|
Broadcast To Allied Merchant Ships
Broadcast to Allied Merchant Ships (BAMS) was a protocol and system of broadcasts for Allied Maritime transport, merchant ship convoys that was used during World War II to provide for the transmission of official messages to merchant ships in any part of the world. The BAMS system is designed for communication by the best employment of radio stations available. Background On the outbreak of World War II, the British Admiralty took over control from the GPO, and the embryo merchant ship broadcast system, called ''GBMS'' came into force. Ships listened at routine times to the Rugby Radio Station and to area stations, otherwise keeping watch on the international distress frequency at 500 kHz. After the fall of France, the Admiralty assumed control of all Allied merchant shipping which complied with British procedures. When America entered the war, the world was divided into two strategic zones, the Admiralty being responsible for merchant shipping in one, and the United States N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maritime Transport
Maritime transport (or ocean transport) and hydraulic effluvial transport, or more generally waterborne transport, is the transport of people ( passengers) or goods ( cargo) via waterways. Freight transport by sea has been widely used throughout recorded history. The advent of aviation has diminished the importance of sea travel for passengers, though it is still popular for short trips and pleasure cruises. Transport by water is cheaper than transport by air, despite fluctuating exchange rates and a fee placed on top of freighting charges for carrier companies known as the currency adjustment factor. Maritime transport accounts for roughly 80% of international trade, according to UNCTAD in 2020. Maritime transport can be realized over any distance by boat, ship, sailboat or barge, over oceans and lakes, through canals or along rivers. Shipping may be for commerce, recreation, or military purposes. While extensive inland shipping is less critical today, the majo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultra (cryptography)
adopted by British military intelligence in June 1941 for wartime signals intelligence obtained by breaking high-level encrypted enemy radio and teleprinter communications at the Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS) at Bletchley Park. ''Ultra'' eventually became the standard designation among the western Allies for all such intelligence. The name arose because the intelligence obtained was considered more important than that designated by the highest British security classification then used (''Most Secret'') and so was regarded as being ''Ultra Secret''. Several other cryptonyms had been used for such intelligence. The code name ''Boniface'' was used as a cover name for ''Ultra''. In order to ensure that the successful code-breaking did not become apparent to the Germans, British intelligence created a fictional MI6 master spy, Boniface, who controlled a fictional series of agents throughout Germany. Information obtained through code-breaking was often attributed to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio During World War II
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connected to an antenna which radiates the waves, and received by another antenna connected to a radio receiver. Radio is very widely used in modern technology, in radio communication, radar, radio navigation, remote control, remote sensing, and other applications. In radio communication, used in radio and television broadcasting, cell phones, two-way radios, wireless networking, and satellite communication, among numerous other uses, radio waves are used to carry information across space from a transmitter to a receiver, by modulating the radio signal (impressing an information signal on the radio wave by varying some aspect of the wave) in the transmitter. In radar, used to locate and track objects like aircraft, ships, spacecraft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
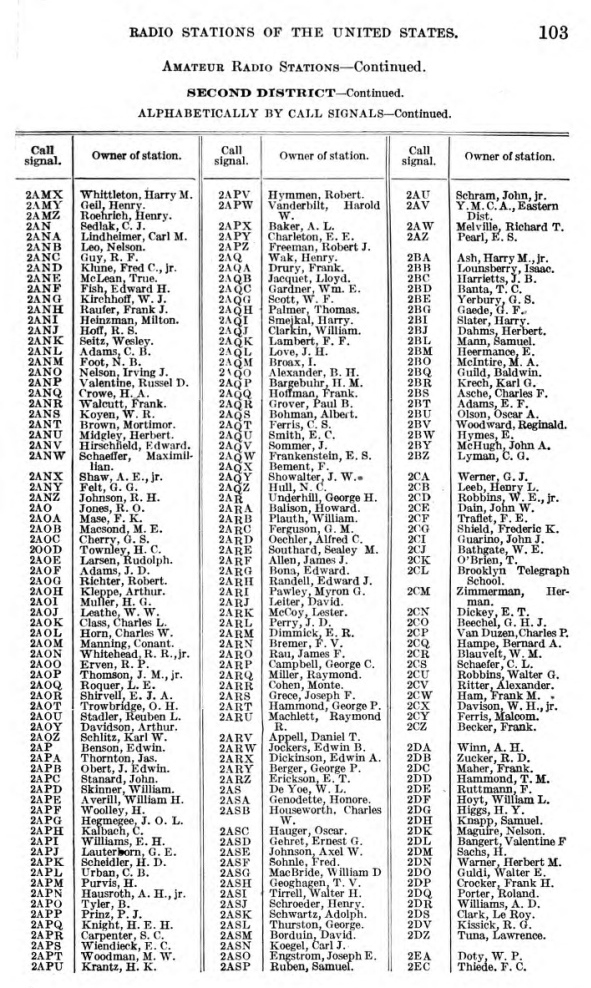
Call Sign
In broadcasting and radio communications, a call sign (also known as a call name or call letters—and historically as a call signal—or abbreviated as a call) is a unique identifier for a transmitter station. A call sign can be formally assigned by a government agency, informally adopted by individuals or organizations, or even cryptographically encoded to disguise a station's identity. The use of call signs as unique identifiers dates to the landline railroad telegraph system. Because there was only one telegraph line linking all railroad stations, there needed to be a way to address each one when sending a telegram. In order to save time, two-letter identifiers were adopted for this purpose. This pattern continued in radiotelegraph operation; radio companies initially assigned two-letter identifiers to coastal stations and stations onboard ships at sea. These were not globally unique, so a one-letter company identifier (for instance, 'M' and two letters as a Marcon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Q Code
The Q-code is a standardised collection of three-letter codes that each start with the letter "Q". It is an operating signal initially developed for commercial radiotelegraph communication and later adopted by other radio services, especially amateur radio. To distinguish the use of a Q-code transmitted as a question from the same Q-code transmitted as a statement, operators either prefixed it with the military network question marker "" (dit dit dah dit dah) or suffixed it with the standard Morse question mark (dit dit dah dah dit dit). Although Q-codes were created when radio used Morse code exclusively, they continued to be employed after the introduction of voice transmissions. To avoid confusion, transmitter call signs are restricted; no country is ever issued an ITU prefix starting with "Q". Codes in the range QAA–QNZ are reserved for aeronautical use; QOA–QQZ for maritime use and QRA–QUZ for all services. "Q" has no official meaning, but it is sometimes assig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British And US Radio Stations Used By BAMS, Page 1
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies. ** Britishness, the British identity and common culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in the United Kingdom or, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *''Brit(ish)'', a 2018 memoir by Afua Hirsch *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) See also * Terminology of the British Isles * Alternative names for the British * English (other) * Britannic (other) * British Isles * Brit (other) * Bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belize
Belize (; bzj, Bileez) is a Caribbean and Central American country on the northeastern coast of Central America. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and Guatemala to the west and south. It also shares a water boundary with Honduras to the southeast. It has an area of and a population of 441,471 (2022). Its mainland is about long and wide. It is the least populated and least densely populated country in Central America. Its population growth rate of 1.87% per year (2018 estimate) is the second-highest in the region and one of the highest in the Western Hemisphere. Its capital is Belmopan, and its largest city is the namesake city of Belize City. Belize is often thought of as a Caribbean country in Central America because it has a history similar to that of English-speaking Caribbean nations. Indeed, Belize’s institutions and official language reflect its history as a British colony. The Maya civilization spread into the area of B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panama Sea Frontier
The Panama Sea Frontier was a U.S. Navy command responsible during and shortly after World War II for the defense of the Pacific and Atlantic sea approaches to the Panama Canal and naval shore facilities in the Central America region. The Sea Frontier headquarters were located in Balboa, Panama. On the west coast of the Americas, the responsibility of the Panama Sea Frontier was to protect Allied shipping in an ocean area extending from the Mexico- Guatemala border and out around the Galapagos, then to latitude 5 degree south. On the eastern side of Panama, the sea frontier was responsible for the coastal areas from the Mexico-British Honduras boundary on the Yucatán Peninsula along latitude 18 degrees 5 minutes north to longitude 80 degrees 27 minutes west, and thence to Punta de Gallinas. However, the prime responsibility of this sea frontier was the protection and defense of the Panama Canal and its operating equipment. The Panama Sea Frontier also had to contend with politi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commodore (rank)
Commodore is a senior naval rank used in many navies which is equivalent to brigadier and air commodore. It is superior to a navy captain, but below a rear admiral. It is either regarded as the most junior of the flag officers rank or may not hold the jurisdiction of a flag officer at all depending on the officer's appointment. Non-English-speaking nations commonly use the rank of flotilla admiral, counter admiral, or senior captain as an equivalent, although counter admiral may also correspond to ''rear admiral lower half'' abbreviated as RDML. Traditionally, "commodore" is the title for any officer assigned to command more than one ship, even temporarily, much as "captain" is the traditional title for the commanding officer of a single ship even if the officer's official title in the service is a lower rank. As an official rank, a commodore typically commands a flotilla or squadron of ships as part of a larger task force or naval fleet commanded by an admiral. A commod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Call Sign
In broadcasting and radio communications, a call sign (also known as a call name or call letters—and historically as a call signal—or abbreviated as a call) is a unique identifier for a transmitter station. A call sign can be formally assigned by a government agency, informally adopted by individuals or organizations, or even cryptographically encoded to disguise a station's identity. The use of call signs as unique identifiers dates to the landline railroad telegraph system. Because there was only one telegraph line linking all railroad stations, there needed to be a way to address each one when sending a telegram. In order to save time, two-letter identifiers were adopted for this purpose. This pattern continued in radiotelegraph operation; radio companies initially assigned two-letter identifiers to coastal stations and stations onboard ships at sea. These were not globally unique, so a one-letter company identifier (for instance, 'M' and two letters as a Marcon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BAMS Arranging Authorities List, Page 1
''Bild am Sonntag'' (''BamS'') is the largest-selling German national Sunday newspaper published in Berlin, Germany. History and profile ''Bild am Sonntag'' was first published on 29 April 1956.Helmut Böger, ''Bild'', 8 May 2011Die Story von BamS ist auch seine Story/ref> The paper is published weekly by Axel Springer AG and is a sister paper to the Monday-to-Saturday ''Bild''. Its editor from 2008 to 2013 was Walter Mayer.Personalien: Chefredakteurswechsel bei BILD am SONNTAG, B.Z./B.Z. am Sonntag und Hamburger Abendblatt ''Axel Springer''. 10 July 2008 The new editorship is taken by Marion Horn since 2013. The paper publishes the '' [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_off_Balboa_1943.jpg)