|
Burroughs B6x00-7x00 Instruction Set
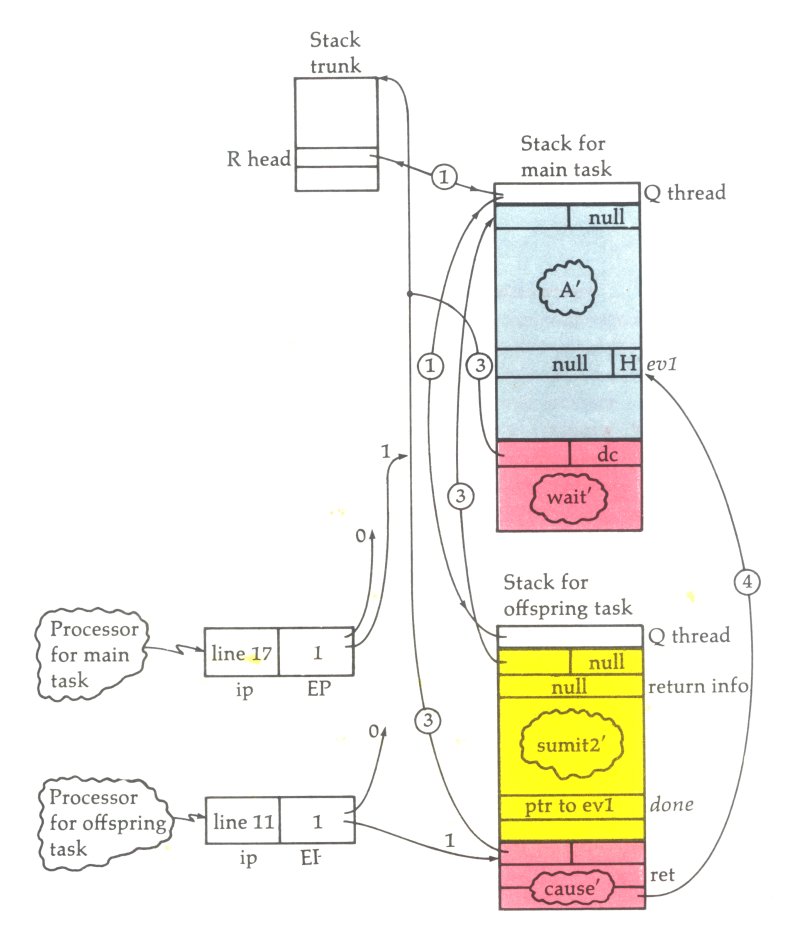
The Burroughs B6x00-7x00 instruction set includes the set of valid operations for the Burroughs B6500, B7500 and later Burroughs large systems, including the current (as of 2006) Unisys Clearpath/MCP systems; it does not include the instruction for other Burroughs large systems including the B5000, B5500, B5700 and the B8500. These unique machines have a distinctive design and instruction set. Each word of data is associated with a type, and the effect of an operation on that word can depend on the type. Further, the machines are stack based to the point that they had no user-addressable registers. Overview As you would expect from the unique architecture used in these systems, they also have an interesting instruction set. Programs are made up of 8-bit syllables, which may be Name Call, be Value Call or form an operator, which may be from one to twelve syllables in length. There are less than 200 operators, all of which fit into 8-bit syllables. If we ignore the powerful st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burroughs Large Systems
The Burroughs Large Systems Group produced a family of large 48-bit mainframes using stack machine instruction sets with dense syllables.E.g., 12-bit syllables for B5000, 8-bit syllables for B6500 The first machine in the family was the B5000 in 1961. It was optimized for compiling ALGOL 60 programs extremely well, using single-pass compilers. It evolved into the B5500. Subsequent major redesigns include the B6500/B6700 line and its successors, as well as the separate B8500 line. In the 1970s, the Burroughs Corporation was organized into three divisions with very different product line architectures for high-end, mid-range, and entry-level business computer systems. Each division's product line grew from a different concept for how to optimize a computer's instruction set for particular programming languages. "Burroughs Large Systems" referred to all of these large-system product lines together, in contrast to the COBOL-optimized Medium Systems (B2000, B3000, and B4000) or the fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exponent
Exponentiation is a mathematical operation, written as , involving two numbers, the '' base'' and the ''exponent'' or ''power'' , and pronounced as " (raised) to the (power of) ". When is a positive integer, exponentiation corresponds to repeated multiplication of the base: that is, is the product of multiplying bases: b^n = \underbrace_. The exponent is usually shown as a superscript to the right of the base. In that case, is called "''b'' raised to the ''n''th power", "''b'' (raised) to the power of ''n''", "the ''n''th power of ''b''", "''b'' to the ''n''th power", or most briefly as "''b'' to the ''n''th". Starting from the basic fact stated above that, for any positive integer n, b^n is n occurrences of b all multiplied by each other, several other properties of exponentiation directly follow. In particular: \begin b^ & = \underbrace_ \\ ex& = \underbrace_ \times \underbrace_ \\ ex& = b^n \times b^m \end In other words, when multiplying a base raised to one e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instruction Processing
Instruction or instructions may refer to: Computing * Instruction, one operation of a processor within a computer architecture instruction set * Computer program, a collection of instructions Music * Instruction (band), a 2002 rock band from New York City, US * "Instruction" (song), a 2017 song by English DJ Jax Jones * ''Instructions'' (album), a 2001 album by Jermaine Dupri Other uses * Instruction, teaching or education performed by a teacher * Sebayt, a work of the ancient Egyptian didactic literature aiming to teach ethical behaviour * Instruction, the pre-trial phase of an investigation led by a judge in an inquisitorial system of justice * Instruction manual, an instructional book or booklet ** Instruction manual (gaming), a booklet that instructs the player on how to play the game See also * Instructor (other) Instructor may refer to: Education * Instructor, a teacher of a specialised subject that involves skill: ** Teaching assistant ** Tutor ** Lecturer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buffer Overflow
In information security and programming, a buffer overflow, or buffer overrun, is an anomaly whereby a program, while writing data to a buffer, overruns the buffer's boundary and overwrites adjacent memory locations. Buffers are areas of memory set aside to hold data, often while moving it from one section of a program to another, or between programs. Buffer overflows can often be triggered by malformed inputs; if one assumes all inputs will be smaller than a certain size and the buffer is created to be that size, then an anomalous transaction that produces more data could cause it to write past the end of the buffer. If this overwrites adjacent data or executable code, this may result in erratic program behavior, including memory access errors, incorrect results, and crashes. Exploiting the behavior of a buffer overflow is a well-known security exploit. On many systems, the memory layout of a program, or the system as a whole, is well defined. By sending in data designed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compilers
In computing, a compiler is a computer program that translates computer code written in one programming language (the ''source'' language) into another language (the ''target'' language). The name "compiler" is primarily used for programs that translate source code from a high-level programming language to a low-level programming language (e.g. assembly language, object code, or machine code) to create an executable program. Compilers: Principles, Techniques, and Tools by Alfred V. Aho, Ravi Sethi, Jeffrey D. Ullman - Second Edition, 2007 There are many different types of compilers which produce output in different useful forms. A '' cross-compiler'' produces code for a different CPU or operating system than the one on which the cross-compiler itself runs. A '' bootstrap compiler'' is often a temporary compiler, used for compiling a more permanent or better optimised compiler for a language. Related software include, a program that translates from a low-level language to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
String (computer Science)
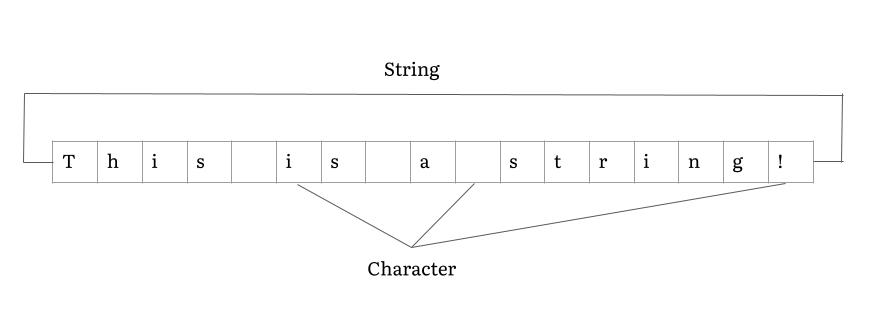
In computer programming, a string is traditionally a sequence of characters, either as a literal constant or as some kind of variable. The latter may allow its elements to be mutated and the length changed, or it may be fixed (after creation). A string is generally considered as a data type and is often implemented as an array data structure of bytes (or words) that stores a sequence of elements, typically characters, using some character encoding. ''String'' may also denote more general arrays or other sequence (or list) data types and structures. Depending on the programming language and precise data type used, a variable declared to be a string may either cause storage in memory to be statically allocated for a predetermined maximum length or employ dynamic allocation to allow it to hold a variable number of elements. When a string appears literally in source code, it is known as a string literal or an anonymous string. In formal languages, which are used in mathemati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thunk
In computer programming, a thunk is a subroutine used to inject a calculation into another subroutine. Thunks are primarily used to delay a calculation until its result is needed, or to insert operations at the beginning or end of the other subroutine. They have many other applications in compiler code generation and modular programming. The term originated as a whimsical irregular form of the verb ''think''. It refers to the original use of thunks in ALGOL 60 compilers, which required special analysis (thought) to determine what type of routine to generate. Background The early years of compiler research saw broad experimentation with different evaluation strategies. A key question was how to compile a subroutine call if the arguments can be arbitrary mathematical expressions rather than constants. One approach, known as "call by value", calculates all of the arguments before the call and then passes the resulting values to the subroutine. In the rival "call by name" approach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Call-by-name
In a programming language, an evaluation strategy is a set of rules for evaluating expressions. The term is often used to refer to the more specific notion of a ''parameter-passing strategy'' that defines the kind of value that is passed to the function for each parameter (the ''binding strategy'') and whether to evaluate the parameters of a function call, and if so in what order (the ''evaluation order''). The notion of reduction strategy is distinct, although some authors conflate the two terms and the definition of each term is not widely agreed upon. To illustrate, executing a function call f(a,b) may first evaluate the arguments a and b, store the results in references or memory locations ref_a and ref_b, then evaluate the function's body with those references passed in. This gives the function the ability to look up the argument values, to modify them via assignment as if they were local variables, and to return values via the references. This is the call-by-reference evalu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Addressing Mode
Addressing modes are an aspect of the instruction set architecture in most central processing unit (CPU) designs. The various addressing modes that are defined in a given instruction set architecture define how the machine language instructions in that architecture identify the operand(s) of each instruction. An addressing mode specifies how to calculate the effective memory address of an operand by using information held in registers and/or constants contained within a machine instruction or elsewhere. In computer programming, addressing modes are primarily of interest to those who write in assembly languages and to compiler writers. For a related concept see orthogonal instruction set which deals with the ability of any instruction to use any addressing mode. Caveats Note that there is no generally accepted way of naming the various addressing modes. In particular, different authors and computer manufacturers may give different names to the same addressing mode, or the sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operands
In mathematics, an operand is the object of a mathematical operation, i.e., it is the object or quantity that is operated on. Example The following arithmetic expression shows an example of operators and operands: :3 + 6 = 9 In the above example, '+' is the symbol for the operation called addition. The operand '3' is one of the inputs (quantities) followed by the addition operator, and the operand '6' is the other input necessary for the operation. The result of the operation is 9. (The number '9' is also called the sum of the augend 3 and the addend 6.) An operand, then, is also referred to as "one of the inputs (quantities) for an operation". Notation Expressions as operands Operands may be complex, and may consist of expressions also made up of operators with operands. :(3 + 5) \times 2 In the above expression '(3 + 5)' is the first operand for the multiplication operator and '2' the second. The operand '(3 + 5)' is an expression in itself, which co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integers
An integer is the number zero (), a positive natural number (, , , etc.) or a negative integer with a minus sign ( −1, −2, −3, etc.). The negative numbers are the additive inverses of the corresponding positive numbers. In the language of mathematics, the set of integers is often denoted by the boldface or blackboard bold \mathbb. The set of natural numbers \mathbb is a subset of \mathbb, which in turn is a subset of the set of all rational numbers \mathbb, itself a subset of the real numbers \mathbb. Like the natural numbers, \mathbb is countably infinite. An integer may be regarded as a real number that can be written without a fractional component. For example, 21, 4, 0, and −2048 are integers, while 9.75, , and are not. The integers form the smallest group and the smallest ring containing the natural numbers. In algebraic number theory, the integers are sometimes qualified as rational integers to distinguish them from the more general algebraic in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unisys
Unisys Corporation is an American multinational information technology (IT) services and consulting company headquartered in Blue Bell, Pennsylvania. It provides digital workplace solutions, cloud, applications, and infrastructure solutions, enterprise computing solutions, and business process solutions for organizations around the world. History Founding Unisys was formed in 1986 through the merger of mainframe corporations Sperry and Burroughs, with Burroughs buying Sperry for $4.8 billion. The name was chosen from over 31,000 submissions in an internal competition when Christian Machen submitted the word "Unisys" which was composed of parts of the words ''united'', ''information'' and ''systems''. The merger was the largest in the computer industry at the time and made Unisys the second largest computer company with annual revenue of $10.5 billion. Michael Blumenthal became CEO and Chairman. Soon after the merger, the market for proprietary mainframe-class systems� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |