|
1920 In Science
The year 1920 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below. Astronomy and space science * January 13 – ''The New York Times'' ridicules rocket scientist Robert H. Goddard, stating that spaceflight is impossible. In 1969, with Apollo 11 on its way to the Moon, the newspaper will publicly retract this position. * December 13 – The red giant star Betelgeuse is the first to have its diameter determined by an optical astronomical interferometer, the Michelson stellar interferometer on Mount Wilson Observatory's reflector telescope. Biology * Andrew Douglass proposes dendrochronology dating. * Approximate date – The HIV pandemic almost certainly originates in Léopoldville, modern-day Kinshasa, the capital of the Belgian Congo. Chemistry * July 15 – F. W. Aston shows that the molar mass of chlorine (35.45) is a weighted average of the almost integral masses for the two isotopes 35Cl and 37Cl. History of science and technology * September 10 – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Oxford
The University of Oxford is a collegiate university, collegiate research university in Oxford, England. There is evidence of teaching as early as 1096, making it the oldest university in the English-speaking world and the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, second-oldest continuously operating university globally. It expanded rapidly from 1167, when Henry II of England, Henry II prohibited English students from attending the University of Paris. When disputes erupted between students and the Oxford townspeople, some Oxford academics fled northeast to Cambridge, where they established the University of Cambridge in 1209. The two English Ancient university, ancient universities share many common features and are jointly referred to as ''Oxbridge''. The University of Oxford comprises 43 constituent colleges, consisting of 36 Colleges of the University of Oxford, semi-autonomous colleges, four permanent private halls and three societies (colleges that are depar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narcotic
The term narcotic (, from ancient Greek ναρκῶ ''narkō'', "I make numb") originally referred medically to any psychoactive compound with numbing or paralyzing properties. In the United States, it has since become associated with opiates and opioids, commonly morphine and heroin, as well as derivatives of many of the compounds found within raw opium latex. The primary three are morphine, codeine, and thebaine (while thebaine itself is only very mildly psychoactive, it is a crucial precursor in the vast majority of semi-synthetic opioids, such as oxycodone or hydrocodone). Legally speaking, the term "narcotic" may be imprecisely defined and typically has negative connotations. When used in a legal context in the U.S., a narcotic drug is totally prohibited, such as heroin, or one that is used in violation of legal regulation (in this word sense, equal to any controlled substance or illicit drug). In the medical community, the term is more precisely defined and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrocodone
Hydrocodone, also known as dihydrocodeinone, is a semi-synthetic opioid used to treat pain and as a cough suppressant. It is taken by mouth. Typically, it is dispensed as the combination acetaminophen/hydrocodone or ibuprofen/hydrocodone for pain severe enough to require an opioid and in combination with homatropine methylbromide to relieve cough. It is also available by itself in a long-acting form sold under the brand name Zohydro ER, among others, to treat severe pain of a prolonged duration. Hydrocodone is a controlled drug: in the United States, it is classified as a Schedule II Controlled Substance. Common side effects include dizziness, sleepiness, nausea, and constipation. Serious side effects may include low blood pressure, seizures, QT prolongation, respiratory depression, and serotonin syndrome. Rapidly decreasing the dose may result in opioid withdrawal. Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding is generally not recommended. Hydrocodone is believed to work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
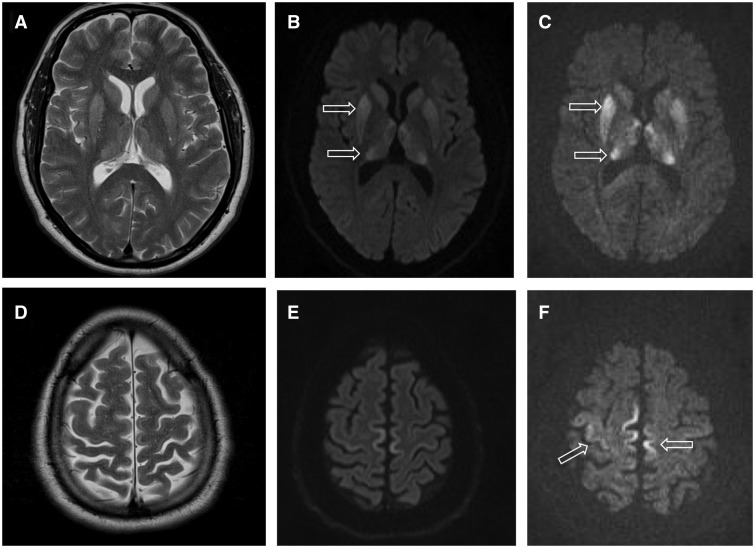
Creutzfeldt–Jakob Disease
Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (CJD) is an incurable, always fatal neurodegenerative disease belonging to the transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSE) group. Early symptoms include memory problems, behavioral changes, poor coordination, visual disturbances and auditory disturbances. Later symptoms include dementia, involuntary movements, blindness, deafness, weakness, and coma. About 70% of sufferers die within a year of diagnosis. The name "Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease" was introduced by Walther Spielmeyer in 1922, after the German neurologists Hans Gerhard Creutzfeldt and Alfons Maria Jakob. CJD is caused by abnormal folding of a protein known as a prion. Infectious prions are misfolded proteins that can cause normally folded proteins to also become misfolded. About 85% of cases of CJD occur for unknown reasons, while about 7.5% of cases are inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Exposure to brain or spinal tissue from an infected person may also result in spread. Ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Gerhard Creutzfeldt
Hans Gerhard Creutzfeldt (June 2, 1885 – December 30, 1964) was a German neurologist and neuropathologist. Although he is typically credited as the physician to first describe the Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease, this has been disputed. He was born in Harburg an der Elbe and died in Munich. Biography Creutzfeldt was born into a medical family, on June 2, 1885, at Harburg an der Elbe, Germany, which was incorporated into Hamburg in 1937. In 1903, at the age of 18, he was drafted into the German army and spent his service stationed in Kiel. Afterwards, he attended the School of Medicine of the University of Jena and the University of Rostock, receiving his doctorate at the latter in 1909. Part of his practical training was undertaken at ''St. Georg'' – Hospital in Hamburg. After qualification he sought adventure as a ship's surgeon, voyaging the Pacific Ocean, taking the opportunity to study local crafts, linguistics, and tropical plants. After returning to Germany in 1912, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Best (medical Scientist)
Charles Herbert Best (February 27, 1899 – March 31, 1978), was an American-Canadian medical scientist and one of the co-discoverers of insulin with Frederick Banting. He served as the chair of the Banting and Best Department of Medical Research at the University of Toronto and was further involved in research concerning choline and heparin. Early life Charles Herbert Best was born in Pembroke, Maine, on February 27, 1899, to Luella (Lulu) Fisher and Herbert Huestis Best, a Canadian-born physician from Nova Scotia. His father, Herbert Best, was a doctor in a small Maine town with a limited economy based mostly on sardine-packing. His mother Lulu was a soprano singer, organist, and pianist. Charles Best grew up in Pembroke before going to Toronto, Ontario, to study medicine in 1915. By the time Best had reached college age and was choosing between such schools as McGill University and the University of Toronto, family connections persuaded him to pursue his studies in Toron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of the body becoming unresponsive to insulin's effects. Classic symptoms include polydipsia (excessive thirst), polyuria (excessive urination), polyphagia (excessive hunger), weight loss, and blurred vision. If left untreated, the disease can lead to various health complications, including disorders of the cardiovascular system, eye, kidney, and nerves. Diabetes accounts for approximately 4.2 million deaths every year, with an estimated 1.5 million caused by either untreated or poorly treated diabetes. The major types of diabetes are type 1 and type 2. The most common treatment for type 1 is insulin replacement therapy (insulin injections), while anti-diabetic medications (such as metformin and semaglutide) and lifestyle modificatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and protein by promoting the absorption of glucose from the blood into cells of the liver, fat cell, fat, and skeletal muscles. In these tissues the absorbed glucose is converted into either glycogen, via glycogenesis, or Fatty acid metabolism#Glycolytic end products are used in the conversion of carbohydrates into fatty acids, fats (triglycerides), via lipogenesis; in the liver, glucose is converted into both. Glucose production and secretion by the liver are strongly inhibited by high concentrations of insulin in the blood. Circulating insulin also affects the synthesis of proteins in a wide variety of tissues. It is thus an anabolic hormone, promoting the conversion of small molecules in the blood into large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Banting
Sir Frederick Grant Banting (November 14, 1891 – February 21, 1941) was a Canadian pharmacologist, orthopedist, and field surgeon. For his co-discovery of insulin and its therapeutic potential, Banting was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine with John Macleod (physiologist), John Macleod. Banting and his student, Charles Best (medical scientist), Charles Best, isolated insulin at the University of Toronto in the lab of Scottish physiologist John Macleod. When he and Macleod received the 1923 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, Banting shared the honours and award money with Best. That same year, the government of Canada granted Banting a lifetime annuity to continue his work. Frederick Banting, who received the Nobel Prize at age 32, is the youngest Nobel laureate for Physiology/Medicine. Early life Banting was born on November 14, 1891, in his family's farmhouse in Essa, Ontario, two miles from nearby Alliston. He was the youngest of five children of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newcomen Society
The Newcomen Society is an international learned society that promotes and celebrates the history of engineering and technology. It was founded in London in 1920,The Newcomen Society. '' Journal of the Royal Society of Arts'' 72 (3709): 84 (1923) and takes its name from Thomas Newcomen, one of the inventors associated with the early development of the steam engine and who is widely considered the "father of the Industrial Revolution". An early president was Loughnan St. L. Pendred. The society is concerned with all branches of engineering: civil, mechanical, electrical, electronic, structural, aeronautical, marine, chemical and manufacturing as well as biography and invention. The Newcomen Society is based at the Science Museum in London. There are regional branches in England: Midlands (Birmingham), North West (Manchester), North East (Newcastle), Western (Bristol) and Southern (Portsmouth), South Yorkshire (Sheffield) and one in Scotland (Glasgow and Edinburgh). It pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features Peer review, peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2022 ''Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 50.5), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in the autumn of 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander MacMillan (publisher), Alexander MacMillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |