|
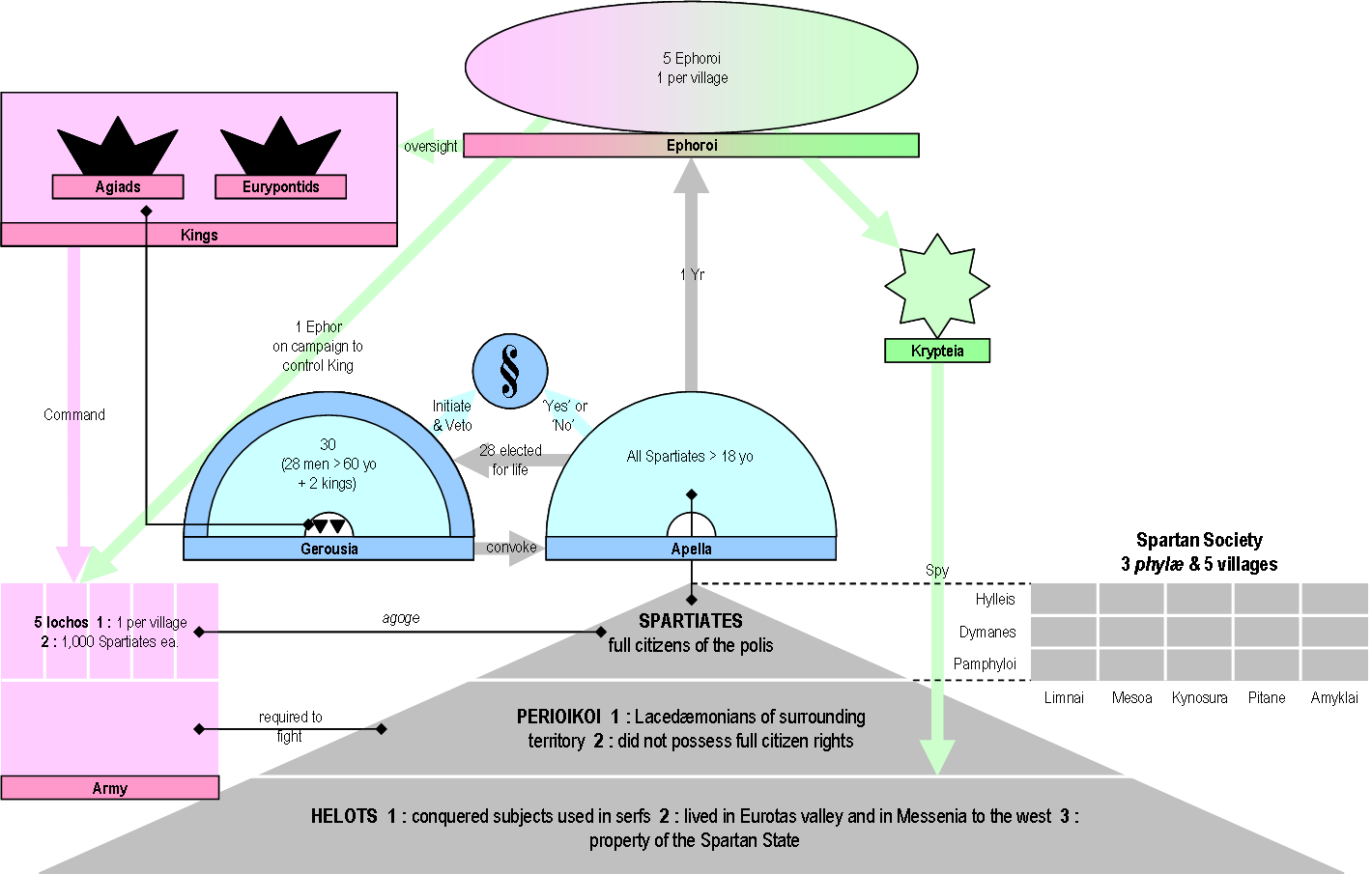
Agiad Kings Of Sparta
The Agiad dynasty (, ''Agiádai'') was one of the two List of kings of Sparta, royal families of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek Polis, city-state of Sparta. They Diarchy, ruled jointly along with the List of kings of Sparta#Eurypontid dynasty, Eurypontid dynasty, possibly from the 8th century BC onwards, being the senior of the two houses. The hypothetical founder of the dynasty was Agis I, possibly the first king of Sparta at the end of the 10th century BC, who subsequently gave his name to the dynasty. The two lines, who maintained an enduring rivalry, were, according to tradition, respectively descended from the twins Eurysthenes and Procles, both Heracleidae, descendants of Heracles. The most famous member of the Agiad dynasty was Leonidas I, known for his heroic death at the Battle of Thermopylae in 480 BC. The last Agiad king was Agesipolis III, deposed by the Eurypontid Lycurgus (king of Sparta), Lycurgus in 215 BC. History In order to explain the peculiarity of the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurypon
Eurypon, otherwise called Eurytion (), son of Soos and grandson of Procles, was the third king of that house at Sparta, and thenceforward gave it the name of Eurypontidae. Plutarch talks of his having relaxed the kingly power, and played the demagogue; and Polyaenus relates a war with the Arcadians of Mantineia under his command.Polyaen. ii. 13. He was succeeded by his son Prytanis, the father of Polydectes, in turn father of Eunomus (father of Charilaus) and Lycurgus Lycurgus (; ) was the legendary lawgiver of Sparta, credited with the formation of its (), involving political, economic, and social reforms to produce a military-oriented Spartan society in accordance with the Delphic oracle. The Spartans i .... Notes References * {{Kings of Sparta Eurypontid kings of Sparta 9th-century BC Greek people 9th-century BC monarchs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pythia
Pythia (; ) was the title of the high priestess of the Temple of Apollo (Delphi), Temple of Apollo at Delphi. She specifically served as its oracle and was known as the Oracle of Delphi. Her title was also historically glossed in English as the Pythoness. The Pythia was established at the latest in the 8th century BC (though some estimates date the shrine to as early as 1400 BC), and was widely credited for her prophecy, prophecies uttered under divine possession (enthusiasmos) by Apollo. The Pythian priestess emerged pre-eminent by the end of the 7th century BC and continued to be consulted until the late 4th century AD. During this period, the Delphic Oracle was the most prestigious and authoritative oracle among the Greeks, and she was among the most powerful women of the classical world. The oracle is one of the best-documented religious institutions of the classical Greeks. Authors who mention the oracle include Aeschylus, Aristotle, Clement of Alexandria, Diodorus, Diogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amyclae
Amyclae or Amyklai () was a city of ancient Laconia, situated on the right or western bank of the Eurotas, 20 stadia south of Sparta, in a district remarkable for the abundance of its trees and its fertility. Amyclae was one of the most celebrated cities of Peloponnesus in the Greek Heroic Age. It is said to have been founded by the Lacedaemonian king Amyclas, the father of Hyacinthus, and to have been the abode of Tyndarus, and of Castor and Pollux, who are hence called ''Amyclaei Fratres''. Amyclae is mentioned by Homer, and it continued to maintain its independence as an Achaean town long after the conquest of Peloponnesus by the Dorians. Conquest by Sparta According to the common tradition, which represented the conquest of Peloponnesus as effected in one generation by the descendants of Heracles, Amyclae was given by the Dorians to Philonomus, as a reward for his having betrayed to them his native city Sparta. Philonomus is further said to have peopled the town w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cynosura (Laconia)
Cynosura or Kynosoura () was a settlement that existed before the Dorian conquest. It was united with three other such settlements ( Pitane, Limnae, and Mesoa) by a common sacrifice to Artemis, and eventually coalesced into ancient Sparta Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement in the valley of Evrotas river in Laconia, in southeastern Pe .... It is probable that Cynosura was in the southwest part of the city. Its site is unlocated. References Populated places in ancient Laconia Former populated places in Greece Lost ancient cities and towns Sparta {{AncientLaconia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limnae (Sparta)
Limnae or Limnai () was a settlement that existed before the Dorian conquest. It was united with three other such settlements ( Mesoa, Pitane, and Cynosura) by a common sacrifice to Artemis, and eventually coalesced into ancient Sparta. Limnae was situated upon the Eurotas In Greek mythology, Eurotas (; Ancient Greek: Εὐρώτας) was a king of Laconia. Family Eurotas was the son of King Myles of Laconia and grandson of Lelex, eponymous ancestor of the Leleges. The ''Bibliotheca (Pseudo-Apollodorus), Bibliothe ..., having derived its name from the marshy ground which once existed there; and as the Dromus occupied a great part of the lower level towards the southern extremity, it is probable that Limnae occupied the northern. Its site is unlocated. References Populated places in ancient Laconia Former populated places in Greece Lost ancient cities and towns Sparta {{AncientLaconia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoa
Mesoa (), or Messoa (Μεσσόα), was a settlement that existed before the Dorian conquest. It was united with three other such settlements ( Pitane, Limnae, and Cynosura) by a common sacrifice to Artemis, and eventually coalesced into ancient Sparta Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement in the valley of Evrotas river in Laconia, in southeastern Pe .... It is probable that Mesoa was in the southeast part of the city. Its site is unlocated. References Populated places in ancient Laconia Former populated places in Greece Lost ancient cities and towns Sparta {{AncientLaconia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitane (Laconia)
Pitane (), or Pitana (Πιτάνα), was a settlement that existed before the Dorian conquest. It was united with three other such settlements ( Mesoa, Limnae, and Cynosura) by a common sacrifice to Artemis, and eventually coalesced into ancient Sparta. Pitane is called a polis by Euripides, and is also mentioned as a place by Pindar. Herodotus, who had been there, calls it a deme. He also mentions a λόχος Πιτανάτης ("company of Pitane"); and Caracalla, in imitation of antiquity, composed a λόχος Πιτανάτης of Spartans. Thucydides claims that the "λόχος Πιτανάτης" cited by Herodotus never actually existed, and cites the story as an example of baseless hearsay propagated by "other Hellenes." It appears from the passage of Pindar quoted above, that Pitane was at the ford of the Eurotas, and consequently in the northern part of the city. It was the favourite and fashionable place of residence at Sparta, like Collytus at ancient Athens and Cra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synoecism
Synoecism or synecism ( ; , ''sunoikismos'', ), also spelled synoikism ( ), was originally the amalgamation of villages in Ancient Greece into ''poleis'', or city-states. Etymologically, the word means "dwelling together (''syn'') in the same house (''oikos'')." Subsequently, any act of civic union between polities of any size was described by the word ''synoikismos'', in addition to the Latinized synoecism. Synoecism is opposed to Greek dioecism (διοικισμóς, ''dioikismos''), the creation of independent communities within the territory of a polis. Synoecism is the result of a few major factors, mainly an increase in population density of adjacent settlements, with an incorporation proposed for economic, political or ideological advantages, such as the synoecism of the communities of Attica into Athens, or by imposition of a ruling power, such as the synoecism of Messenia into the newly built city of Messene. Additionally, synoecism may be the result of less active forc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charilaus
Charilaus (), also spelled Charilaos, Charillos, or Charillus, was a king of Sparta in the middle of the 8th century BC. He was probably the first historical king of the Eurypontid dynasty. Life and reign Sparta was a diarchy, with two kings of equal powers from distinct dynasties. However, in its earliest history, Sparta was likely ruled by only one king, from the Agiad dynasty. In the 8th century, a synoecism occurred on the site of Sparta, where four villages merged to create the polis of Sparta. At this occasion, two of the villages ( Limnai and Kynosoura) probably requested to also have a king from their territory sharing power with the Agiad one, who was based in the other two villages ( Pitana and Mesoa). In later times, the Spartans crafted a mythical story making the second dynasty—the Eurypontids—as old as the Agiads, notably by inventing several kings to make the two dynasties symmetrical. Modern scholars consider instead that Charilaus was the first historica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archelaus Of Sparta
Archelaus (, ''Ἀrkhélaos''; reigned from c. 790 to c. 760 BC) was the 7th Agiad dynasty king of Sparta. He was a son of Agesilaus I. Together with Charilaus, he conquered Elis. During his reign he also conquered the city of Aegys and sold the inhabitants into slavery. He was succeeded as king by his son, Teleclus Teleclus or Teleklos (Greek: Τήλεκλος) was the 8th Agiad dynasty king of Sparta during the eighth century BC. He was the son of King Archelaus and grandson of King Agesilaus I. Pausanias reports that Teleclus' reign saw the conquest of .... References 8th-century BC monarchs 8th-century BC Spartans Agiad kings of Sparta {{AncientGreece-royal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lycurgus (lawgiver)
Lycurgus (; ) was the legendary lawgiver of Sparta, credited with the formation of its (), involving political, economic, and social reforms to produce a military-oriented Spartan society in accordance with the Delphic oracle. The Spartans in the historical period honoured him as a god. As a historical figure, almost nothing is known for certain about him, including when he lived and what he did in life. The stories of him place him at multiple times. Nor is it clear when the political reforms attributed to him, called the Great Rhetra, occurred. Ancient dates range from – putting aside the implausibly early Xenophonic 11th century BC – the early ninth century () to as late as early eighth century (). There remains no consensus as to when he lived; some modern scholars deny that he existed at all. The reforms at various times attributed to him touch all aspects of Spartan society. They included the creation of the Spartan constitution (in most traditions a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |