|
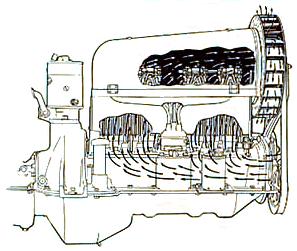
Air-cooled Aircraft Piston Engines
Air-cooled engines rely on the circulation of air directly over heat dissipation fins or hot areas of the engine to cool them in order to keep the engine within operating temperatures. Air-cooled designs are far simpler than their liquid-cooled counterparts, which require a separate radiator, coolant reservoir, piping and pumps. Air-cooled engines are widely seen in applications where weight or simplicity is the primary goal. Their simplicity makes them suited for uses in small applications like chainsaws and lawn mowers, as well as small generators and similar roles. These qualities also make them highly suitable for aviation use, where they are widely used in general aviation aircraft and as auxiliary power units on larger aircraft. Their simplicity, in particular, also makes them common on motorcycles. Introduction Most modern internal combustion engines are cooled by a closed circuit carrying liquid coolant through channels in the engine block and cylinder head. A fluid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fin (extended Surface)
In the study of heat transfer, fins are surfaces that extend from an object to increase the rate of heat transfer to or from the environment by increasing convection. The amount of conduction, convection, or radiation of an object determines the amount of heat it transfers. Increasing the temperature gradient between the object and the environment, increasing the convection heat transfer coefficient, or increasing the surface area of the object increases the heat transfer. Sometimes it is not feasible or economical to change the first two options. Thus, adding a fin to an object, increases the surface area and can sometimes be an economical solution to heat transfer problems. One-piece finned heat sinks are produced by extrusion, casting, skiving, or milling. General case To create a tractable equation for the heat transfer of a fin, many assumptions need to be made: # Steady state # Constant material properties (independent of temperature) # No internal heat generation # One ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motor Oil
Motor oil, engine oil, or engine lubricant is any one of various substances used for the lubrication of internal combustion engines. They typically consist of base oils enhanced with various additives, particularly antiwear additives, detergents, dispersants, and, for multi-grade oils, viscosity index improvers. The main function of motor oil is to reduce friction and wear on moving parts and to clean the engine from sludge (one of the functions of dispersants) and varnish (detergents). It also neutralizes acids that originate from fuel and from oxidation of the lubricant (detergents), improves the sealing of piston rings, and cools the engine by carrying heat away from moving parts. In addition to the aforementioned basic constituents, almost all lubricating oils contain corrosion and oxidation inhibitors. Motor oil may be composed of only a lubricant base stock in the case of non-detergent oil, or a lubricant base stock plus additives to improve the oil's detergency, extreme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tatra T97
The Tatra 97 (T97) is a Czechoslovak mid-size car built by Tatra in Kopřivnice, Moravia, from 1936 to 1939. History The Tatra 97 was designed to complement two full-size cars in the Tatra range: the Tatra 77 launched in 1934 and the Tatra 87 launched in 1936 along with the Type 97. Each of the three models has an air-cooled rear engine and share similar aerodynamic fastback four-door sedan bodies. But whereas types 77 and 87 each have a large V8 engine, Type 97 has a flat-four engine. The Type 97 is distinguished by having two headlights and a one-piece windscreen, whereas the 77 and 87 have three headlights and a three-piece windscreen. The Type 97's flat-four engine displaces 1,759 cc and produces , giving it top speed of . Tatra already had a mid-size car in the same class, the more conventional 1,688 cc Tatra 75 that it had launched in 1933. Tatra continued to produce the Type 75 alongside the futuristic Type 97. In fact production of the Type 75 outlived that of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tatra T87
The Tatra 87 (T87) is a car built by Czechoslovak manufacturer Tatra from 1936 to 1950. It was powered by a rear-mounted 2.9-litre air-cooled 90-degree overhead cam V8 engine that produced 85 horsepower and could drive the car at nearly . It is ranked among the fastest production cars of its time. Competing cars in this class, however, used engines with almost twice the displacement, and with fuel consumption of 20 liters per 100 km (11.8 mpg). Thanks to its aerodynamic shape, the Tatra 87 had a consumption of just 12.5 litres per 100 km (18.8 mpg). After the war between 1950 and 1953, T87s were fitted with more-modern 2.5-litre V8 T603 engines. The 87 was used by Hanzelka and Zikmund for their travel through Africa and Latin America from 1947 to 1950. Design The Tatra 87 has unique bodywork. Its streamlined shape was designed by Hans Ledwinka and Erich Übelacker and was based on the Tatra 77, the first car designed with aerodynamics in mind. The body design was ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tatra T77
The Tatra 77 (T77) is one of the first serial-produced, truly aerodynamically-designed automobiles, produced by Czechoslovak company Tatra from 1934 to 1938. It was developed by Hans Ledwinka and Paul Jaray, the Zeppelin aerodynamic engineer. Launched in 1934, the Tatra 77 is a coach-built automobile, constructed on a platform chassis with a pressed box-section steel backbone rather than Tatra's trademark tubular chassis, and is powered by a rear-mounted 2.97-litre air-cooled V8 engine, in later series increased to a 3.4-litre engine. It possessed advanced engineering features, such as overhead valves, hemispherical combustion chambers, a dry sump, fully independent suspension, rear swing axles and extensive use of lightweight magnesium alloy for the engine, transmission, suspension and body. The average drag coefficient of a 1:5 model of Tatra 77 was recorded as 0.2455. The later model T77a, introduced in 1935, has a top speed of over due to its advanced aerodynamic design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tatra 11
The Tatra T11 is an automobile that was produced from 1923 through 1927. It was the first Tatra model to use backbone tube chassis, swinging half-axles and air-cooled engine, the development of which is still in use on the trucks produced by Tatra to this day. Origins Hans Ledwinka created the design of the T11 while working for Steyr in Austria. He believed there was a need for a small car, and carried out the work in his own time. His design offered to the Steyr management was rejected. He left the company soon after to work for a previous employer, Nesseldorfer, in Moravia Moravia ( ; ) is a historical region in the eastern Czech Republic, roughly encompassing its territory within the Danube River's drainage basin. It is one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia. The medieval and early ..., which was soon to become Tatra. This was in 1921 and the development of the T11 started soon after. The T11 was produced between 1923 and 1927 with 3,847 exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tatra (company)
Tatra is a Czech vehicle manufacturer from Kopřivnice. It is owned by the TATRA TRUCKS a.s. company, and it is the third oldest company in the world producing motor vehicles with an unbroken history. The company was founded in 1850 as ''Ignatz Schustala & Cie''. In 1890 the company became a joint-stock company and was renamed the ''Nesselsdorfer Wagenbau-Fabriksgesellschaft''. In 1897, the ''Nesselsdorfer Wagenbau-Fabriksgesellschaft'' produced the Präsident, which was the first factory-produced automobile with a petrol engine to be made in Central and Eastern Europe. The First Truck was made a year later, in 1898. In 1918, the company was renamed ''Kopřivnická vozovka a.s.'', and in 1919 it changed from the Nesselsdorfer marque to the ''Tatra'' badge, named after the nearby Tatra Mountains on the Czechoslovak- Polish border (now on the Polish- Slovak border). In the interwar period, Tatra came to international prominence with its line of affordable cars based on ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chevrolet Series M Copper-Cooled
The 1923 Chevrolet Series M Copper-Cooled was an automobile made to be completely air-cooled engine, air-cooled by Chevrolet in 1923. It was designed by Charles F. Kettering, head engineer of Dayton Engineering Laboratories Co., Delco, the General Motors research division wing in Dayton, Ohio. The automobile used a body style from its predecessor, but incorporated an air-cooled engine. Air cooling, as opposed to water-based cooling, was much more practical in a sense because it did not require a radiator, nor the piping that came with it. Although air cooling was not new to the time period, it was new to engines of that scale. The Copper-Cooled Chevrolet was in fact a feasible project; however, the final product did not live up to the standards that Kettering had imagined. The car dangerously overheated in hot weather, and posed a safety hazard to the drivers. Only a few made it to the sales floor, only to be recalled and destroyed by Chevrolet. The 1923 Chevrolet Series M Copper-C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Way (automobile)
New Way may refer to: Political parties * New Way (Israel), a short-lived political faction in Israel in 2001 * New Way (Turkey), the Turkish section of the reunified Fourth International Publications * ''New Way'' (Jewish newspaper), , a newspaper of the Russian Empire subtitled *''New Way'' (''Naujas Kelias''), a Neo-Nazi Publication in Lithuania * Novy Put, , a magazine of the Russian Empire Many other Russian publications and topics are entitled . Towns * New Way, Ohio, a community in the United States *New Way, Essex, United Kingdom, a hamlet near Harlow Harlow is a town and local government district located in the west of Essex, England. Founded as a Planned community, new town in 1947, it is situated on the border with Hertfordshire, and occupies a large area of land on the south bank of the ... Music *" New Way (To Light Up an Old Flame)", a single by American country music artist Joe Diffie {{disambiguation, political ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franklin (automobile)
The Franklin Automobile Company was an American automobile manufacturer between 1902 and 1934 in Syracuse, New York. Herbert H. Franklin, the founder, began his career in the metal die casting business before establishing his automobile enterprise. Controlled by Herbert H. Franklin it had very few other significant shareholders. Franklin bought its vehicles from the H. H. Franklin Manufacturing Company which was only moderately profitable and frequently missed dividends on common stock. The two major characteristics of their automobiles were their air-cooled engines and in the early years their lightness and responsiveness when compared with other luxury cars. The Franklin companies suffered financial collapse in April 1934. Aside from his consequent retirement CEO Herbert Franklin's lifestyle was unaffected. Franklin innovations All Franklin cars were air-cooled, which the company considered simpler and more reliable than water cooling, and the company considered light weight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Straight-four Engine
A straight-four engine (also referred to as an inline-four engine) is a four-cylinder Reciprocating engine, piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft. The majority of automotive four-cylinder engines use a straight-four layout (with the exceptions of the flat-four engines produced by Subaru and Porsche) and the layout is also very common in motorcycles and other machinery. Therefore the term "four-cylinder engine" is usually synonymous with straight-four engines. When a straight-four engine is installed at an inclined angle (instead of with the cylinders oriented vertically), it is sometimes called a Slant-4 engine, slant-four. Between 2005 and 2008, the proportion of new vehicles sold in the United States with four-cylinder engines rose from 30% to 47%. By the 2020 model year, the share for light-duty vehicles had risen to 59%. Design A four-stroke straight-four engine always has a cylinder on its power stroke, unlike engines with fewer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flat Engine
A flat engine is a piston engine where the cylinders are located on either side of a central crankshaft. Flat engines are also known as horizontally opposed engines, however this is distinct from the less common opposed-piston engine design, whereby each cylinder has two pistons sharing a central combustion chamber. The most common configuration of flat engines is the boxer engine configuration, in which the pistons of each opposed pair of cylinders move inwards and outwards at the same time. The other configuration is effectively a V engine with a 180-degree angle between the cylinder banks: in this configuration each pair of cylinders shares a single crankpin, so that as one piston moves inward, the other moves outward. The first flat engine (Benz Contramotor) was built in 1897 by Karl Benz. Flat engines have been used in aviation, motorcycle and automobile applications. They are now less common in cars than straight engines (for engines with fewer than six cylinders) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |