|
Bruach Na Frìthe
Bruach na Frìthe is one of the principal summits on the Black Cuillin ridge, on the Isle of Skye, Scotland. Like the rest of the range it is composed of gabbro, a rock with excellent grip for mountaineering. The Bruach cannot be seen in the popular view from Sligachan - the right hand peak which is often mistaken for it is the lower Sgurr a' Bhasteir. This is one of the easiest and probably the most ascended of the main Black Cuillin peaks, requiring no scrambling ability. The simplest route ascends via Fionn Coire, though the slightly harder Northwest Ridge is also a popular route. All routes cross steep ground and scree. The summit is one of the best viewpoints in the Cuillin. Though not the highest peak in the range, it is the only one to have an Ordnance Survey pillar. References External links YouTube video of ascent of Bruach na Frithe via Fionn ChoireGuide to an ascent of Bruach na Frithe {{DEFAULTSORT:Bruach Na Frithe Munros Mountains and hills of the Isle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuillin
The Cuillin () is a range of mostly jagged rocky mountains on the Isle of Skye in Scotland. The main Cuillin ridge is also called the Black Cuillin to distinguish it from the Red Cuillin ('), which lie to the east of Glen Sligachan.R. Anderson & Tom Prentice. ''The Grahams & The Donalds - Scottish Mountaineering Club Hillwalkers' Guide'', pp. 304–309. Published 2015. The peaks of the Black Cuillin are mainly composed of gabbro, a very rough igneous rock which provides a superb grip for mountaineering, mountaineers; and basalt, which can be very slippery when wet.D. Bennet & R. Anderson. ''The Munros: Scottish Mountaineering Club Hillwalkers Guide'', pp. 258–275. Published 2016. The rocks forming the ridge of the Black Cuillin (and outliers such Blà Bheinn) are dark, particularly in the shade, but when in sunlight the Black Cuillin can appear grey to brown. The main ridge forms a narrow crest, with steep cliffs and scree slopes. The ridge is about long (from Gars-bheinn in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munro
A Munro (; ) is defined as a mountain in Scotland with a height over , and which is on the Scottish Mountaineering Club (SMC) official list of Munros; there is no explicit topographical prominence requirement. The best known Munro is Ben Nevis (Beinn Nibheis), the highest mountain in the British Isles at 4,411 ft (1,345 m). Munros are named after Sir Hugh Munro, 4th Baronet (1856–1919), who produced the first list of such hills, known as ''Munro's Tables'', in 1891. Also included were what Munro considered lesser peaks, now known as Munro Tops, which are also over 3,000 feet but are lower than the nearby primary mountain. The publication of the original list is usually considered to be the Epoch (reference date), epoch event of modern peak bagging. The list has been the subject of subsequent variation and , the Scottish Mountaineering Club has listed 282 Munros and 226 Munro Tops. "Munro bagging" is the activity of climbing all the listed Munros. , 7,654 people had rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Gaelic Language
Scottish Gaelic (, ; Endonym and exonym, endonym: ), also known as Scots Gaelic or simply Gaelic, is a Celtic language native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a member of the Goidelic language, Goidelic branch of Celtic, Scottish Gaelic, alongside both Irish language, Irish and Manx language, Manx, developed out of Old Irish. It became a distinct spoken language sometime in the 13th century in the Middle Irish period, although a Classical Gaelic, common literary language was shared by the Gaels of both Ireland and Scotland until well into the 17th century. Most of modern Scotland was once Gaelic-speaking, as evidenced especially by Gaelic-language place names. In the 2011 United Kingdom census#2011 Census for Scotland, 2011 census of Scotland, 57,375 people (1.1% of the Scottish population, three years and older) reported being able to speak Gaelic, 1,275 fewer than in 2001. The highest percentages of Gaelic speakers were in the Outer Hebrides. Nevertheless, there is a language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
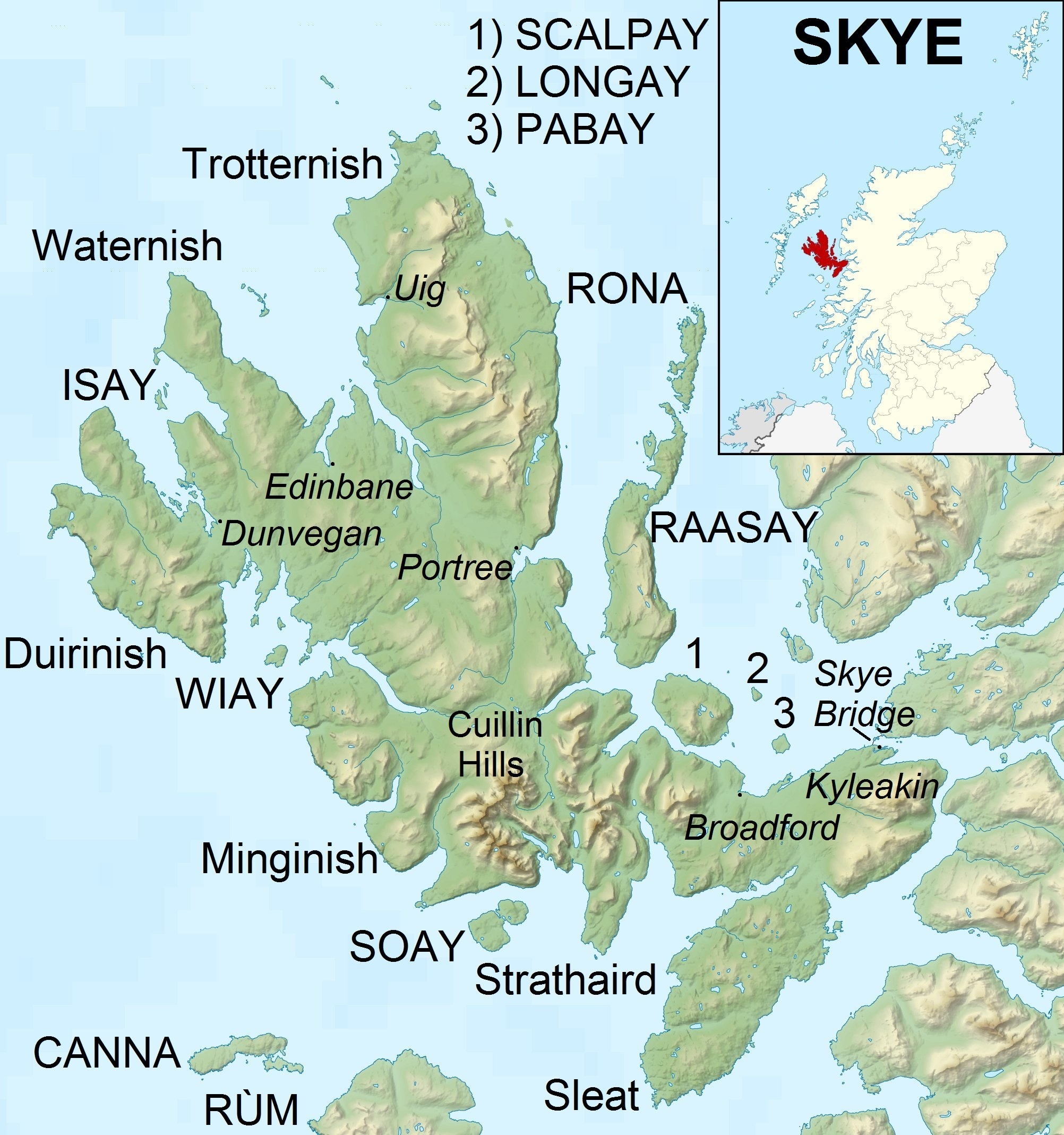
Isle Of Skye
The Isle of Skye, or simply Skye, is the largest and northernmost of the major islands in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The island's peninsulas radiate from a mountainous hub dominated by the Cuillin, the rocky slopes of which provide some of the most dramatic mountain scenery in the country.#Slesser70, Slesser (1981) p. 19. Although has been suggested to describe a winged shape, no definitive agreement exists as to the name's origin."Gaelic Culture" . VisitScotland. Retrieved 5 January 2013. The island has been occupied since the Mesolithic period, and over its history has been occupied at various times by Celtic tribes including the Picts and the Gaels, Scandinavian Vikings, and most notably the powerful integrated Norse-Gaels clans of Clan MacLeod, MacLeod and Clan Donald, MacDonald. The island was considered to be under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjacent Islands of Scotland, islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. To the south-east, Scotland has its Anglo-Scottish border, only land border, which is long and shared with England; the country is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the north-east and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. The population in 2022 was 5,439,842. Edinburgh is the capital and Glasgow is the most populous of the cities of Scotland. The Kingdom of Scotland emerged as an independent sovereign state in the 9th century. In 1603, James VI succeeded to the thrones of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, forming a personal union of the Union of the Crowns, three kingdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordnance Survey
The Ordnance Survey (OS) is the national mapping agency for Great Britain. The agency's name indicates its original military purpose (see Artillery, ordnance and surveying), which was to map Scotland in the wake of the Jacobite rising of 1745. There was also a more general and nationwide need in light of the potential threat of invasion during the Napoleonic Wars. Since 1 April 2015, the Ordnance Survey has operated as Ordnance Survey Ltd, a state-owned enterprise, government-owned company, 100% in public ownership. The Ordnance Survey Board remains accountable to the Secretary of State for Science, Innovation and Technology. It was also a member of the Public Data Group. Paper maps represent only 5% of the company's annual revenue. It produces digital map data, online route planning and sharing services and mobile apps, plus many other location-based products for business, government and consumers. Ordnance Survey mapping is usually classified as either "Scale (map), lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scrambling
Scrambling is a mountaineering term for ascending steep terrain using one's hands to assist in holds and balance.''New Oxford American Dictionary''. It can be described as being between hiking and climbing, rock climbing. "A scramble" is a related term, denoting terrain that could be ascended in this way. Sure-footedness and a head for heights are essential. Canyoning and stream climbing both involve scrambling. Overview Scrambling is ascending or traversing a grade without technical apparatus. Unroped ascent in exposure (heights), exposed situations is potentially one of the most dangerous of mountaineering activities. As soon as an ascent involves a rope, going up or down, it is no longer a scramble. Alpine scrambling Alpine scrambling is scrambling in high mountains and may not follow a defined or waymarked path. The Seattle Mountaineers climbing organization defines alpine scrambling as follows: Alpine Scrambles are off-trail trips, often on snow or rock, with a 'non-t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruach Na Frithe Cairn Arp
Lillian Beckwith (25 April 1916 – 3 January 2004), real name Lillian Comber, was an English writer best known for her series of semi-autobiographical books set on the Outer Hebrides. Born Lilian Lloyd in Ellesmere Port, Cheshire, she married Edward Comber in 1937, and in 1942 she moved with him to Elgol, Isle of Skye, under doctor's orders for a rest. Moving to the nearby and smaller Isle of Soay, Skye, Soay, she eventually bought and ran her own croft (land), croft. Her life on the island provided the basis for seven books published between 1959 and 1978, although allegedly, some of her neighbours later felt that the somewhat comical characters on Beckwith's fictional island of Bruach were too close to real persons, causing Beckwith to become something of a ''persona non grata'' in her former home. She moved to the Isle of Man in 1962 and died on 3 January 2004 aged 87. Bibliography Skye series *1959 - ''The Hills is Lonely'' �Chapter 1 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Cuillin
The Cuillin () is a range of mostly jagged rocky mountains on the Isle of Skye in Scotland. The main Cuillin ridge is also called the Black Cuillin to distinguish it from the Red Cuillin ('), which lie to the east of Glen Sligachan.R. Anderson & Tom Prentice. ''The Grahams & The Donalds - Scottish Mountaineering Club Hillwalkers' Guide'', pp. 304–309. Published 2015. The peaks of the Black Cuillin are mainly composed of gabbro, a very rough igneous rock which provides a superb grip for mountaineering, mountaineers; and basalt, which can be very slippery when wet.D. Bennet & R. Anderson. ''The Munros: Scottish Mountaineering Club Hillwalkers Guide'', pp. 258–275. Published 2016. The rocks forming the ridge of the Black Cuillin (and outliers such Blà Bheinn) are dark, particularly in the shade, but when in sunlight the Black Cuillin can appear grey to brown. The main ridge forms a narrow crest, with steep cliffs and scree slopes. The ridge is about long (from Gars-bheinn in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
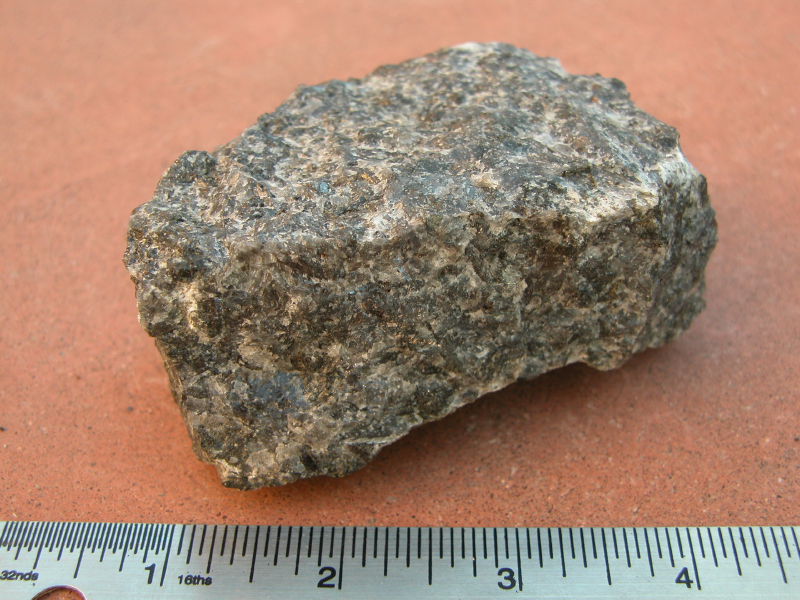
Gabbro
Gabbro ( ) is a phaneritic (coarse-grained and magnesium- and iron-rich), mafic intrusive igneous rock formed from the slow cooling magma into a holocrystalline mass deep beneath the Earth's surface. Slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro is chemically equivalent to rapid-cooling, fine-grained basalt. Much of the Earth's oceanic crust is made of gabbro, formed at mid-ocean ridges. Gabbro is also found as plutons associated with continental volcanism. Due to its variant nature, the term ''gabbro'' may be applied loosely to a wide range of intrusive rocks, many of which are merely "gabbroic". By rough analogy, gabbro is to basalt as granite is to rhyolite. Etymology The term "gabbro" was used in the 1760s to name a set of rock types that were found in the ophiolites of the Apennine Mountains in Italy. It was named after Gabbro, a hamlet near Rosignano Marittimo in Tuscany. Then, in 1809, the German geologist Christian Leopold von Buch used the term more restrictively in his d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountaineering
Mountaineering, mountain climbing, or alpinism is a set of outdoor activities that involves ascending mountains. Mountaineering-related activities include traditional outdoor climbing, skiing, and traversing via ferratas that have become mountain sports, sports in their own right. Indoor climbing, sport climbing, and bouldering are also considered variants of mountaineering by some, but are part of a wide group of mountain sports. Unlike most sports, mountaineering lacks widely applied formal rules, regulations, and governance; mountaineers adhere to a large variety of techniques and philosophies (including grade (climbing), grading and climbing guidebook, guidebooks) when climbing mountains. Numerous local alpine clubs support mountaineers by hosting resources and social activities. A federation of alpine clubs, the International Climbing and Mountaineering Federation (UIAA), is the International Olympic Committee-recognized world organization for mountaineering and climbing. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scree
Scree is a collection of broken rock fragments at the base of a cliff or other steep rocky mass that has accumulated through periodic rockfall. Landforms associated with these materials are often called talus deposits. The term ''scree'' is applied both to an unstable steep mountain slope composed of rock fragments and other debris, and to the mixture of rock fragments and debris itself. It is loosely synonymous with talus, material that accumulates at the base of a projecting mass of rock, or talus slope, a landform composed of talus. The term ''scree'' is sometimes used more broadly for any sheet of loose rock fragments mantling a slope, while ''talus'' is used more narrowly for material that accumulates at the base of a cliff or other rocky slope from which it has obviously eroded. Scree is formed by rockfall, which distinguishes it from colluvium. Colluvium is rock fragments or soil deposited by rainwash, sheetwash, or slow downhill creep, usually at the base of gentle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |