|
Bulinus Angolensis
''Bulinus'' is a genus of small tropical freshwater snails, aquatic animal, aquatic gastropod mollusks in the family (biology), family Bulinidae, the ramshorn snails and their allies.MolluscaBase eds. (2020). MolluscaBase. Bulinus O. F. Müller, 1781. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=224352 on 2020-06-27 This genus is medically important because several species of ''Bulinus'' function as intermediate host (biology), hosts for the schistosomiasis blood Trematoda, fluke. Description The shell of species in the genus ''Bulinus'' is Sinistral and dextral, sinistral. It has a very large body whorl and a small spire. Distribution and habitat Species of the genus are widespread in Africa including List of non-marine molluscs of Madagascar, Madagascar and the Middle East. This genus has not yet become established in the USA, but it is considered to represent a potentially serious threat as a pest (organism) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulinus Wrighti
''Bulinus wrighti'' is a species of small tropical air-breathing freshwater snail with a sinistral shell, an aquatic animal, aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family (biology), family Bulinidae.Brown D. S. (1994). ''Freshwater Snails of Africa and their Medical Importance''. Taylor & Francis. . pages 260-261. Distribution The type locality (biology), type locality is Wadi Hatib, at about 1280 m,southeast of Nisab District, Upper Aulaqui District at Rassais, South Yemen. References Bulinus Gastropods described in 1965 {{Planorbidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
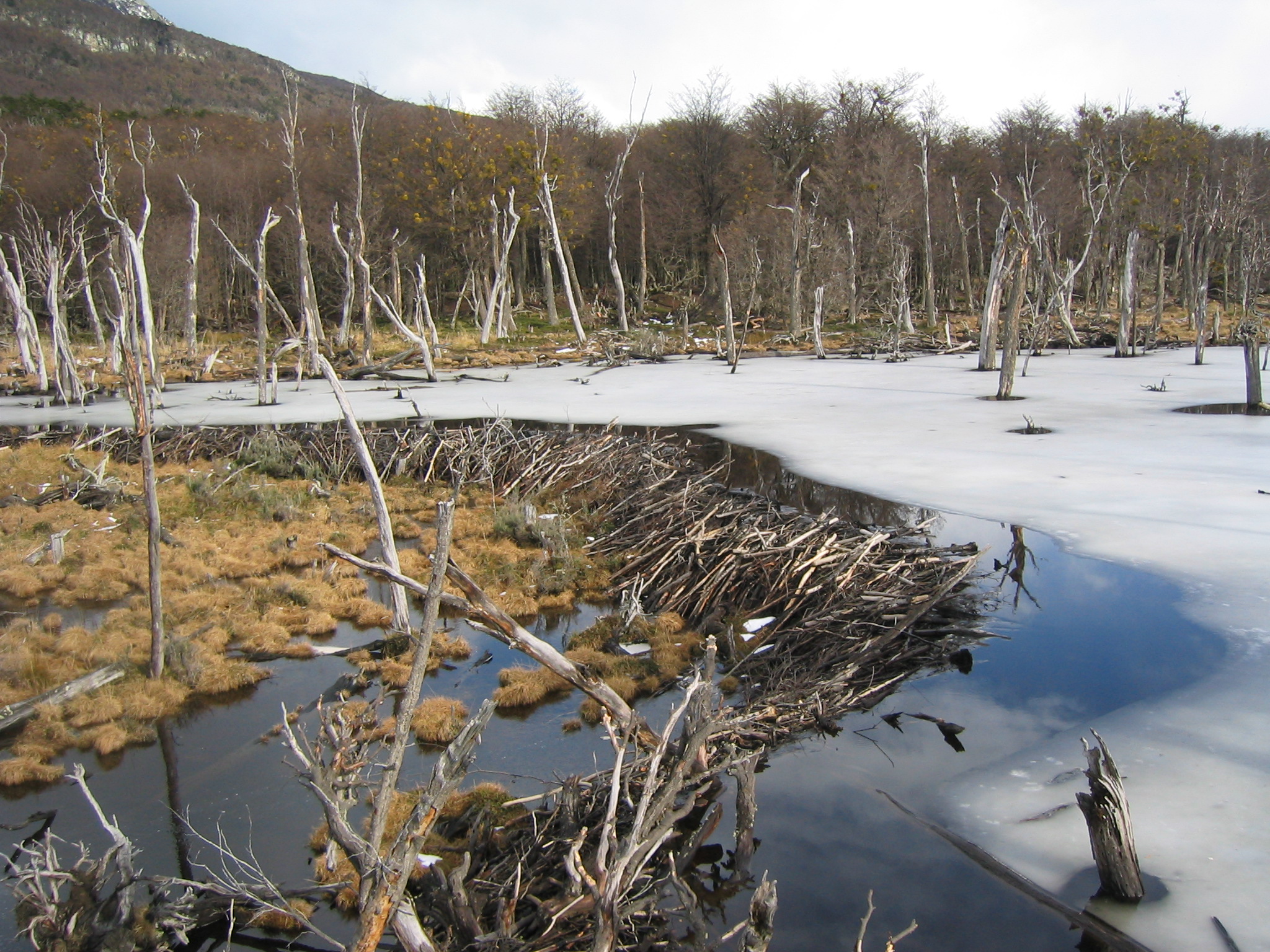
Invasive Species
An invasive species is an introduced species that harms its new environment. Invasive species adversely affect habitats and bioregions, causing ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage. The term can also be used for native species that become harmful to their native environment after human alterations to its food web. Since the 20th century, invasive species have become serious economic, social, and environmental threats worldwide. Invasion of long-established ecosystems by organisms is a natural phenomenon, but human-facilitated introductions have greatly increased the rate, scale, and geographic range of invasion. For millennia, humans have served as both accidental and deliberate dispersal agents, beginning with their earliest migrations, accelerating in the Age of Discovery, and accelerating again with the spread of international trade. Notable invasive plant species include the kudzu vine, giant hogweed (''Heracleum mantegazzianum''), Japanese knotw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aestivation
Aestivation ( (summer); also spelled estivation in American English) is a state of animal dormancy, similar to hibernation, although taking place in the summer rather than the winter. Aestivation is characterized by inactivity and a lowered metabolic rate, that is entered in response to high temperatures and arid conditions. It takes place during times of heat and dryness, which are often the summer months. Invertebrate and vertebrate animals are known to enter this state to avoid damage from high temperatures and the risk of desiccation. Both terrestrial and aquatic animals undergo aestivation. Fossil records suggest that aestivation may have evolved several hundred million years ago. Physiology Organisms that aestivate appear to be in a fairly "light" state of dormancy, as their physiological state can be rapidly reversed, and the organism can quickly return to a normal state. A study done on '' Otala lactea'', a snail native to parts of Europe and Northern Africa, shows t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radula
The radula (; : radulae or radulas) is an anatomical structure used by mollusks for feeding, sometimes compared to a tongue. It is a minutely toothed, chitinous ribbon, which is typically used for scraping or cutting food before the food enters the esophagus. The radula is unique to the mollusks, and is found in every class of mollusk except the bivalves, which instead use cilia, waving filaments that bring minute organisms to the mouth. Within the gastropods, the radula is used in feeding by both herbivorous and carnivorous snails and slugs. The arrangement of teeth ( denticles) on the radular ribbon varies considerably from one group to another. In most of the more ancient lineages of gastropods, the radula is used to graze, by scraping diatoms and other microscopic algae off rock surfaces and other substrates. Predatory marine snails such as the Naticidae use the radula plus an acidic secretion to bore through the shell of other mollusks. Other predatory marine snails, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
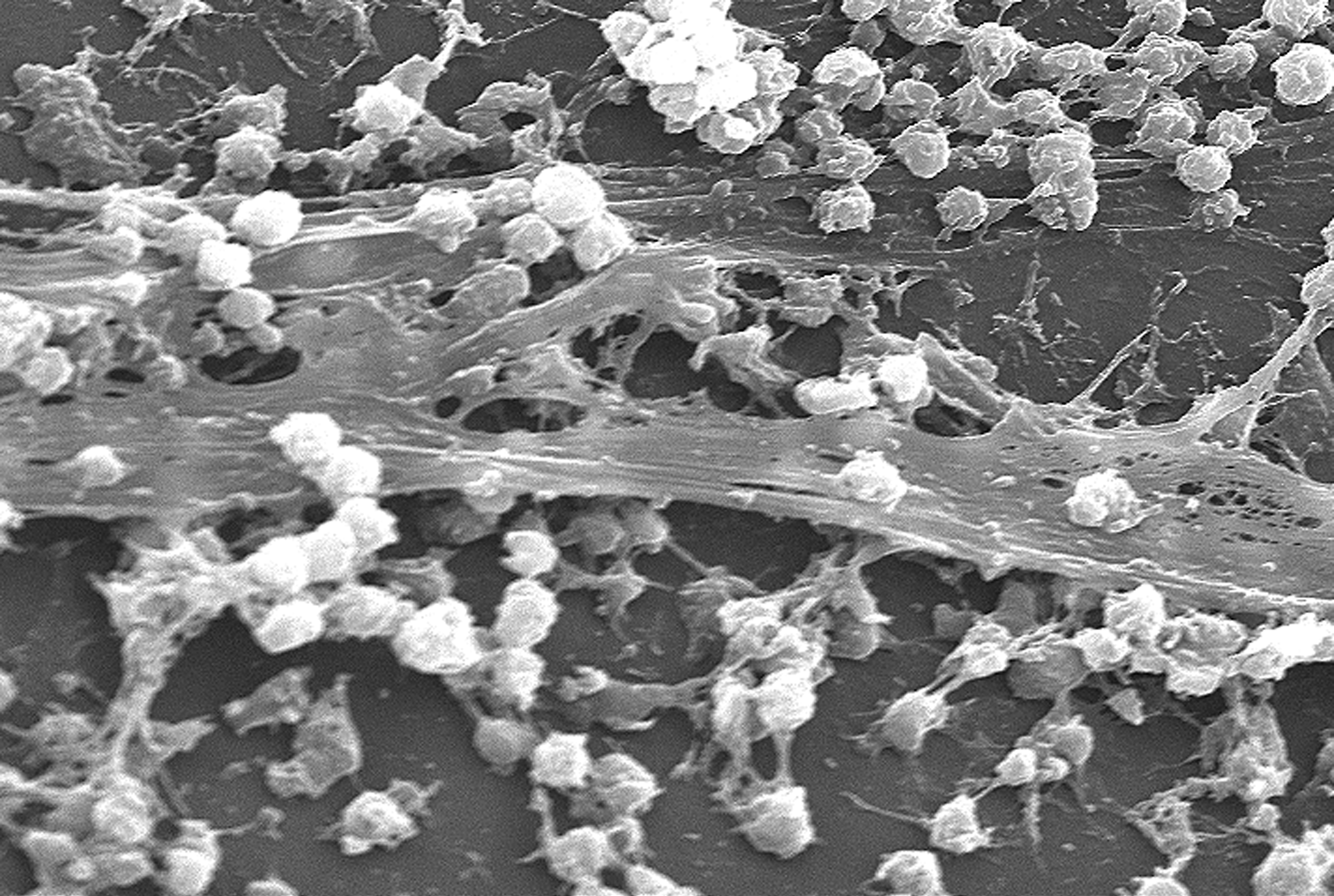
Biofilm
A biofilm is a Syntrophy, syntrophic Microbial consortium, community of microorganisms in which cell (biology), cells cell adhesion, stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs). The cells within the biofilm produce the EPS components, which are typically a polymeric combination of extracellular polysaccharides, proteins, lipids and DNA. Because they have a three-dimensional structure and represent a community lifestyle for microorganisms, they have been metaphorically described as "cities for microbes". Biofilms may form on living (biotic) or non-living (abiotic) surfaces and can be common in natural, industrial, and hospital settings. They may constitute a microbiome or be a portion of it. The microbial cells growing in a biofilm are physiology, physiologically distinct from planktonic cells of the same organism, which, by contrast, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detritus
In biology, detritus ( or ) is organic matter made up of the decomposition, decomposing remains of organisms and plants, and also of feces. Detritus usually hosts communities of microorganisms that colonize and decomposition, decompose (Remineralisation, remineralise) it. Such microorganisms may be decomposers, detritivores, or coprophages. In terrestrial ecosystems detritus is present as plant litter and other organic matter that is intermixed with soil, known as soil organic matter. The detritus of aquatic ecosystems is organic substances suspended in the water and accumulated in depositions on the floor of the body of water; when this floor is a seabed, such a deposition is called marine snow. Theory The remains of decaying plants or animals, or their tissue parts, and feces gradually lose their form due to physical processes and the action of decomposers, including grazers, bacteria, and fungi. Decomposition, the process by which organic matter is decomposed, occurs in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthesis, photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular microalgae, such as cyanobacteria, ''Chlorella'', and diatoms, to multicellular macroalgae such as kelp or brown algae which may grow up to in length. Most algae are aquatic organisms and lack many of the distinct cell and tissue types, such as stomata, xylem, and phloem that are found in embryophyte, land plants. The largest and most complex marine algae are called seaweeds. In contrast, the most complex freshwater forms are the Charophyta, a Division (taxonomy), division of green algae which includes, for example, ''Spirogyra'' and stoneworts. Algae that are carried passively by water are plankton, specifically phytoplankton. Algae constitute a Polyphyly, polyphyletic group because they do not include a common ancestor, and although Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemism
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or, in scientific literature, as an ''endemite''. Similarly, many species found in the Western ghats of India are examples of endemism. Endemism is an important concept in conservation biology for measuring biodiversity in a particular place and evaluating the risk of extinction for species. Endemism is also of interest in evolutionary biology, because it provides clues about how changes in the environment cause species to undergo range shifts (potentially expanding their range into a larger area or b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lotic
River ecosystems are flowing waters that drain the landscape, and include the biotic (living) interactions amongst plants, animals and micro-organisms, as well as abiotic (nonliving) physical and chemical interactions of its many parts.Angelier, E. 2003. Ecology of Streams and Rivers. Science Publishers, Inc., Enfield. Pp. 215."Biology Concepts & Connections Sixth Edition", Campbell, Neil A. (2009), page 2, 3 and G-9. Retrieved 2010-06-14. River ecosystems are part of larger watershed networks or catchments, where smaller headwater streams drain into mid-size streams, which progressively drain into larger river networks. The major zones in river ecosystems are determined by the river bed's gradient or by the velocity of the current. Faster moving turbulent water typically contains greater concentrations of dissolved oxygen, which supports greater biodiversity than the slow-moving water of pools. These distinctions form the basis for the division of rivers into upland and lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lentic
A lake ecosystem or lacustrine ecosystem includes biotic (living) plants, animals and micro-organisms, as well as abiotic (non-living) physical and chemical interactions. Lake ecosystems are a prime example of lentic ecosystems (''lentic'' refers to stationary or relatively still freshwater, from the Latin ''lentus'', which means "sluggish"), which include ponds, lakes and wetlands, and much of this article applies to lentic ecosystems in general. Lentic ecosystems can be compared with lotic ecosystems, which involve flowing terrestrial waters such as rivers and streams. Together, these two ecosystems are examples of freshwater ecosystems. Lentic systems are diverse, ranging from a small, temporary rainwater pool a few inches deep to Lake Baikal, which has a maximum depth of 1642 m. The general distinction between pools/ponds and lakes is vague, but Brown states that ponds and pools have their entire bottom surfaces exposed to light, while lakes do not. In addition, some lakes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Elgon
Mount Elgon is an extinct shield volcano on the border of Uganda and Kenya, north of Kisumu and west of Kitale. The mountain's highest point, named "Wagagai", is located entirely within Uganda."Mount Elgon, Uganda" Peakbagger.com. Retrieved 11 January 2012 Although there is no verifiable evidence of its earliest volcanic activity, geologists estimate that Mount Elgon is at least 24 million years old, making it the oldest known extinct volcano in . The mountain's name originates from its Maasai name, “Ol Doinyo Ilgoon” (Breast Mountain). ...
|
Sky Island
Sky islands are isolated mountains surrounded by radically different lowland environments. The term originally referred to those found on the Mexican Plateau and has extended to similarly isolated high-elevation forests. The isolation has significant implications for these natural habitats. Endemism, altitudinal migration, and relict populations are some of the natural phenomena to be found on sky islands. The complex dynamics of species richness on sky islands draws attention from the discipline of biogeography, and likewise the biodiversity is of concern to conservation biology. One of the key elements of a sky island is separation by physical distance from the other mountain ranges, resulting in a habitat island, such as a forest surrounded by desert. Some sky islands serve as refugia for boreal species stranded by warming climates since the last glacial period. In other cases, localized populations of plants and animals tend towards speciation, similar to oceanic isl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |