|
Airspeed Aircraft
In aviation, airspeed is the speed of an aircraft relative to the air it is flying through (which itself is usually moving relative to the ground due to wind). In contrast, the ground speed is the speed of an aircraft with respect to the surface of the Earth (whether over land or presumed-stationary water). It is difficult to measure the exact airspeed of the aircraft (true airspeed), but other measures of airspeed, such as indicated airspeed and Mach number give useful information about the capabilities and limitations of airplane performance. The common measures of airspeed are: * Indicated airspeed (IAS), what is read on an airspeed gauge connected to a pitot-static system. * Calibrated airspeed (CAS), indicated airspeed adjusted for pitot system position and installation error. * True airspeed (TAS) is the actual speed the airplane is moving through the air. When combined with aircraft direction, wind speed and direction, it can be used to calculate ground speed and direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knot (unit)
The knot () is a unit of speed equal to one nautical mile per hour, exactly (approximately or ). The ISO standard symbol for the knot is kn. The same symbol is preferred by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers ( IEEE), while kt is also common, especially in aviation, where it is the form recommended by the International Civil Aviation Organization ( ICAO). The knot is a non- SI unit. The knot is used in meteorology, and in maritime and air navigation. A vessel travelling at 1 knot along a meridian travels approximately one minute of geographic latitude in one hour. Definitions ;1 international knot = :1 nautical mile per hour (by definition), : (exactly), : (approximately), : (approximately), : (approximately) : (approximately). The length of the internationally agreed nautical mile is . The US adopted the international definition in 1954, having previously used the US nautical mile (). The UK adopted the international nautical mile defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground Track
A satellite ground track or satellite ground trace is the path on the surface of a planet directly below a satellite's trajectory. It is also known as a suborbital track or subsatellite track, and is the vertical projection of the satellite's orbit onto the surface of the Earth (or whatever body the satellite is orbiting). A satellite ground track may be thought of as a path along the Earth's surface that traces the movement of an imaginary line between the satellite and the center of the Earth. In other words, the ground track is the set of points at which the satellite will pass directly overhead, or cross the zenith, in the frame of reference of a ground observer.. The ground track of a satellite can take a number of different forms, depending on the values of the orbital elements, parameters that define the size, shape, and orientation of the satellite's orbit, although identification of the always reliant upon the recognition of the physical form that is in motion; This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velocity
Velocity is a measurement of speed in a certain direction of motion. It is a fundamental concept in kinematics, the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of physical objects. Velocity is a vector (geometry), vector Physical quantity, quantity, meaning that both magnitude and direction are needed to define it. The Scalar (physics), scalar absolute value (Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude) of velocity is called , being a coherent derived unit whose quantity is measured in the International System of Units, SI (metric system) as metres per second (m/s or m⋅s−1). For example, "5 metres per second" is a scalar, whereas "5 metres per second east" is a vector. If there is a change in speed, direction or both, then the object is said to be undergoing an ''acceleration''. Definition Average velocity The average velocity of an object over a period of time is its Displacement (geometry), change in position, \Delta s, divided by the duration of the period, \Delt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
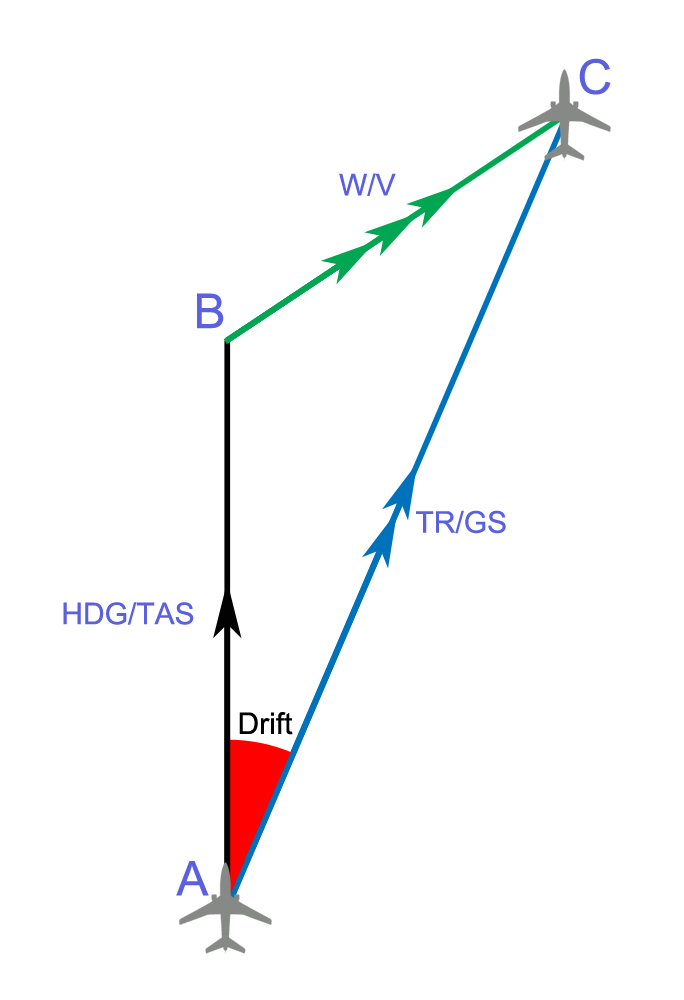
Aircraft Heading
In navigation, the heading of a vessel or aircraft is the compass direction in which the craft's bow or nose is pointed. Note that the heading may not necessarily be the direction that the vehicle actually travels, which is known as its '' course''. Any difference between the heading and course is due to the motion of the underlying medium, the air or water, or other effects like skidding or slipping. The difference is known as the ''drift'', and can be determined by the ''wind triangle''. At least seven ways to measure the heading of a vehicle have been described. Heading is typically based on cardinal directions, so 0° (or 360°) indicates a direction toward true north, 90° true east, 180° true south, and 270° true west. TVMDC TVMDC,AW is a mnemonic for converting from true heading, to magnetic and compass headings. TVMDC is a mnemonic initialism for true heading, variation, magnetic heading, deviation, compass heading, add westerly. The most common use of the TVMDC met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernoulli's Equation
Bernoulli's principle is a key concept in fluid dynamics that relates pressure, speed and height. For example, for a fluid flowing horizontally Bernoulli's principle states that an increase in the speed occurs simultaneously with a decrease in static pressure, pressure The principle is named after the Swiss mathematician and physicist Daniel Bernoulli, who published it in his book ''Hydrodynamica'' in 1738. Although Bernoulli deduced that pressure decreases when the flow speed increases, it was Leonhard Euler in 1752 who derived Bernoulli's equation in its usual form. Bernoulli's principle can be derived from the principle of conservation of energy. This states that, in a steady flow, the sum of all forms of energy in a fluid is the same at all points that are free of viscous forces. This requires that the sum of kinetic energy, potential energy and internal energy remains constant. Thus an increase in the speed of the fluid—implying an increase in its kinetic energy—occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Pressure
In compressible fluid dynamics, impact pressure ( dynamic pressure) is the difference between total pressure (also known as pitot pressure or stagnation pressure) and static pressure. In aerodynamics notation, this quantity is denoted as q_c or Q_c. When input to an airspeed indicator, impact pressure is used to provide a calibrated airspeed reading. An air data computer with inputs of pitot and static pressures is able to provide a Mach number and, if static temperature is known, true airspeed. Some authors in the field of compressible flows use the term ''dynamic pressure'' or ''compressible dynamic pressure'' instead of ''impact pressure''. L. J. Clancy (1975) ''Aerodynamics'', Section 3.12 and 3.13"the dynamic pressure is equal to ''half rho vee squared'' only in incompressible flow."Houghton, E.L. and Carpenter, P.W. (1993), ''Aerodynamics for Engineering Students'', Section 2.3.1 Isentropic flow In isentropic flow the ratio of total pressure to static pressure is given ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ratio Of Specific Heats
In thermal physics and thermodynamics, the heat capacity ratio, also known as the adiabatic index, the ratio of specific heats, or Laplace's coefficient, is the ratio of the heat capacity at constant pressure () to heat capacity at constant volume (). It is sometimes also known as the ''isentropic expansion factor'' and is denoted by (gamma) for an ideal gasγ first appeared in an article by the French mathematician, engineer, and physicist Siméon Denis Poisson: * On p. 332, Poisson defines γ merely as a small deviation from equilibrium which causes small variations of the equilibrium value of the density ρ. In Poisson's article of 1823 – * γ was expressed as a function of density D (p. 8) or of pressure P (p. 9). Meanwhile, in 1816 the French mathematician and physicist Pierre-Simon Laplace had found that the speed of sound depends on the ratio of the specific heats. * However, he didn't denote the ratio as γ. In 1825, Laplace stated that the speed of sound is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speed Of Sound
The speed of sound is the distance travelled per unit of time by a sound wave as it propagates through an elasticity (solid mechanics), elastic medium. More simply, the speed of sound is how fast vibrations travel. At , the speed of sound in air is about , or in or one mile in . It depends strongly on temperature as well as the medium through which a sound wave is propagating. At , the speed of sound in dry air (sea level 14.7 psi) is about . The speed of sound in an ideal gas depends only on its temperature and composition. The speed has a weak dependence on frequency and pressure in dry air, deviating slightly from ideal behavior. In colloquial speech, ''speed of sound'' refers to the speed of sound waves in Earth's atmosphere, air. However, the speed of sound varies from substance to substance: typically, sound travels most slowly in gases, faster in liquids, and fastest in solids. For example, while sound travels at in air, it travels at in water (almost 4.3 times a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
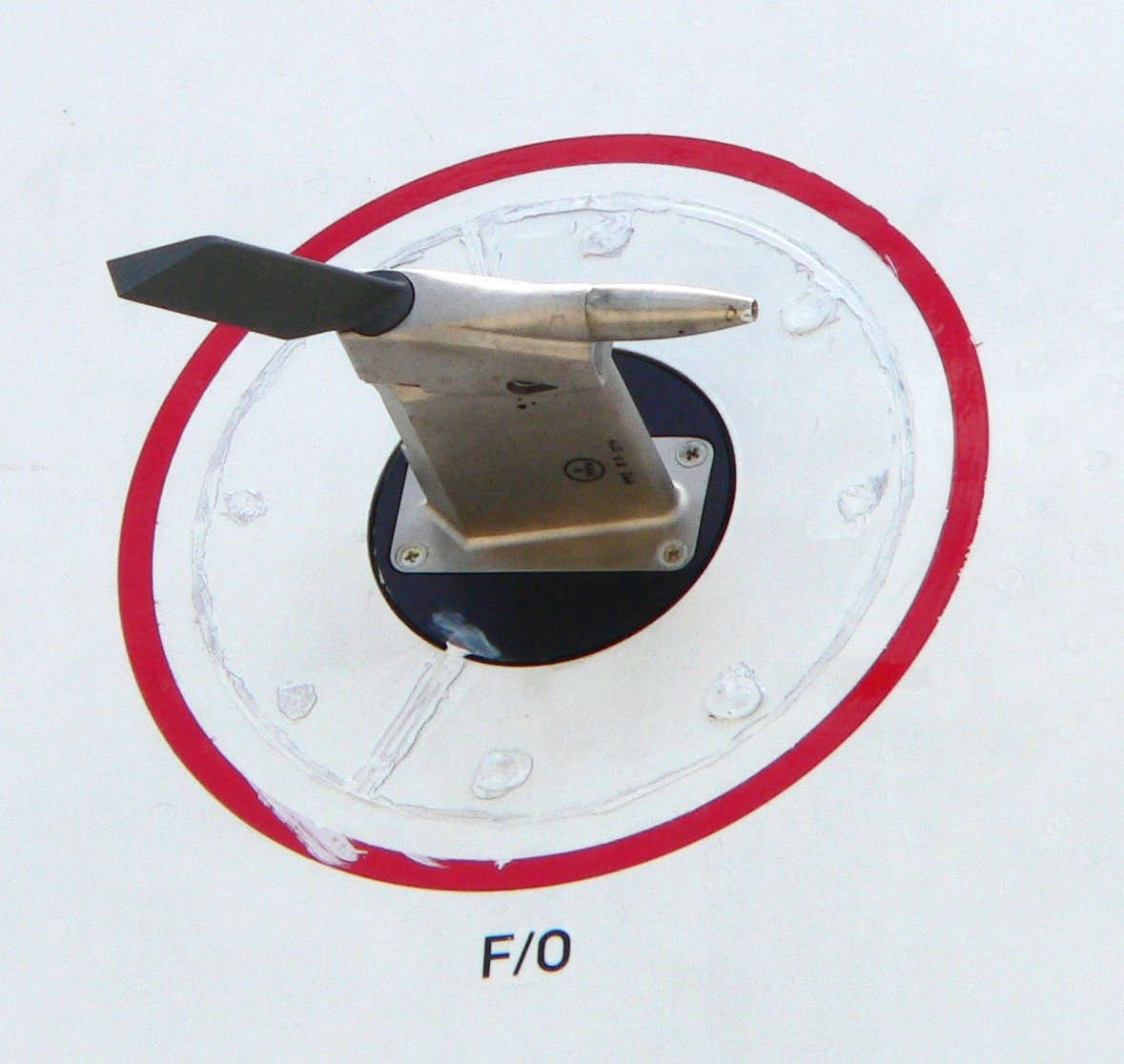
Position Error
Position error is one of the errors affecting the systems in an aircraft for measuring airspeed and altitude. It is not practical or necessary for an aircraft to have an airspeed indicating system and an altitude indicating system that are exactly accurate. A small amount of error is tolerable. It is caused by the location of the static vent that supplies air pressure to the airspeed indicator and altimeter; there is no position on an aircraft where, at all angles of attack, the static pressure is always equal to atmospheric pressure. Static system All aircraft are equipped with a small hole in the surface of the aircraft called the static port. The air pressure in the vicinity of the static port is conveyed by a conduit to the altimeter and the airspeed indicator. This static port and the conduit constitute the aircraft's static system. The objective of the static system is to sense the pressure of the air at the altitude at which the aircraft is flying. In an ideal stati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
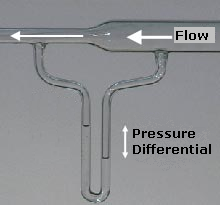
Pitot Tube
A pitot tube ( ; also pitot probe) measures fluid flow velocity. It was invented by French engineer Henri Pitot during his work with aqueducts and published in 1732, and modified to its modern form in 1858 by Henry Darcy. It is widely used to determine the airspeed of aircraft; the water speed of boats; and the flow velocity of liquids, air, and gases in industry. Theory of operation The basic pitot tube consists of a tube pointing directly into the oncoming fluid flow. Pressure in the tube can be measured as the moving fluid cannot escape and stagnates. This pressure is the stagnation pressure of the fluid, also known as the total pressure or (particularly in aviation) the pitot pressure. The measured stagnation pressure cannot just by itself be used to determine the fluid flow velocity (airspeed in aviation) directly. However, with a measured static pressure as well it can be determined by the use of Bernoulli's equation which states: :Stagnation pressure = static pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Static Pressure
In fluid mechanics the term static pressure refers to a term in Bernoulli's equation written words as ''static pressure + dynamic pressure = total pressure''. Since pressure measurements at any single point in a fluid always give the static pressure value, the 'static' is often dropped. In the design and operation of aircraft, ''static pressure'' is the air pressure in the aircraft's static pressure system. Static pressure in fluid dynamics The concept of pressure is central to the study of fluids. A pressure can be identified for every point in a body of fluid, regardless of whether the fluid is in motion. Pressure can be measured using an aneroid, Bourdon tube, mercury column, or various other methods. The concepts of ''total pressure'' and '' dynamic pressure'' arise from Bernoulli's equation and are significant in the study of all fluid flows. These two pressures are not pressures in the usual sense - they cannot be measured using a pressure sensor. To avoid potential ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |