|
Buddy Bolden
Charles Joseph "Buddy" Bolden (September 6, 1877 – November 4, 1931) was an American cornetist who was regarded by contemporaries and later jazz scholars as a key figure in the development of a New Orleans style of ragtime music, or "jass", which later came to be known as jazz. Childhood When he was born, Bolden's father, Westmore Bolden, was working as a driver for William Walker, the former employer of Buddy's grandfather Gustavus Bolden, who was born in Louisiana in 1806 and died in 1866. Gustavus was most likely born into slavery, though no definitive records say. His mother, Alice (née Harris), was aged 18 when she married Westmore on August 14, 1873. Westmore Bolden was around 25 at the time, as records show that he was 19 in August 1866. When Buddy was six years old, his father died, after which the boy lived with his mother and other family members. In records of the period the family name is variously spelled ''Bolen'', ''Bolding'', ''Boldan'', and ''Bolden'', t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Orleans
New Orleans (commonly known as NOLA or The Big Easy among other nicknames) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of municipalities in Louisiana, most populous city in Louisiana and the French Louisiana region, the second-most populous in the Deep South, and the twelfth-most populous in the Southeastern United States. The city is coextensive with Orleans Parish, Louisiana, Orleans Parish. New Orleans serves as a major port and a commercial hub for the broader Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf Coast region. The New Orleans metropolitan area has a population of approximately 1 million, making it the most populous metropolitan area in Louisiana and the List of metropolitan statistical areas, 59th-most populous in the United States. New Orleans is world-renowned for Music of New Orleans, its distincti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freddie Keppard
Freddie Keppard (sometimes rendered as Freddy Keppard; February 27, 1890 – July 15, 1933) was an American jazz cornetist who once held the title of "King" in the New Orleans jazz scene. This title was previously held by Buddy Bolden and succeeded by Joe Oliver. Early life and career in New Orleans Keppard (pronounced in the French fashion, with relatively even accentuation and a silent ''d'') was born in the Creole of Color community of downtown New Orleans, Louisiana. Born in 1890, Keppard was Buddy Bolden's junior by thirteen years and Louis Armstrong's senior by eleven years. Keppard's father, Louis Keppard Sr., had been a New Orleans man and had worked as a cook in the Vieux Carré until his early death. His mother, Emily (Peterson) Keppard, was from St. James parish. His older brother, Louis, was his elder by two years and also became a professional musician later in life. The first tune they learned to play together was called "Just Because She Made Dem Goo-Goo Ey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dementia Praecox
Dementia praecox (meaning a "premature dementia" or "precocious madness") is a disused psychiatric diagnosis that originally designated a chronic, deteriorating psychotic disorder characterized by rapid cognitive disintegration, usually beginning in the late teens or early adulthood. Over the years, the term ''dementia praecox'' was gradually replaced by the term ''schizophrenia'', which initially had a meaning that included what is today considered the autism spectrum. The term ''dementia praecox'' was first used by German psychiatrist Heinrich Schüle in 1880. It was also used in 1891 by Arnold Pick (1851–1924), a professor of psychiatry at Karl-Ferdinands-Universität, Charles University in Prague. In a brief clinical report, he described a person with a psychotic disorder resembling "hebephrenia" (an adolescent-onset psychotic condition). German psychiatrist Emil Kraepelin (1856–1926) popularised the term ''dementia praecox'' in his first detailed textbook descriptions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychosis
In psychopathology, psychosis is a condition in which a person is unable to distinguish, in their experience of life, between what is and is not real. Examples of psychotic symptoms are delusions, hallucinations, and disorganized or incoherent thoughts or speech. Psychosis is a description of a person's state or symptoms, rather than a particular mental illness, and it is not related to psychopathy (a personality construct characterized by impaired empathy and remorse, along with bold, disinhibited, and egocentric traits). Common causes of chronic (i.e. ongoing or repeating) psychosis include schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder, bipolar disorder, and brain damage (usually as a result of alcoholism). Acute (temporary) psychosis can also be caused by severe distress, sleep deprivation, sensory deprivation, some medications, and drug use (including alcohol, cannabis, hallucinogens, and stimulants). Acute psychosis is termed primary if it results from a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
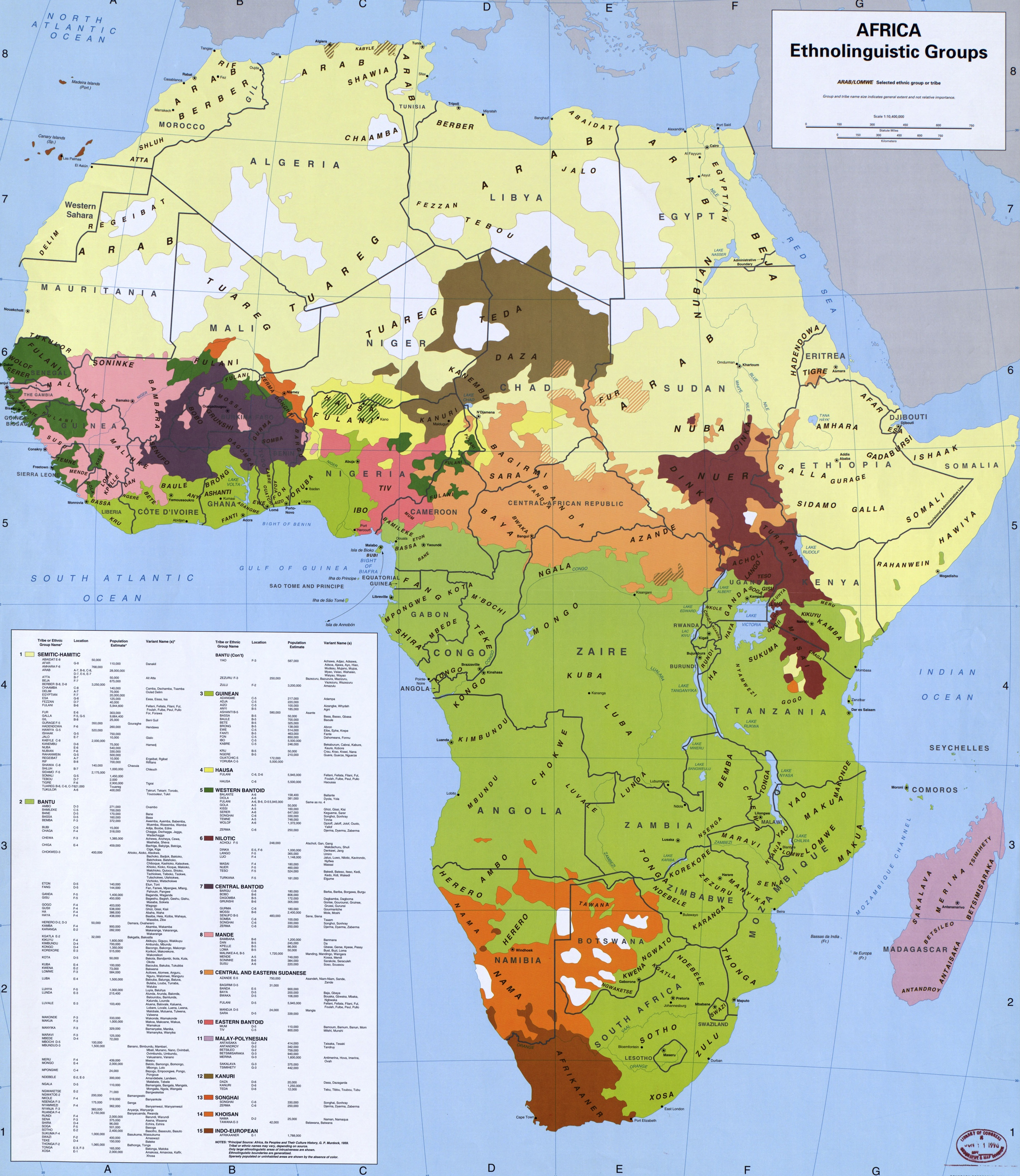
Sub-Saharan African Music Traditions
In many parts of sub-Saharan Africa, the use of music is not limited to entertainment: it serves a purpose to the local community and helps in the conduct of daily routines. Traditional African music supplies appropriate music and dance for work and for religious ceremonies of birth, naming, rites of passage, marriage and funerals. The beats and sounds of the drum are used in communication as well as in cultural expression. African dances are largely participatory: there are traditionally no barriers between dancers and onlookers except with regard to spiritual, religious and initiation dances. Even ritual dances often have a time when spectators participate. Dances help people work, mature, praise or criticize members of the community, celebrate festivals and funerals, compete, recite history, proverbs and poetry and encounter gods. They inculcate social patterns and values. Many dances are performed by only males or females. Dances are often segregated by gender, reinforcing ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habanera (music)
''Contradanza'' (also called ''contradanza criolla'', ''danza'', ''danza criolla'', or ''habanera'') is the Spanish and Spanish-American version of the contradanse, which was an internationally popular style of music and dance in the 18th century, derived from the English country dance and adopted at the court of France. Contradanza was brought to America and there took on folkloric forms that still exist in Bolivia, Mexico, Venezuela, Colombia, Peru, Panama and Ecuador. In Cuba during the 19th century, it became an important genre, the first written music to be rhythmically based on an African rhythm pattern and the first Cuban dance to gain international popularity, the progenitor of danzón, mambo and cha-cha-cha, with a characteristic "habanera rhythm" and sung lyrics. Outside Cuba, the Cuban contradanza became known as the ''habanera'' – the dance of Havana – and that name was adopted in Cuba itself subsequent to its international popularity in the later 19th centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jazz (miniseries)
''Jazz'' is a 2001 television documentary miniseries directed by Ken Burns. It was broadcast on Public Broadcasting Service, PBS in 2001 and was nominated for an Emmy Awards, Emmy Award for Primetime Emmy Award for Outstanding Documentary or Nonfiction Series, Outstanding Documentary or Nonfiction Series. Its chronological and thematic episodes provided a history of jazz, emphasizing innovative composers and musicians and American history. Swing (jazz performance style), Swing musicians Louis Armstrong and Duke Ellington are the central figures.Mark GilbertAmazon.co.ukreview Several episodes discussed the later contributions of Charlie Parker and Dizzy Gillespie to bebop, and of Miles Davis, Ornette Coleman, and John Coltrane to free jazz, free and cool jazz. Of this 10-part documentary surveying jazz in the years from 1917 to 2001, all but the last episode are devoted to music pre-1961. The series was produced by Florentine Films in cooperation with the BBC and in association wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Half Time (music)
In popular music, half-time is a type of meter and tempo that alters the rhythmic feel by essentially ''doubling the tempo resolution'' or metric division/level in comparison to common-time. Thus, two measures of approximate a single measure of , while a single measure of 4/4 emulates 2/2. Half-time is not to be confused with '' alla breve'' or odd time. Though notes usually get the same value relative to the tempo, the way the beats are divided is altered. While much music typically has a backbeat on quarter note (crotchet) beats two and four, half time would increase the interval between backbeats to double, thus making it hit on beats three and seven, or the third beat of each measure (count out of an 8 beat measure (bar), common practice in half time): 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 3 4 Essentially, a half time 'groove' is one that expands one measure over the course of two. The ''length'' of each note is doubled whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wynton Marsalis
Wynton Learson Marsalis (born October 18, 1961) is an American trumpeter, composer, and music instructor, who is currently the artistic director of Jazz at Lincoln Center. He has been active in promoting classical and jazz music, often to young audiences. Marsalis has won nine Grammy Awards, and his oratorio '' Blood on the Fields'' was the first jazz composition to win the Pulitzer Prize for Music. Marsalis is the only musician to have won a Grammy Award in both jazz and classical categories in the same year. Early years Marsalis was born in New Orleans, Louisiana, on October 18, 1961, and grew up in the suburb of Kenner. He is the second of six sons born to Dolores Ferdinand Marsalis and Ellis Marsalis Jr., a pianist and music teacher.Stated on ''Finding Your Roots'', PBS, March 25, 2012 He was named after jazz pianist Wynton Kelly. Branford Marsalis is his older brother and Jason Marsalis and Delfeayo Marsalis are younger. All three are jazz musicians. While sitting at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ken Burns Jazz
''Jazz'' is a 2001 television documentary miniseries directed by Ken Burns. It was broadcast on PBS in 2001 and was nominated for an Emmy Award for Outstanding Documentary or Nonfiction Series. Its chronological and thematic episodes provided a history of jazz, emphasizing innovative composers and musicians and American history. Swing musicians Louis Armstrong and Duke Ellington are the central figures.Mark GilbertAmazon.co.ukreview Several episodes discussed the later contributions of Charlie Parker and Dizzy Gillespie to bebop, and of Miles Davis, Ornette Coleman, and John Coltrane to free and cool jazz. Of this 10-part documentary surveying jazz in the years from 1917 to 2001, all but the last episode are devoted to music pre-1961. The series was produced by Florentine Films in cooperation with the BBC and in association with WETA-TV, Washington. Overview The documentary concerned the history of jazz music in the United States, from its origins at the turn of the 20th centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoffrey C
Geoffrey, Geoffroy, Geoff, etc., may refer to: People * Geoffrey (given name), including a list of people with the name Geoffrey or Geoffroy * Geoffroy (surname), including a list of people with the name * Geoffroy (musician) (born 1987), Canadian singer and songwriter Fictional characters * Geoffrey the Giraffe, the Toys "R" Us mascot * Geoff Peterson, an animatronic robot sidekick on ''The Late Late Show with Craig Ferguson'' * Geoff, a character from the cartoon series ''Total Drama'' * Geoff, Mark Corrigon's romantic rival on ''Peep Show (British TV series), Peep Show'' Other uses * Geoff (Greyhawk), a fictional land in the World of Greyhawk ''Dungeons & Dragons'' campaign setting See also * Galfrid * Geof * Gofraid/Goraidh * Godfrey (name) * Gottfried * Godefroy (other) * Goffredo * Jeffery (name) * Jeffrey (name) * Jeffries * Jeffreys * Jeffers * Jeoffry (cat) * Jeff {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ken Burns
Kenneth Lauren Burns (born July 29, 1953) is an American filmmaker known for his documentary films and television series, many of which chronicle American history and culture. His work is often produced in association with WETA-TV or the National Endowment for the Humanities and distributed by PBS. Burns lives in the small town of Walpole, New Hampshire. Burns's widely known documentary series include '' The Civil War'' (1990), ''Baseball'' (1994), ''Jazz'' (2001), '' The War'' (2007), '' The National Parks: America's Best Idea'' (2009), ''Prohibition'' (2011), '' The Roosevelts'' (2014), '' The Vietnam War'' (2017), and ''Country Music'' (2019). He was also executive producer of both '' The West'' (1996), and '' Cancer: The Emperor of All Maladies'' (2015). Burns's documentaries have earned two Academy Award nominations (for 1981's '' Brooklyn Bridge'' and 1985's '' The Statue of Liberty'') and have won several Emmy Awards, among other honors. Early life and education Burns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |