|
1990 In Science
The year 1990 in science and technology involved some significant events. Astronomy and space exploration * January 24 – Japan launches the Hiten spacecraft, the first lunar probe launched by a country other than the Soviet Union or the United States. * February 14 – The '' Pale Blue Dot'' photograph of Earth is sent back from the ''Voyager 1'' probe after completing its primary mission, from around 3.5 billion miles away. * April 24 – The Space Shuttle ''Discovery'' places the Hubble Space Telescope into orbit. * August 16 – Steven Balbus makes his first discovery leading to elucidation of magnetorotational instability. * October 13 – Earth-grazing meteoroid of 13 October 1990: A 44 kilogram, 41.5 km/s meteoroid passes above Czechoslovakia and Poland at 97.9 km. It is the first time calculations of the orbit of such a body based on photographic records from two distant places is made. Biology * The term "rewilding" is first used in print. Computer scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Victor Kolyvagin
Victor Alexandrovich Kolyvagin (, born 11 March, 1955) is a Russian mathematician who wrote a series of papers on Euler systems, leading to breakthroughs on the Birch and Swinnerton-Dyer conjecture, and Iwasawa's conjecture for cyclotomic fields. His work also influenced Andrew Wiles's work on Fermat's Last Theorem. Career Kolyvagin received his Ph.D. in Mathematics in 1981 from Moscow State University, where his advisor was Yuri I. Manin. He then worked at Steklov Institute of Mathematics in Moscow until 1994. Since 1994 he has been a professor of mathematics in the United States The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 .... He was a professor at Johns Hopkins University until 2002 when he became the first person to hold the Mina Rees Chair in mathematics at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Numerical Integration
In analysis, numerical integration comprises a broad family of algorithms for calculating the numerical value of a definite integral. The term numerical quadrature (often abbreviated to quadrature) is more or less a synonym for "numerical integration", especially as applied to one-dimensional integrals. Some authors refer to numerical integration over more than one dimension as cubature; others take "quadrature" to include higher-dimensional integration. The basic problem in numerical integration is to compute an approximate solution to a definite integral :\int_a^b f(x) \, dx to a given degree of accuracy. If is a smooth function integrated over a small number of dimensions, and the domain of integration is bounded, there are many methods for approximating the integral to the desired precision. Numerical integration has roots in the geometrical problem of finding a square with the same area as a given plane figure ('' quadrature'' or ''squaring''), as in the quadrature of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
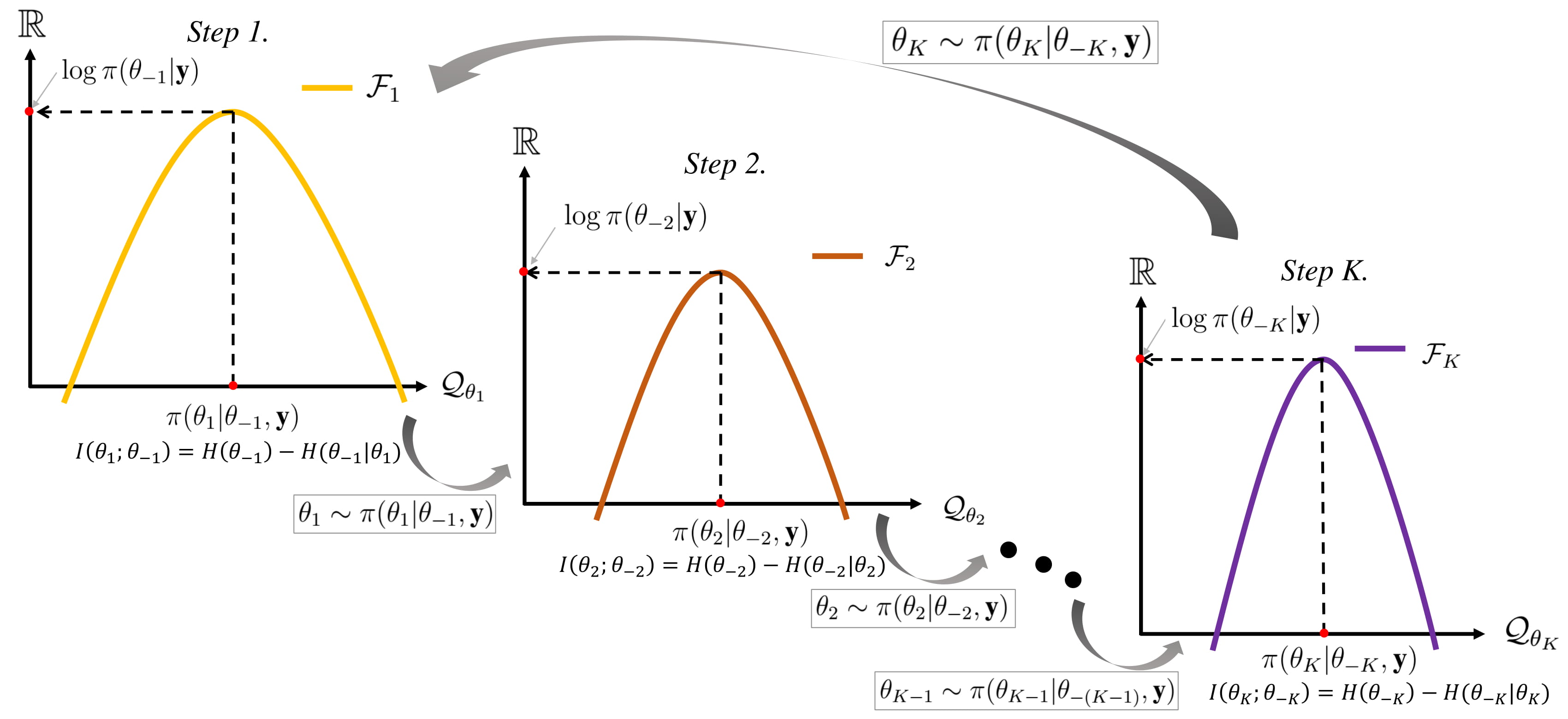 |
Gibbs Sampler
In statistics, Gibbs sampling or a Gibbs sampler is a Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) algorithm for sampling from a specified multivariate probability distribution when direct sampling from the joint distribution is difficult, but sampling from the conditional distribution is more practical. This sequence can be used to approximate the joint distribution (e.g., to generate a histogram of the distribution); to approximate the marginal distribution of one of the variables, or some subset of the variables (for example, the unknown parameters or latent variables); or to compute an integral (such as the expected value of one of the variables). Typically, some of the variables correspond to observations whose values are known, and hence do not need to be sampled. Gibbs sampling is commonly used as a means of statistical inference, especially Bayesian inference. It is a randomized algorithm (i.e. an algorithm that makes use of random number generation, random numbers), and is an alte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |