|
Abderites
Abderites or Abderite may refer to: *People associated with the ancient city of Abdera, Thrace *Adherents of the philosophical school of Abdera *Abderite, a reference to Democritus Democritus (, ; , ''Dēmókritos'', meaning "chosen of the people"; – ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Pre-Socratic philosophy, pre-Socratic philosopher from Abdera, Thrace, Abdera, primarily remembered today for his formulation of an ..., native of Abdera; later acquired the generic meaning of "scoffer" *Abderites, archetypical fools in classical Greece, akin of the Wise Men of Gotham *The satirical book ''Die Abderiten, eine sehr wahrscheinliche Geschichte'' by Christoph Martin Wieland * ''Abderites'' (mammal), a genus of Paucituberculata from South America {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Democritus
Democritus (, ; , ''Dēmókritos'', meaning "chosen of the people"; – ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Pre-Socratic philosophy, pre-Socratic philosopher from Abdera, Thrace, Abdera, primarily remembered today for his formulation of an atomism, atomic theory of the universe. Democritus wrote extensively on a wide variety of topics. None of Democritus' original work has survived, except through second-hand references. Many of these references come from Aristotle, who viewed him as an important rival in the field of natural philosophy. He was known in antiquity as the ‘laughing philosopher’ because of his emphasis on the value of cheerfulness. Life Although many anecdotes about Democritus' life survive, their authenticity cannot be verified and modern scholars doubt their accuracy. According to Aristotle, Democritus was born in Abdera, on the coast of Thrace. He was a polymath and prolific writer, producing nearly eighty treatises on subjects such as poetry, harmon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christoph Martin Wieland
Christoph Martin Wieland (; ; 5 September 1733 – 20 January 1813) was a German poet and writer, representative of literary Rococo. He is best-remembered for having written the first ''Bildungsroman'' (''Geschichte des Agathon''), as well as the epic '' Oberon'', which formed the basis for both Friederike Sophie Seyler's opera of the same name and Carl Maria von Weber's opera of the same name. His thought was representative of the cosmopolitanism of the German Enlightenment, exemplified in his remark: "Only a true cosmopolitan can be a good citizen." He was a key figure of Weimar Classicism and a collaborator of Abel Seyler's theatre company. Biography Christoph Martin Wieland was born in Oberholzheim (now part of Achstetten), half of which then belonged to the Free Imperial City of Biberach an der Riss and the other half to Gutenzell Abbey in the south-east of the modern-day state of Baden-Württemberg. His father, who was pastor in Oberholzheim and subsequently i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
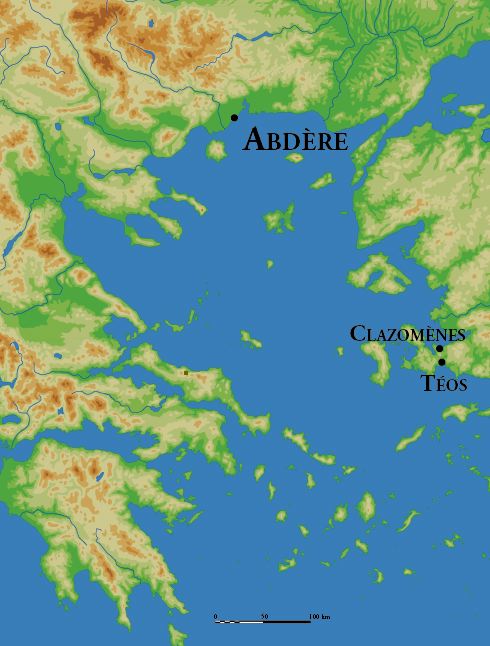
Abdera, Thrace
Abdera () is a municipality in the Xanthi regional unit of Thrace, Greece. In classical antiquity, it was a major Greek ''polis'' on the Thracian coast. The ancient polis is to be distinguished from the municipality, which was named in its honor. The polis lay 17 km east-northeast of the mouth of the Nestos River, almost directly opposite the island of Thasos. It was a colony placed in previously unsettled Thracian territory, not then a part of Hellas, during the age of Greek colonization. The city that developed from it became of major importance in ancient Greece. After the 4th centuryAD it declined, contracted to its acropolis, and was abandoned, never to be reoccupied except by archaeologists. During the Early Middle Ages, a new settlement emerged near the ancient city. It was called Polystylon (), and later considered as the New Abdera (). In 2011 the modern municipality of Abdera was synoecized from three previous municipalities comprising a number of modern settl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
School Of Abdera
Atomism () is a natural philosophy proposing that the physical universe is composed of fundamental indivisible components known as atoms. References to the concept of atomism and its atoms appeared in both ancient Greek and ancient Indian philosophical traditions. Leucippus is the earliest figure whose commitment to atomism is well attested and he is usually credited with inventing atomism. He and other ancient Greek atomists theorized that nature consists of two fundamental principles: ''atom'' and ''void''. Clusters of different shapes, arrangements, and positions give rise to the various macroscopic substances in the world.Berryman, Sylvia, "Ancient Atomism", ''The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' (Fall 2008 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.)online/ref> Indian Buddhists, such as Dharmakirti ( 6th or 7th century) and others, developed distinctive theories of atomism, for example, involving momentary (instantaneous) atoms ( ''kalapa''s) that flash in and out of existence. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wise Men Of Gotham
Wise Men of Gotham is the early name given to the people of the village of Gotham, Nottinghamshire, in allusion to an incident where they supposedly feigned idiocy to avoid a Royal visit. Legend The story goes that John of England, King John intended to travel through the neighbourhood. At that time in England, any road the king travelled on had to be made a public highway, but the people of Gotham did not want a public highway through their village. The villagers feigned imbecility when the royal messengers arrived. Wherever the messengers went, they saw the rustics engaged in some absurd task. Based on this report, John determined to have his hunting lodge elsewhere, and the wise men boasted, "We ween there are more fools pass through Gotham than remain in it."G. Seal, ''Encyclopedia of folk heroes'' (ABC-CLIO, 2001), pp. 272–3 According to the 1874 edition of Blount's ''Tenures of Land'', King John's messengers "found some of the inhabitants engaged in endeavouring to drown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |