|
1733 In Great Britain
Events from the year 1733 in Great Britain. Incumbents * Monarch – George II * Prime Minister – Robert Walpole ( Whig) Events * 23 January – first performance of George Frideric Handel's opera ''Orlando'', at the His Majesty's Theatre in London. * 12 February – British colonist James Oglethorpe founds Savannah, Georgia. * 25 March – English replaces Latin and Law French as the official language of English and Scottish courts on coming into effect of the Proceedings in Courts of Justice Act 1730. * 6 April – after Prime Minister Robert Walpole's proposed excise tax bill to replace tariffs on wine and tobacco results in rioting over the imposition of additional taxes and the use of government agents to collect them, Walpole informs the House of Commons that he will withdraw the legislation. * 17 May – the Molasses Act becomes law: intended to regulate the colonial molasses trade in favour of the British West Indies, it causes resentment in British North America. * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proceedings In Courts Of Justice Act 1730
The Proceedings in Courts of Justice Act 1730 ( 4 Geo. 2 c. 26) was an Act of the Parliament of Great Britain which made English (instead of Law French and Latin) the obligatory language for use in the courts of England and in the court of exchequer in Scotland. The Act followed a medieval law from 1362 (the Pleading in English Act 1362), which had made it permissible to debate cases in English, but all written records had continued to be in Latin. The 1730 Act was amended shortly later to extend it to the courts in Wales, and to exempt from its provisions the "court of the receipt of his Majesty's exchequer" in England. It never applied to cases heard overseas in the court of admiralty. A similar act was passed on 22 November 1650 by the Rump Parliament during the Commonwealth of England: ''An Act for turning the Books of the Law and all Process and Proceedings in Courts of Justice into the English Tongue''. As with all purported Acts passed without royal assent during the rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Chancellor
The Lord Chancellor, formally titled Lord High Chancellor of Great Britain, is a senior minister of the Crown within the Government of the United Kingdom. The lord chancellor is the minister of justice for England and Wales and the highest-ranking Great Officers of State (United Kingdom), Great Officer of State in Scotland and England, nominally outranking the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, prime minister. The lord chancellor is appointed and dismissed by the British monarchy, sovereign on the advice of the prime minister. Prior to the Acts of Union 1707, union of England and Scotland into the Kingdom of Great Britain, there were separate lord chancellors for the Kingdom of England (including Wales) and the Kingdom of Scotland. Likewise, the Lordship of Ireland and its successor states (the Kingdom of Ireland and History of Ireland (1801–1923), United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland) maintained the office of Lord Chancellor of Ireland, lord chancellor of Ireland u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Wedderburn, 1st Earl Of Rosslyn
Alexander Wedderburn, 1st Earl of Rosslyn, Privy Council of the United Kingdom, PC, King's Counsel, KC (3 February 1733 – 2 January 1805) was a Scottish lawyer and politician who sat in the House of Commons between 1761 and 1780 when he was raised to the peerage as Baron Loughborough. He served as Lord Chancellor, Lord High Chancellor of Great Britain from 1793 to 1801. Life Wedderburn was the eldest son of Peter Wedderburn, Lord Chesterhall (a lord of session), and was born at Chesterhall near Dunbar in East Lothian. He received his initial education at Dalkeith and then the Royal High School (Edinburgh), Royal High School, Edinburgh, and matriculated at the University of Edinburgh aged 14. During his studies in Edinburgh he resided at his father's townhouse on Elphinstone Court, south of the Royal Mile, around 200m from the university. He qualified as an advocate serving in Scotland in 1752 aged only 19. He did not see eye to eye with others in the courts and on one occa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1834 In The United Kingdom
Events from the year 1834 in the United Kingdom. Uniquely, four Prime Ministers serve during the year. Incumbents * Monarch – William IV * Prime Minister – Charles Grey, 2nd Earl Grey ( Whig) (until 16 July); William Lamb, 2nd Viscount Melbourne ( Whig) (starting 16 July, until 14 November); Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington (Tory) (starting 14 November, until 10 December); Robert Peel (Conservative) (starting 10 December) * Foreign Secretary – Henry John Temple, 3rd Viscount Palmerston (until 14 November) Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington (starting 14 November) * Secretary of War – Edward Smith-Stanley (until 5 June) Thomas Spring Rice (5 June until 14 November) Duke of Wellington (17 November to 9 December) Lord Aberdeen (starting 20 December) Events * February – Robert Owen organises the Grand National Consolidated Trades Union. * March – William Whewell (anonymously) first publishes the term ''scientist'' in the ''Quarterly Review'' (but note ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Escurial
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between sovereign states and/or international organizations that is governed by international law. A treaty may also be known as an international agreement, protocol, covenant, convention, pact, or exchange of letters, among other terms; however, only documents that are legally binding on the parties are considered treaties under international law. Treaties may be bilateral (between two countries) or multilateral (involving more than two countries). Treaties are among the earliest manifestations of international relations; the first known example is a border agreement between the Sumerian city-states of Lagash and Umma around 3100 BC. International agreements were used in some form by most major civilizations and became increasingly common and more sophisticated during the early modern era. The early 19th century saw developments in diplomacy, foreign policy, and international law reflected by the widespread use of treat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Europe and the fourth-most populous European Union member state. Spanning across the majority of the Iberian Peninsula, its territory also includes the Canary Islands, in the Eastern Atlantic Ocean, the Balearic Islands, in the Western Mediterranean Sea, and the Autonomous communities of Spain#Autonomous cities, autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla, in mainland Africa. Peninsular Spain is bordered to the north by France, Andorra, and the Bay of Biscay; to the east and south by the Mediterranean Sea and Gibraltar; and to the west by Portugal and the Atlantic Ocean. Spain's capital and List of largest cities in Spain, largest city is Madrid, and other major List of metropolitan areas in Spain, urban areas include Barcelona, Valencia, Seville, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlantic, North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and List of islands of France, many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean, giving it Exclusive economic zone of France, one of the largest discontiguous exclusive economic zones in the world. Metropolitan France shares borders with Belgium and Luxembourg to the north; Germany to the northeast; Switzerland to the east; Italy and Monaco to the southeast; Andorra and Spain to the south; and a maritime border with the United Kingdom to the northwest. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea. Its Regions of France, eighteen integral regions—five of which are overseas—span a combined area of and hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flying Shuttle
The flying shuttle is a type of weaving shuttle. It was a pivotal advancement in the mechanisation of weaving during the initial stages of the Industrial Revolution, and facilitated the weaving of considerably broader fabrics, enabling the production of wider textiles. Moreover, its mechanical implementation paved the way for the introduction of automatic machine looms. The brainchild of John Kay, the flying shuttle received a patent in the year 1733 during the Industrial Revolution. Its implementation brought about an acceleration of the previously manual weaving process and resulted in a significant reduction in the required labour force. Formerly, a broad-cloth loom necessitated the presence of a weaver on each side, but with the advent of the flying shuttle, a solitary operator could handle the task proficiently. Prior to this breakthrough, the textile industry relied upon the coordination of four spinners to support a single weaver. The widespread adoption of the fly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Kay (flying Shuttle)
John Kay (17 June 1704 – c. 1779) was an English inventor whose most important creation was the flying shuttle, which was a key contribution to the Industrial Revolution. He is often confused with his namesake, ( John Kay's essay on the two John Kays of the Industrial Revolution). who built the first "spinning frame". Early life John Kay was born on 17 June 1704 in the Lancashire hamlet of Walmersley, just north of Bury. His yeoman farmer father, Robert, owned the "Park" estate in Walmersley, and John was born there. Robert died before John was born, leaving Park House to his eldest son. As Robert's fifth son (out of ten children), John was bequeathed £40 (at age 21) and an education until the age of 14. His mother was responsible for educating him until she remarried. Apprenticeship He apprenticed with a hand-loom reed maker, but is said to have returned home within a month claiming to have mastered the business. He designed a metal substitute for the natural reed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
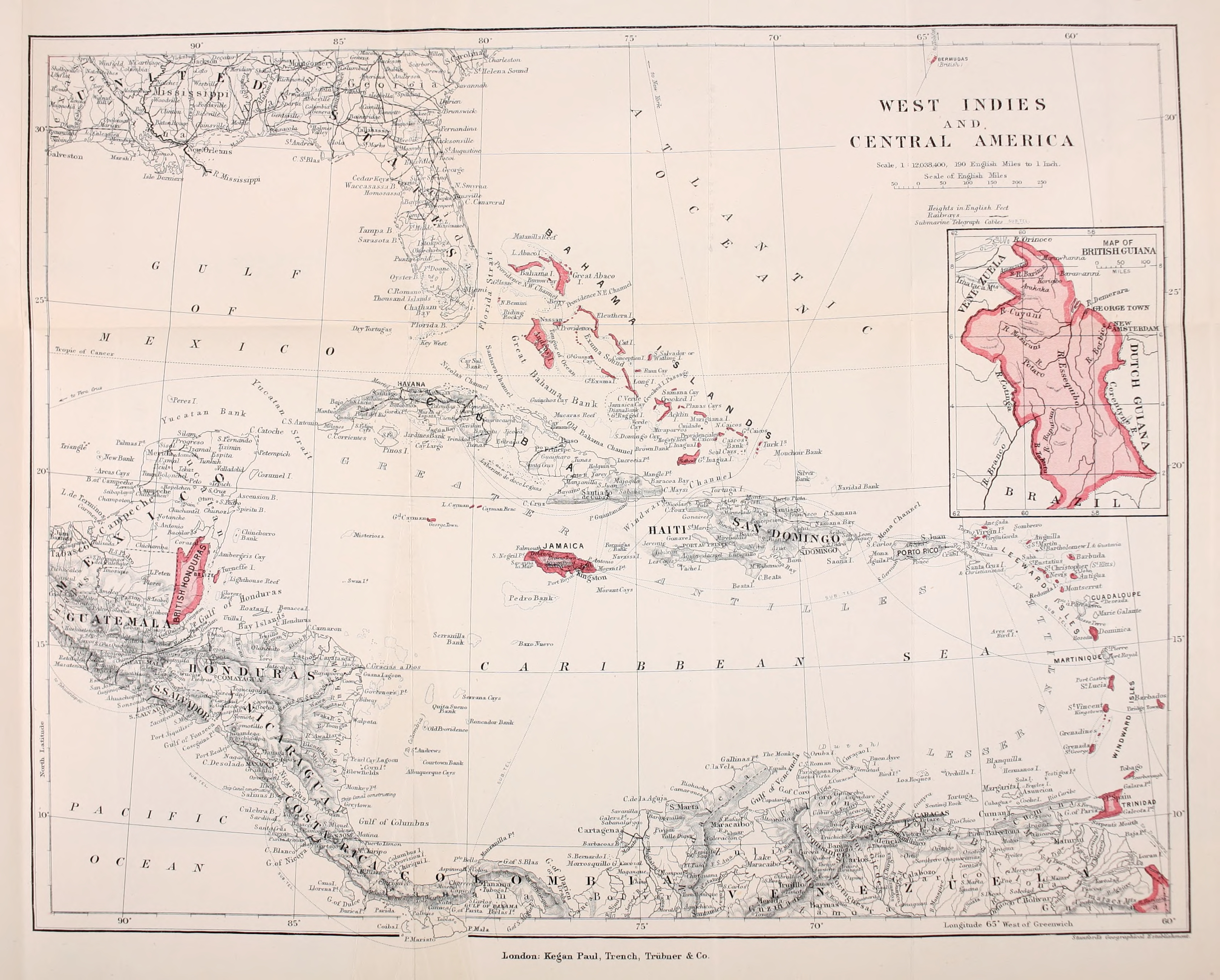
British West Indies
The British West Indies (BWI) were the territories in the West Indies under British Empire, British rule, including Anguilla, the Cayman Islands, the Turks and Caicos Islands, Montserrat, the British Virgin Islands, Bermuda, Antigua and Barbuda, the Bahamas, Barbados, Dominica, Grenada, Jamaica, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, British Honduras, British Guiana and Trinidad and Tobago. The Kingdom of England first English overseas possessions, established colonies in the region during the 17th century. Financed by valuable extractive commodities such as sugar production, the colonies were also at the centre of the Atlantic slave trade, with around 2.3 million slaves being brought to the British West Indies. The colonies also served as bases to project the power of the British Empire through the Royal Navy and Britain's Merchant Marine, and to expand and protect British overseas trade. Before the decolonization of the Americas in the later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |