he transferred this business to Arnheim, and in the following year to Amsterdam. In 1805, having given up his first line of trade, Brockhaus began business as a publisher. Two journals projected by him were not allowed by the government to survive for any length of time, and in 1810 the complications in the affairs of Holland induced him to return homewards. In 1811 he settled at Altenburg. About three years previously he had purcha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |