|
Byzantine–Bulgarian War Of 894–896
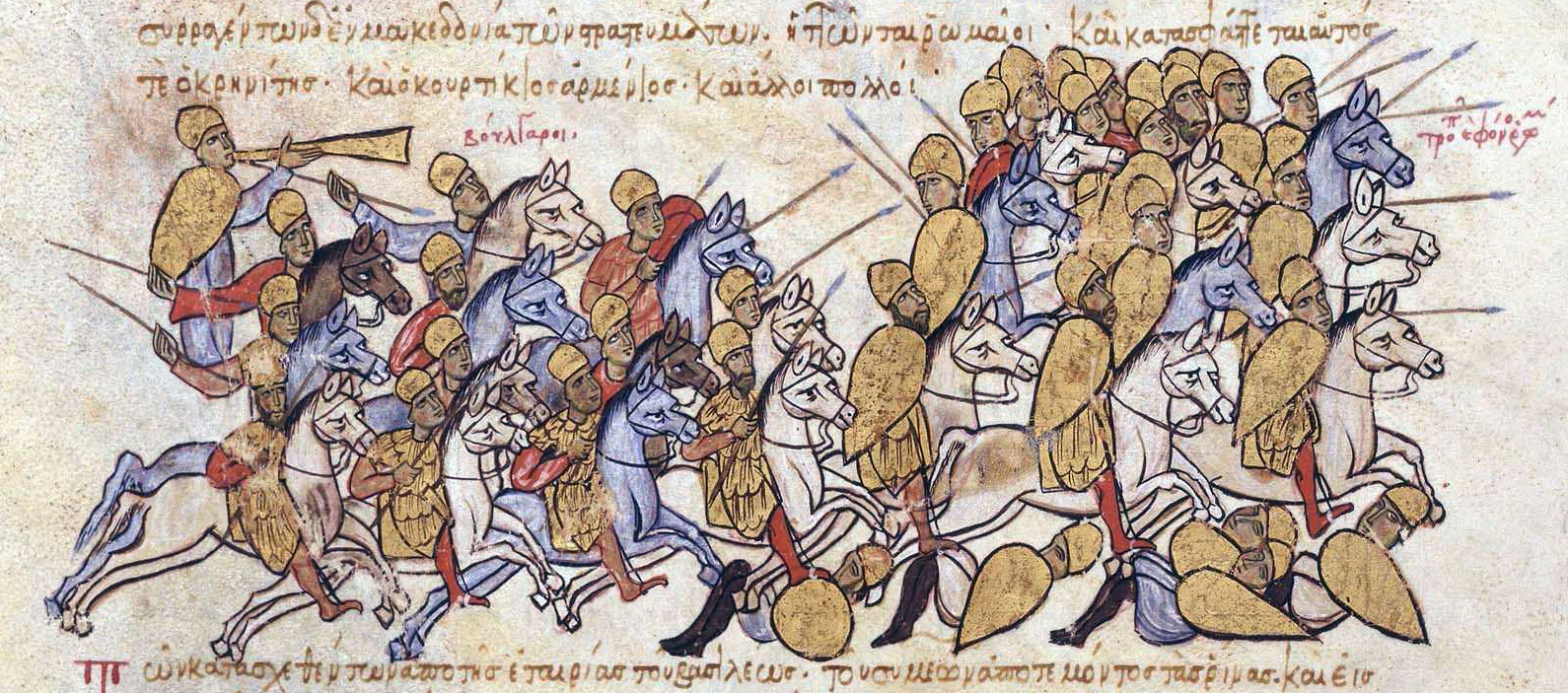
The Byzantine–Bulgarian war of 894–896 () was fought between the Bulgarian Empire and the Byzantine Empire as a result of the decision of the Byzantine emperor Leo VI to move the Bulgarian market from Constantinople to Thessalonica which would greatly increase the expenses of the Bulgarian merchants. Following the defeat of the Byzantine army in the initial stages of the war in 894 Leo VI sought aid from the Magyars who at the time inhabited the steppes to the north-east of Bulgaria. Aided by the Byzantine navy, in 895 the Magyars invaded Dobruja and defeated the Bulgarian troops. Simeon I called for truce and deliberately protracted the negotiations with the Byzantines until securing the assistance of the Pechenegs. Cornered between the Bulgarians and the Pechanegs, the Magyars suffered a crushing defeat at the hands of the Bulgarian army and had to migrate westwards, settling in Pannonia. With the Magyar threat eliminated, Simeon led his hosts south and routed the By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Boulgarophygon
The Battle of Boulgarophygon (; ) was fought in the summer of 896 near the town of Boulgarophygon (modern Babaeski, Turkey) between the Byzantine Empire and the First Bulgarian Empire. The result was an annihilation of the Byzantine army which determined the Bulgarian victory in the Byzantine–Bulgarian war of 894–896, trade war of 894–896. Despite the initial difficulties in the war against the Magyars, who acted as Byzantine allies, the battle of Boulgarophygon proved to be the first decisive victory of the young and ambitious Bulgarian ruler Simeon I of Bulgaria, Simeon I against the Byzantine Empire. Simeon would go on to inflict a number of defeats on the Byzantines in pursuit of his ultimate goal, the throne in Constantinople. The peace treaty that was signed as a result of the battle confirmed the Bulgarian domination in the Balkans. Background During the rule of Boris I of Bulgaria, Boris I (r. 852–889), Bulgaria underwent major changes – the Christianization o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Navy
The Byzantine navy was the Navy, naval force of the Byzantine Empire. Like the state it served, it was a direct continuation from its Roman navy, Roman predecessor, but played a far greater role in the defence and survival of the state than its earlier iteration. While the fleets of the Roman Empire faced few great naval threats, operating as a policing force vastly inferior in power and prestige to the Roman army, army, command of the sea became vital to the very existence of the Byzantine state, which several historians have called a "maritime empire". The first threat to Roman hegemony in the Mediterranean Sea was posed by the Vandals in the 5th century, but their threat was ended by the wars of Justinian I in the 6th century. The re-establishment of a permanently maintained fleet and the introduction of the dromon galley in the same period also marks the point when the Byzantine navy began departing from its late Roman roots and developing its own characteristic identity. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Of Bulgaria
Vladimir-Rasate () was the ruler of the First Bulgarian Empire from 889 to 893. Biography In 853 or 854, the Bulgar Army led by Vladimir, the son of Boris I of Bulgaria, invaded Serbia in an attempt to exact vengeance for the previous defeat of Presian in 839-842 against Vlastimir. The Serbian Army, led by Mutimir and his brothers, defeated the Bulgars, capturing Vladimir and 12 boyars.''The early medieval Balkans''p. 141/ref> Boris I and Mutimir agreed on peace (and perhaps an alliance), and Mutimir sent his sons Pribislav and Stefan to the border to escort the prisoners, where they exchanged items as a sign of peace. Boris gave them "rich gifts", while he was given "two slaves, two falcons, two dogs, and 80 furs". Vladimir became ruler ( Knyaz) of Bulgaria when his father Boris-Mihail I (Boris adopted the name Mihail - Michael - after his baptism) decided to retire to a monastery after a reign of 36 years. Preserved seals with the inscription "Michael the Monk, who i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Preslav
The People's Council of Preslav () took place in 893. It was among the most important events in the history of the First Bulgarian Empire and was a cornerstone of the Christianization of Bulgaria under prince Boris I. Background and sources In 889 Boris I abdicated and retired to a monastery and was succeeded by his eldest son Vladimir-Rasate who tried to restore Tengrism, the traditional religion of the country since 681. After Vladimir-Rasate was deposed by his father in 893, the latter gathered a People's Council in Preslav to legitimate the changes.Andreev, p. 85 Since the issues to be discussed were of great importance for the whole country, the attendance and approval of the higher and lower nobility, the clergy and representatives of all provinces was needed.Zlatarski, p. 257 There is no direct mention of the Council in medieval sources. The most detailed description of the events that led to the downfall of Vladimir-Rasate comes from the Benedictine abbot Regino of Prü ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, officially the Orthodox Catholic Church, and also called the Greek Orthodox Church or simply the Orthodox Church, is List of Christian denominations by number of members, one of the three major doctrinal and jurisdictional groups of Christianity, with approximately 230 million baptised members. It operates as a Communion (Christian), communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its Bishop (Orthodox Church), bishops via local Holy Synod, synods. The church has no central doctrinal or governmental authority analogous to the pope of the Catholic Church. Nevertheless, the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople is recognised by them as ''primus inter pares'' (), a title held by the patriarch of Rome prior to 1054. As one of the oldest surviving religious institutions in the world, the Eastern Orthodox Church has played an especially prominent role in the history and culture of Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeastern Europe. Since 2018, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecumenical Patriarchate Of Constantinople
The Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople (, ; ; , "Roman Orthodox Patriarchate, Ecumenical Patriarchate of Istanbul") is one of the fifteen to seventeen autocephalous churches that together compose the Eastern Orthodox Church. It is headed by the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople. Because of its historical location as the capital of the former Eastern Roman Empire and its role as the mother church of most modern Eastern Orthodox churches, Constantinople holds a special place of honor within Eastern Orthodox Christianity and serves as the seat for the Ecumenical Patriarch, who enjoys the status of '' primus inter pares'' (first among equals) among the world's Eastern Orthodox prelates and is regarded as the representative and spiritual leader of Eastern Orthodox Christians. Phanar (Turkish: '' Fener''), the name of the neighbourhood where ecumenical patriarch resides, is often used as a metaphor or shorthand for the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople. The E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.Gerald O'Collins, O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 Catholic particular churches and liturgical rites#Churches, ''sui iuris'' (autonomous) churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and Eparchy, eparchies List of Catholic dioceses (structured view), around the world, each overseen by one or more Bishops in the Catholic Church, bishops. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the Papal supremacy, chief pastor of the church. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saints Cyril And Methodius
Cyril (; born Constantine, 826–869) and Methodius (; born Michael, 815–885) were brothers, Byzantine Christian theologians and missionaries. For their work evangelizing the Slavs, they are known as the "Apostles to the Slavs". They are credited with devising the Glagolitic alphabet, the first alphabet used to transcribe Old Church Slavonic. After their deaths, their pupils continued their missionary work among other Slavs. Both brothers are venerated in the Eastern Orthodox Church as saints with the title of " equal-to-apostles". In 1880, Pope Leo XIII introduced their feast into the calendar of the Roman Rite of the Catholic Church. In 1980, the first Slav pope, Pope John Paul II declared them co-patron saints of Europe, together with Benedict of Nursia. Apostolic letter of Pope John Paul II, 31 December 1980 Early career Early life The two brothers were born in Thessalonica, at that time in the Byzantine province of the same name (today in Greece) – Cyril in 827 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianization Of Bulgaria
The Christianization of Bulgaria was the process by which 9th-century medieval Bulgaria converted to Christianity. It reflected the need of unity within the religiously divided Bulgarian state as well as the need for equal acceptance on the international stage in Christian Europe. This process was characterized by the shifting political alliances of Boris I of Bulgaria (ruled 852–889) with the kingdom of the East Franks and with the Byzantine Empire, as well as his diplomatic correspondence with the Pope. Because of Bulgaria's strategic position, the churches of both Rome and Constantinople each wanted Bulgaria in their sphere of influence. They regarded Christianization as a means of integrating Slavs into their region. After some overtures to each side, the Khan adopted Christianity from Constantinople in 870. As a result, he achieved his goal of gaining an independent Bulgarian national church and having an archbishop appointed to head it. Background When Khan Boris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boris I Of Bulgaria
Boris I (also ''Bogoris''), venerated as Saint Boris I (Mihail) the Baptizer (, ; died 2 May 907), was the ruler (knyaz) of the First Bulgarian Empire from 852 to 889. Despite a number of military setbacks, the reign of Boris I was marked with significant events that shaped History of Bulgaria, Bulgarian and European history. With the Christianization of Bulgaria in 864, paganism was abolished. A skillful diplomat, Boris I successfully exploited the conflict between the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople, Patriarchate of Constantinople and the Pope, Papacy to secure an Bulgarian Orthodox Church, autocephalous Bulgarian Church, thus dealing with the nobility's concerns about Byzantine interference in Bulgaria's internal affairs. When in 885 the disciples of Saints Cyril and Methodius were banished from Great Moravia, Boris I gave them refuge and provided assistance which saved the Glagolithic and later promoted the development of the Cyrillic script in Preslav and the Sl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strandzha
Strandzha (, also transliterated as ''Strandja'', ; , or ) is a mountain massif in southeastern Bulgaria and East Thrace, the European part of Turkey. It is in the southeastern part of the Balkans between the plains of Thrace to the west, the lowlands near Burgas to the north, and the Black Sea to the east. Its highest peak is Mahya Dağı (, ''Mahiada'') () in Turkey, while the highest point on Bulgarian territory is Golyamo Gradishte () (). The total area is approximately . Geography and climate The climate of the area is considerably influenced by the Black Sea and is predominantly humid continental in the mountains and humid subtropical at the coast. Major rivers in the area are the Veleka ( long) and the border river Rezovska ( long). Strandzha Nature Park Strandzha Nature Park, established in 1995 in the Bulgarian part of the massif, is the largest protected area in Bulgaria. In size it is , or about 1% of Bulgaria's total territory. The İğneada Floodplain Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |