|
1508 In Science
{{Science year nav, 1508 The year 1508 in science and technology included a number of events, some of which are listed here. Events * ''approx. date'' – Leonardo da Vinci completes writing the Codex Leicester. Births * December 9 – Gemma Frisius, Dutch mathematician and cartographer (died 1555). * ''approx. date'' – William Turner, English naturalist (died 1568 Year 1568 ( MDLXVIII) was a leap year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. Events January–March * January 6 – In the Eastern Hungarian Kingdom, the delegates of Unio Trium Nationum to the Diet of Torda convene i ...). Deaths 1508 16th century in science 1500s in science ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which study the physical world, and the social sciences, which study individuals and societies. While referred to as the formal sciences, the study of logic, mathematics, and theoretical computer science are typically regarded as separate because they rely on deductive reasoning instead of the scientific method as their main methodology. Meanwhile, applied sciences are disciplines that use scientific knowledge for practical purposes, such as engineering and medicine. The history of science spans the majority of the historical record, with the earliest identifiable predecessors to modern science dating to the Bronze Age in Ancient Egypt, Egypt and Mesopotamia (). Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped the Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technology
Technology is the application of Conceptual model, conceptual knowledge to achieve practical goals, especially in a reproducible way. The word ''technology'' can also mean the products resulting from such efforts, including both tangible tools such as Kitchen utensil, utensils or machines, and intangible ones such as software. Technology plays a critical role in science, engineering, and everyday life. Technological advancements have led to significant changes in society. The earliest known technology is the stone tool, used during prehistory, followed by the control of fire—which in turn contributed to the Brain size, growth of the human brain and the development of language during the Pleistocene, Ice Age, according to the cooking hypothesis. The invention of the wheel in the Bronze Age allowed greater travel and the creation of more complex machines. More recent technological inventions, including the printing press, telephone, and the Internet, have lowered barriers to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonardo Da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 1452 - 2 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially rested on his achievements as a painter, he has also become known for #Journals and notes, his notebooks, in which he made drawings and notes on a variety of subjects, including anatomy, astronomy, botany, cartography, painting, and palaeontology. Leonardo is widely regarded to have been a genius who epitomised the Renaissance humanism, Renaissance humanist ideal, and his List of works by Leonardo da Vinci, collective works comprise a contribution to later generations of artists matched only by that of his younger contemporary Michelangelo. Born out of wedlock to a successful notary and a lower-class woman in, or near, Vinci, Tuscany, Vinci, he was educated in Florence by the Italian painter and sculptor Andrea del Verrocchio. He began his career ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codex Leicester
The Codex Leicester (also briefly known as the Codex Hammer) is a collection of scientific writings by Leonardo da Vinci. The codex is named after Thomas Coke, Earl of Leicester, who purchased it in 1719. The codex provides an insight into the mind of the Renaissance artist, scientist and thinker, as well as an exceptional illustration of the link between art and science and the creativity of the scientific process. When the manuscript was last sold to Bill Gates at Christie's auction house on 11 November 1994 in New York for (equivalent to $ million in ), it was the most expensive manuscript ever sold. Manuscript The leather-bound notebook comprises 36 sheets, 29 × 22 cm. The manuscript is not a single linear script but a mixture of Leonardo's observations and theories on astronomy and the properties of water, rocks, fossils, air, and celestial light. The topics addressed include: * An explanation of why fossils of sea creatures can be found on mountains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
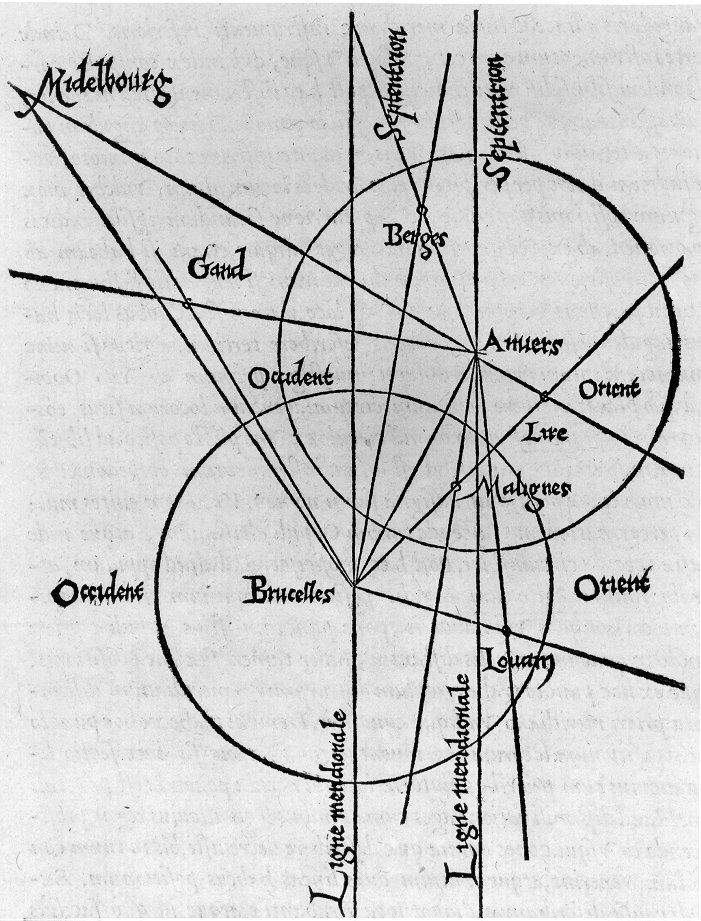
Gemma Frisius
Gemma Frisius (; born Jemme Reinerszoon; December 9, 1508 – May 25, 1555) was a Dutch physician, mathematician, cartographer, philosopher, and instrument maker. He created important globes, improved the mathematical instruments of his day and applied mathematics in new ways to surveying and navigation. Gemma's rings, an astronomical instrument, are named after him. Along with Gerardus Mercator and Abraham Ortelius, Frisius is often considered one of the founders of the Netherlandish school of cartography, and significantly helped lay the foundations for the school's golden age (approximately 1570s–1670s). Biography Frisius was born in Dokkum, Friesland (present-day Netherlands), of poor parents who died when he was young. He moved to Groningen and later studied at the University of Leuven (Louvain), Belgium, beginning in 1525. He received the degree of MD in 1536 and remained on the faculty of medicine of Leuven for the rest of his life where, in addition to teaching ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. The Netherlands consists of Provinces of the Netherlands, twelve provinces; it borders Germany to the east and Belgium to the south, with a North Sea coastline to the north and west. It shares Maritime boundary, maritime borders with the United Kingdom, Germany, and Belgium. The official language is Dutch language, Dutch, with West Frisian language, West Frisian as a secondary official language in the province of Friesland. Dutch, English_language, English, and Papiamento are official in the Caribbean Netherlands, Caribbean territories. The people who are from the Netherlands is often referred to as Dutch people, Dutch Ethnicity, Ethnicity group, not to be confused by the language. ''Netherlands'' literally means "lower countries" i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematician
A mathematician is someone who uses an extensive knowledge of mathematics in their work, typically to solve mathematical problems. Mathematicians are concerned with numbers, data, quantity, mathematical structure, structure, space, Mathematical model, models, and mathematics#Calculus and analysis, change. History One of the earliest known mathematicians was Thales of Miletus (); he has been hailed as the first true mathematician and the first known individual to whom a mathematical discovery has been attributed. He is credited with the first use of deductive reasoning applied to geometry, by deriving four corollaries to Thales's theorem. The number of known mathematicians grew when Pythagoras of Samos () established the Pythagorean school, whose doctrine it was that mathematics ruled the universe and whose motto was "All is number". It was the Pythagoreans who coined the term "mathematics", and with whom the study of mathematics for its own sake begins. The first woman math ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartographer
Cartography (; from , 'papyrus, sheet of paper, map'; and , 'write') is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an imagined reality) can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively. The fundamental objectives of traditional cartography are to: * Set the map's agenda and select traits of the object to be mapped. This is the concern of map editing. Traits may be physical, such as roads or land masses, or may be abstract, such as toponyms or political boundaries. * Represent the terrain of the mapped object on flat media. This is the concern of map projections. * Eliminate the mapped object's characteristics that are irrelevant to the map's purpose. This is the concern of Cartographic generalization, generalization. * Reduce the complexity of the characteristics that will be mapped. This is also the concern of generalization. * Orchestrate the elements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1555 In Science
The year 1555 CE in science and technology included a number of events, some of which are listed here. Biology * Pierre Belon publishes '' L'Histoire de la nature des oyseaux'', a pioneering work in the comparative anatomy of birds. Exploration * Richard Eden publishes ''The Decades of the Newe Worlde or West India'', a translation into English of parts of Pietro Martire d'Anghiera's '' De orbe novo decades'', the Gonzalo Fernández de Oviedo y Valdés work ''Natural hystoria de las Indias'' and others. * Guillaume Le Testu's ''Cosmographie Universelle selon les navigateurs, tant anciens que modernes'' contains maps of Terra Australis. Mathematics * Petrus Ramus publishes ''Arithmétique''. * First German translation of Euclid's elements by Johann Scheubel. Births * June 13 – Giovanni Antonio Magini, Italian astronomer (died 1617) * Andreas Libavius, German physician (died 1616) Deaths * January 14 – Jacques Dubois, French anatomist (born 1478) * May 25 – Gemma Fris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Turner (naturalist)
William Turner (1509/10 – 13 July 1568) was an English people, English Anglicanism#Anglican divines, divine and Protestant Reformer, reformer, a physician and a natural history, natural historian. He has been called “the father of English botany”.Samson, Alexander. ''Locus Amoenus: Gardens and Horticulture in the Renaissance'', 2012 :4 He studied medicine in Italy, and was a friend of the great Swiss people, Swiss naturalist, Conrad Gessner. He was an early herbalist and ornithology, ornithologist, and it is in these fields that the most interest lies today. He is known as being one of the first “parson-naturalists” in England. He first published ''Libellus de Re herbaria'' in Latin in 1538, and later translated it into English because he believed herbalists were not sharing their knowledge. Turner's works were condemned under Henry VIII and under Mary I of England, Mary Tudor. Biography Early years Turner was born in Morpeth, Northumberland, Morpeth, Northumberlan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English People
The English people are an ethnic group and nation native to England, who speak the English language in England, English language, a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language, and share a common ancestry, history, and culture. The English identity began with the History of Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxons, when they were known as the , meaning "Angle kin" or "English people". Their ethnonym is derived from the Angles (tribe), Angles, one of the Germanic peoples who invaded Great Britain, Britain around the 5th century AD. The English largely descend from two main historical population groups: the West Germanic tribes, including the Angles, Saxons, and Jutes who settled in England and Wales, Southern Britain following the withdrawal of the Ancient Rome, Romans, and the Romano-British culture, partially Romanised Celtic Britons who already lived there.Martiniano, R., Caffell, A., Holst, M. et al. "Genomic signals of migration and continuity in Britain before the Anglo-Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naturalist
Natural history is a domain of inquiry involving organisms, including animals, fungi, and plants, in their natural environment, leaning more towards observational than experimental methods of study. A person who studies natural history is called a naturalist or natural historian. Natural history encompasses scientific research but is not limited to it. It involves the systematic study of any category of natural objects or organisms, so while it dates from studies in the ancient Greco-Roman world and the mediaeval Arabic world, through to European Renaissance naturalists working in near isolation, today's natural history is a cross-discipline umbrella of many specialty sciences; e.g., geobiology has a strong multidisciplinary nature. Definitions Before 1900 The meaning of the English term "natural history" (a calque of the Latin ''historia naturalis'') has narrowed progressively with time, while, by contrast, the meaning of the related term "nature" has widened (see also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |