|
Bus Snooping
Bus snooping or bus sniffing is a scheme by which a coherency controller (snooper) in a cache (a snoopy cache) monitors or snoops the bus transactions, and its goal is to maintain a cache coherency in distributed shared memory systems. This scheme was introduced by Ravishankar and Goodman in 1983, under the name "write-once" cache coherency. A cache containing a coherency controller (snooper) is called a snoopy cache. How it works When specific data are shared by several caches and a processor modifies the value of the shared data, the change must be propagated to all the other caches which have a copy of the data. This change propagation prevents the system from violating cache coherency. The notification of data change can be done by bus snooping. All the snoopers monitor every transaction on a bus. If a transaction modifying a shared cache block appears on a bus, all the snoopers check whether their caches have the same copy of the shared block. If a cache has a copy of the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cache (computing)
In computing, a cache ( ) is a hardware or software component that stores data so that future requests for that data can be served faster; the data stored in a cache might be the result of an earlier computation or a copy of data stored elsewhere. A cache hit occurs when the requested data can be found in a cache, while a cache miss occurs when it cannot. Cache hits are served by reading data from the cache, which is faster than recomputing a result or reading from a slower data store; thus, the more requests that can be served from the cache, the faster the system performs. To be cost-effective, caches must be relatively small. Nevertheless, caches are effective in many areas of computing because typical Application software, computer applications access data with a high degree of locality of reference. Such access patterns exhibit temporal locality, where data is requested that has been recently requested, and spatial locality, where data is requested that is stored near dat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
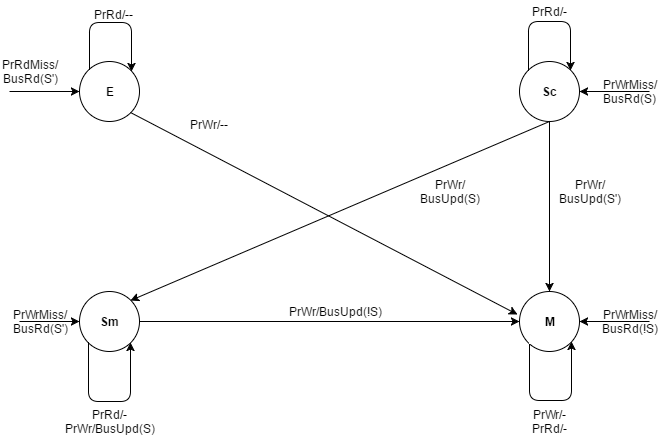
Dragon Protocol
The Dragon Protocol is an update based cache coherence protocol used in multi-processor systems. Write propagation is performed by directly updating all the cached values across multiple processors. Update based protocols such as the Dragon protocol perform efficiently when a write to a cache block is followed by several reads made by other processors, since the updated cache block is readily available across caches associated with all the processors. States Each cache block resides in one of the four states: exclusive-clean, shared-clean, shared-modified and modify. * Exclusive-clean (E): This means that the cache block was first fetched by the current processor and has not been accessed by any other processor since. * Shared clean (Sc): This means that the cache block definitely exists in multiple processor’s caches, and that the current processor is not the last one to write the block. States E and Sc are maintained separately by the protocol to prevent read-write operations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directory-based Coherence Protocols
In computer engineering, directory-based cache coherence is a type of cache coherence mechanism, where directories are used to manage caches in place of bus snooping. Bus snooping methods scale poorly due to the use of broadcasting. These methods can be used to target both performance and scalability of directory systems. Full bit vector format In the full bit vector format, for each possible cache line in memory, a bit is used to track whether every individual processor has that line stored in its cache. The full bit vector format is the simplest structure to implement, but the least scalable. The SGI Origin 2000 uses a combination of full bit vector and coarse bit vector depending on the number of processors. Each directory entry must have 1 bit stored per processor per cache line, along with bits for tracking the state of the directory. This leads to the total size required being ''(number of processors)×number of cache lines'', having a storage overhead ratio of ''(numb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cache Coherent NUMA
Non-uniform memory access (NUMA) is a computer memory design used in multiprocessing, where the memory access time depends on the memory location relative to the processor. Under NUMA, a processor can access its own local memory faster than non-local memory (memory local to another processor or memory shared between processors). NUMA is beneficial for workloads with high memory locality of reference and low lock contention, because a processor may operate on a subset of memory mostly or entirely within its own cache node, reducing traffic on the memory bus. NUMA architectures logically follow in scaling from symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) architectures. They were developed commercially during the 1990s by Unisys, Convex Computer (later Hewlett-Packard), Honeywell Information Systems Italy (HISI) (later Groupe Bull), Silicon Graphics (later Silicon Graphics International), Sequent Computer Systems (later IBM), Data General (later EMC, now Dell Technologies), Digital (later Compa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scalability
Scalability is the property of a system to handle a growing amount of work. One definition for software systems specifies that this may be done by adding resources to the system. In an economic context, a scalable business model implies that a company can increase sales given increased resources. For example, a package delivery system is scalable because more packages can be delivered by adding more delivery vehicles. However, if all packages had to first pass through a single warehouse for sorting, the system would not be as scalable, because one warehouse can handle only a limited number of packages. In computing, scalability is a characteristic of computers, networks, algorithms, networking protocols, programs and applications. An example is a search engine, which must support increasing numbers of users, and the number of topics it indexes. Webscale is a computer architectural approach that brings the capabilities of large-scale cloud computing companies into enterprise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandwidth (computing)
In computing, bandwidth is the maximum rate of data transfer across a given path. Bandwidth may be characterized as network bandwidth, data bandwidth, or digital bandwidth. This definition of ''bandwidth'' is in contrast to the field of signal processing, wireless communications, modem data transmission, digital communications, and electronics, in which ''bandwidth'' is used to refer to the signal bandwidth measured in hertz, meaning the frequency range between lowest and highest attainable frequency while meeting a well-defined impairment level in signal power. The actual bit rate that can be achieved depends not only on the signal bandwidth but also on the noise on the channel. Network capacity The term ''bandwidth'' sometimes defines the net bit rate ''peak bit rate'', ''information rate'', or physical layer ''useful bit rate'', channel capacity, or the maximum throughput of a logical or physical communication path in a digital communication system. For example, bandwi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directory-based Cache Coherence
In computer engineering, directory-based cache coherence is a type of Cache coherence#Coherence mechanisms, cache coherence mechanism, where directories are used to manage caches in place of bus snooping. Bus snooping methods scale poorly due to the use of Broadcasting (networking), broadcasting. These methods can be used to target both Computer performance, performance and scalability of directory systems. Full bit vector format In the full bit vector format, for each possible cache line in Computer_memory, memory, a bit is used to track whether every individual Central processing unit, processor has that line stored in its cache (computing), cache. The full bit vector format is the simplest structure to implement, but the least scalable. The SGI Origin 2000 uses a combination of full bit vector and coarse bit vector depending on the number of processors. Each directory entry must have 1 bit stored per processor per cache line, along with bits for tracking the state of the dir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firefly (cache Coherence Protocol)
The Firefly cache coherence protocol is the schema used in the DEC Firefly multiprocessor workstation, developed by DEC Systems Research Center. This protocol is a 3 State Write Update Cache Coherence Protocol. Unlike the Dragon protocol, the Firefly protocol updates the Main Memory as well as the Local caches on Write Update Bus Transition. Thus the Shared Clean and Shared Modified States present in case of Dragon Protocol, are not distinguished between in case of Firefly Protocol. States In this protocol, the following states can be assigned to each block: * Valid-Exclusive(V): The cache block is valid, clean and only resides in one cache. * Shared(S): The cache block is valid, clean and may reside in multiple caches. * Dirty(D): The block is the only copy of the memory and it is dirty i.e. its value has been modified since being brought from the memory. This is the only state that generates a write-back when the block is replaced in the cache. These states correspond to the ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MESIF Protocol
The MESIF protocol is a cache coherency and memory coherence protocol developed by Intel for cache coherent non-uniform memory architectures. The protocol consists of five states, Modified (M), Exclusive (E), Shared (S), Invalid (I) and Forward (F). The M, E, S and I states are the same as in the MESI protocol. The F state is a specialized form of the S state, and indicates that a cache should act as a designated responder for any requests for the given line. The protocol ensures that, if any cache holds a line in the S state, at most one (other) cache holds it in the F state. In a system of caches employing the MESI protocol, a cache line request that is received by multiple caches holding a line in the S state will be serviced inefficiently. It may either be satisfied from (slow) main memory, or ''all'' the sharing caches could respond, bombarding the requestor with redundant responses. In a system of caches employing the MESIF protocol, a cache line request will be responded t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
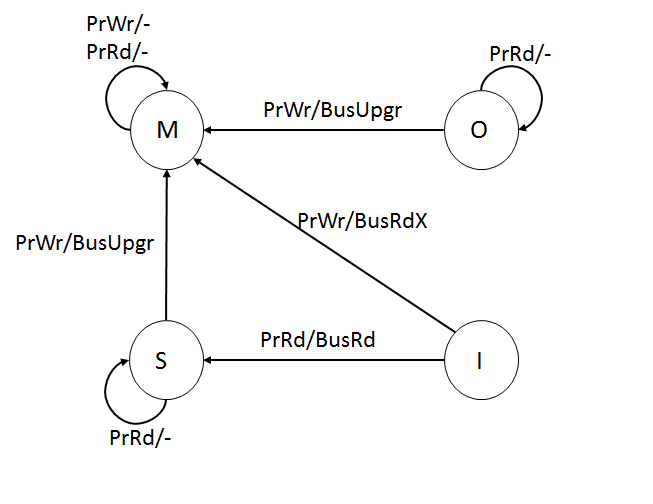
Cache Coherence
In computer architecture, cache coherence is the uniformity of shared resource data that is stored in multiple local caches. In a cache coherent system, if multiple clients have a cached copy of the same region of a shared memory resource, all copies are the same. Without cache coherence, a change made to the region by one client may not be seen by others, and errors can result when the data used by different clients is mismatched. A cache coherence protocol is used to maintain cache coherency. The two main types are snooping and directory-based protocols. Cache coherence is of particular relevance in multiprocessing systems, where each CPU may have its own local cache of a shared memory resource. Overview In a shared memory multiprocessor system with a separate cache memory for each processor, it is possible to have many copies of shared data: one copy in the main memory and one in the local cache of each processor that requested it. When one of the copies of data is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOESI Protocol
Modified Owned Exclusive Shared Invalid (MOESI) is a full cache coherency protocol that encompasses all of the possible states commonly used in other protocols. In addition to the four common MESI protocol states, there is a fifth "Owned" state representing data that is both modified and shared. This avoids the need to write modified data back to main memory before sharing it. While the data must still be written back eventually, the write-back may be deferred . In order for this to be possible, direct cache-to-cache transfers of data must be possible, so a cache with the data in the modified state can supply that data to another reader without transferring it to memory. As discussed in AMD64 Architecture Programmer's Manual Vol. 2 ''System Programming'', each cache line is in one of five states: ;Modified: This cache has the only valid copy of the cache line, and has made changes to that copy. The cached copy may be further modified freely. ;Owned: This line is one of seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOSI Protocol
The MOSI protocol is an extension of the basic MSI cache coherency protocol. It adds the Owned state, which indicates that the current processor owns this block, and will service requests from other processors for the block. Overview of States Following are the permitted states of a given cache line: Modified (M) - Only one cache has a valid copy of the block and the value is likely to be different from the one in main memory. It has almost the same meaning as a dirty state in a write-back cache except for the difference that modified state also implies exclusive ownership of that block. Dirty state just means that the value of the block is different from the one in main memory, whereas, modified implies that the value is different than that of the main memory and that it is cached in only one location. Owned (O) - Multiple caches may hold the most recent and correct value of a block and the value in main memory may or may not be correct. At a time, only one cache can have the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |