|
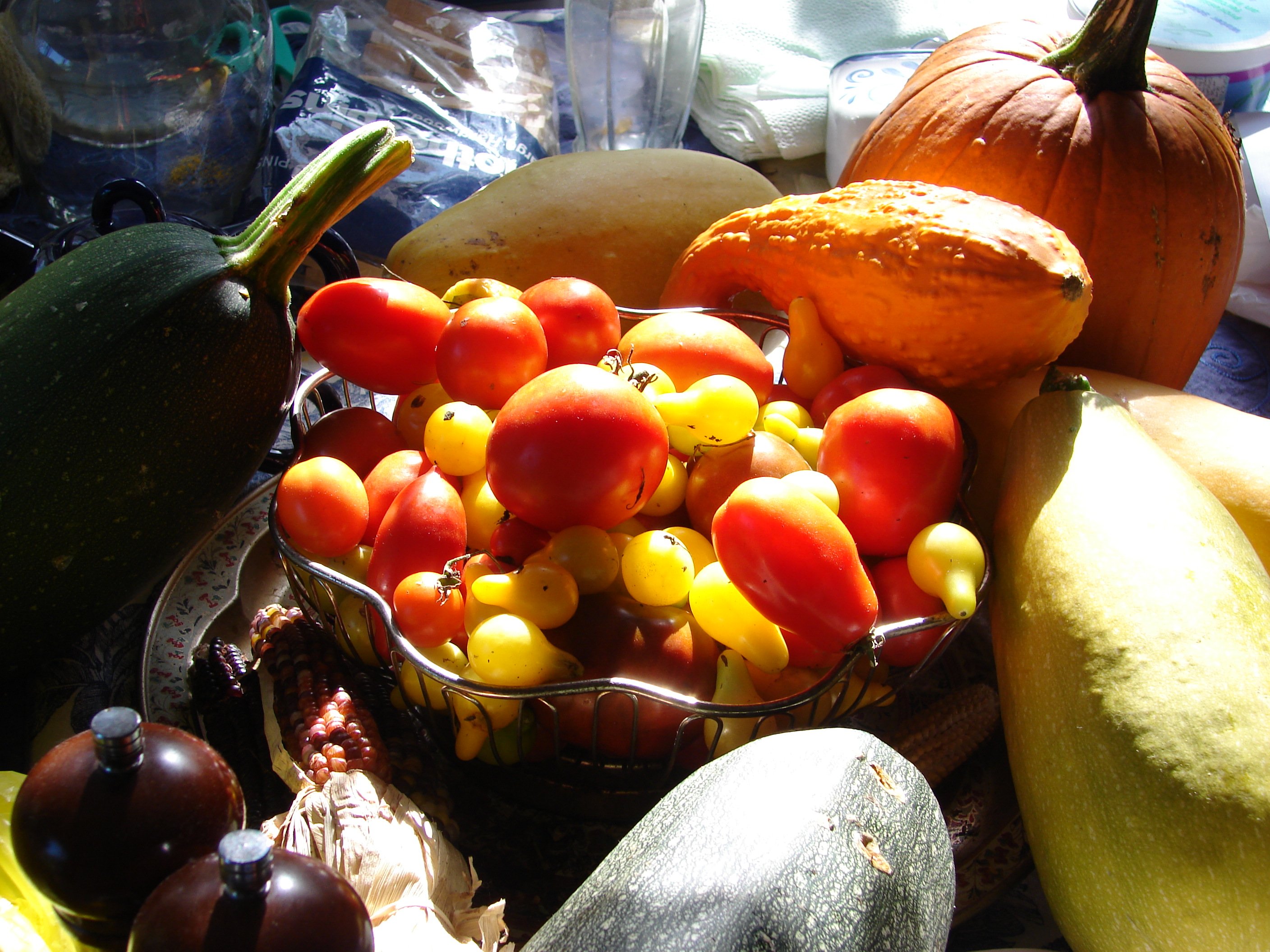
Agriculture In Uganda
Uganda's favorable soil, soil conditions and climate have contributed to the country's agriculture, agricultural success. Most areas of Uganda have usually received plenty of rain. In some years, small areas of the southeast and southwest have averaged more than 150 millimeters per month. In the north, there is often a short dry season in December and January. Temperatures vary only a few degrees above or below 20 °C but are moderated by differences in altitude. These conditions have allowed continuous cultivation in the south but only annual cropping in the north, and the driest northeastern corner of the country has supported only pastoralism. Although population growth has created pressure for land in a few areas, land shortages have been rare, and only about one-third of the estimated area of arable land was under cultivation by 1989.Uganda cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uganda
Uganda, officially the Republic of Uganda, is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the south by Tanzania. The southern part includes a substantial portion of Lake Victoria, shared with Kenya and Tanzania. Uganda is in the African Great Lakes region, lies within the Nile basin, and has a varied equatorial climate. , it has a population of 49.3 million, of whom 8.5 million live in the capital and largest city, Kampala. Uganda is named after the Buganda, Buganda kingdom, which encompasses a large portion of the south, including Kampala, and whose language Luganda is widely spoken; the official language is English. The region was populated by various ethnic groups, before Bantu and Nilotic groups arrived around 3,000 years ago. These groups established influential kingdoms such as the Empire of Kitara. The arrival of Arab trade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uganda Under Idi Amin
The Second Republic of Uganda existed from 1971 to 1979, when Uganda was ruled by Idi Amin's military dictatorship. Amin's rule formally came to an end with the Uganda-Tanzania War, which ended with Tanzania occupying Uganda and Amin fleeing into exile. The Economy of Uganda, Ugandan economy was devastated by Idi Amin's policies, including the Expulsion of Asians from Uganda, expulsion of Asians, the nationalisation of businesses and industry, and the expansion of the public sector. The real value of salaries and wages collapsed by 90% in less than a decade. The number of people killed as a result of his regime is unknown; estimates from international observers and human rights groups range from 100,000 to 500,000. Taking power From Protectorate of Uganda, Uganda's independence from Great Britain in 1962 to early 1971, Milton Obote's regime had terrorized, harassed, and tortured people. Frequent food shortages led to food prices experiencing hyper-inflation, with one contributi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassava
''Manihot esculenta'', common name, commonly called cassava, manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America, from Brazil, Paraguay and parts of the Andes. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively cultivated in tropical and subtropical regions as an annual crop for its edible starchy tuberous root. Cassava is predominantly consumed in boiled form, but substantial quantities are processed to extract cassava starch, called tapioca, which is used for food, animal feed, and industrial purposes. The Brazilian , and the related ''garri'' of West Africa, is an edible coarse flour obtained by grating cassava roots, pressing moisture off the obtained grated pulp, and finally drying it (and roasting in the case of both and ''garri''). Cassava is the third-largest source of carbohydrates in food in the tropics, after rice and maize, making it an important staple food, staple; more than 500 million pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooking Banana
Cooking bananas are a group of banana cultivars in the genus ''Musa (genus), Musa'' whose fruits are generally used in cooking. They are not eaten raw and are generally starchy. Many cooking bananas are referred to as plantains or 'green bananas'. In botanical usage, the term "plantain" is used only for true plantains, while other starchy cultivars used for cooking are called "cooking bananas". True plantains are cooking cultivars belonging to the AAB group, while cooking bananas are any cooking cultivar belonging to the List of banana cultivars, AAB, AAA, ABB, or BBB groups. The currently accepted scientific name for all such cultivars in these groups is Musa × paradisiaca, ''Musa'' × ''paradisiaca''. Fe'i bananas (''Musa'' × ''troglodytarum'') from the Pacific Islands are often eaten roasted or boiled, and are thus informally referred to as "mountain plantains", but they do not belong to any of the species from which all modern banana cultivars are descended. Cooking bananas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fibrous stalks that are rich in sucrose, which accumulates in the Plant stem, stalk internodes. Sugarcanes belong to the grass family, Poaceae, an economically important flowering plant family that includes maize, wheat, rice, and sorghum, and many forage crops. It is native to New Guinea. Sugarcane was an ancient crop of the Austronesian people, Austronesian and Indigenous people of New Guinea, Papuan people. The best evidence available today points to the New Guinea area as the site of the original domestication of ''Saccharum officinarum''. It was introduced to Polynesia, Island Melanesia, and Madagascar in prehistoric times via Austronesian sailors. It was also introduced by Austronesian sailors to India and then to Southern China by 500 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NO TILL
No-till farming (also known as zero tillage or direct drilling) is an agricultural technique for growing crops or pasture without disturbing the soil through tillage. No-till farming decreases the amount of soil erosion tillage causes in certain soils, especially in sandy and dry soils on sloping terrain. Other possible benefits include an increase in the amount of water that infiltrates the soil, soil retention of organic matter, and nutrient cycling. These methods may increase the amount and variety of life in and on the soil. While conventional no-tillage systems use herbicides to control weeds, organic systems use a combination of strategies, such as planting cover crops as mulch to suppress weeds. There are three basic methods of no-till farming. "Sod seeding" is when crops are sown with seeding machinery into a sod produced by applying herbicides on a cover crop (killing that vegetation). "Direct seeding" is when crops are sown through the residue of previous crop. " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulping Coffee Mbale
Pulp is a fibrous lignocellulosic material prepared by chemically, semi-chemically, or mechanically isolating the cellulosic fibers of wood, fiber crops, waste paper, or rags. Mixed with water and other chemicals or plant-based additives, pulp is the major raw material used in papermaking and the industrial production of other paper products. History Before the widely acknowledged invention of papermaking by Cai Lun in China around AD 105, paper-like writing materials such as papyrus and amate were produced by ancient civilizations using plant materials which were largely unprocessed. Strips of bark or bast material were woven together, beaten into rough sheets, dried, and polished by hand. Pulp used in modern and traditional papermaking is distinguished by the process which produces a finer, more regular slurry of cellulose fibers which are pulled out of solution by a screen and dried to form sheets or rolls. The earliest paper produced in China consisted of bast fibers fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants (angiosperms) that is formed from the ovary after flowering. Fruits are the means by which angiosperms disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particular have long propagated using the movements of humans and other animals in a symbiotic relationship that is the means for seed dispersal for the one group and nutrition for the other; humans, and many other animals, have become dependent on fruits as a source of food. Consequently, fruits account for a substantial fraction of the world's agricultural output, and some (such as the apple and the pomegranate) have acquired extensive cultural and symbolic meanings. In common language and culinary usage, ''fruit'' normally means the seed-associated fleshy structures (or produce) of plants that typically are sweet (or sour) and edible in the raw state, such as apples, bananas, grapes, lemons, oranges, and strawberries. In botanical usage, the term ''fruit'' als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sesame Seeds
Sesame (; ''Sesamum indicum'') is a plant in the genus ''Sesamum'', also called benne. Numerous wild relatives occur in Africa and a smaller number in India. It is widely naturalized in tropical regions around the world and is cultivated for its edible seeds, which grow in pods. World production in 2018 was , with Sudan, Myanmar, and India as the largest producers. Sesame seed is one of the oldest oilseed crops known, domesticated well over 3,000 years ago. ''Sesamum'' has many other species, most being wild and native to sub-Saharan Africa. ''S. indicum,'' the cultivated type, originated in India. It tolerates drought conditions well, growing where other crops fail. Sesame has one of the highest oil contents of any seed. With a rich, nutty flavor, it is a common ingredient in cuisines around the world. Like other foods, it can trigger allergic reactions in some people and is one of the nine most common allergens outlined by the Food and Drug Administration. Etymology The wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soybeans
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean. Soy is a staple crop, the world's most grown legume, and an important animal feed. Soy is a key source of food, useful both for its protein and oil content. Soybean oil is widely used in cooking, as well as in industry. Traditional unfermented food uses of soybeans include edamame, as well as soy milk, from which tofu and tofu skin are made. Fermented soy foods include soy sauce, fermented bean paste, nattō, and tempeh. Fat-free (defatted) soybean meal is a significant and cheap source of protein for animal feeds and many TV dinner, packaged meals. For example, soybean products, such as textured vegetable protein (TVP), are ingredients in many meat and dairy substitutes. Soy based foods are traditionally associated with East Asian cuisines, and still constitute a major part of East Asian diets, but processed soy products are increasingly used i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrotyloma Geocarpum
''Macrotyloma geocarpum'' is also known as the ground bean, geocarpa groundnut, Hausa groundnut, or Kersting's groundnut. In French, it is often called ''la lentille de terre''. ''M. geocarpum'' is an herbaceous annual plant and a crop of minor economic importance in sub-Saharan Africa, tolerant of drought, with a growth habit similar to that of the peanut. ''M. geocarpum'' is a pulse belonging to the legume family. It is primarily produced in western Africa, specifically in Benin and surrounding regions. It can provide nutrition, income, and the ability to alleviate hunger given the further production and enhancement of current practices. Yields reach in dry seed.Plant resources of tropical Africa. Cereals and pulses. Plant resources of tropical Africa (PROTA). Backhuys Publishers. Eds. Brink, Grubben, etc. 2006. p. 100. Cites Leung, Busson & Jardin 1968. Early 20th century, West Africa Following the construction of the Nigerian railway system, which extended from Lagos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beans
A bean is the seed of some plants in the legume family (Fabaceae) used as a vegetable for human consumption or animal feed. The seeds are often preserved through drying (a ''pulse''), but fresh beans are also sold. Dried beans are traditionally soaked and boiled, and used in many traditional dishes throughout the world. They can be cooked in many different ways, however, including frying and baking. The unripe seedpods of some varieties are also eaten whole as green beans or ''edamame'' (immature soybean), but many fully ripened beans contain toxins like Phytohaemagglutinin, phytohemagglutinin and require cooking. Terminology The word "bean" and its Germanic cognates (e.g. German language, German ''wikt:Bohne#Noun, Bohne'') have existed in common use in West Germanic languages since before the 12th century, referring to Vicia faba, broad beans, chickpeas, and other pod-borne seeds. This was long before the New World genus ''Phaseolus'' was known in Europe. With the Colum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |