|
British Industrial Architecture
British industrial architecture has been created, mainly from 1700 onwards, to house industries of many kinds in Britain, home of the Industrial Revolution in this period. Both the new industrial technologies and industrial architecture soon spread worldwide. As such, the architecture of surviving industrial buildings records part of the history of the modern world. Some industries were immediately recognisable by the functional shapes of their buildings, as with glass cones and the bottle kilns of potteries. The transport industry was supported first by the growth of a network of canals, then of a network of railways, contributing landmark structures such as the Pontcysyllte Aqueduct and the Ribblehead Viaduct. New materials made available in large quantities by the newly-developed industries enabled novel types of construction, including reinforced concrete and steel. Industrial architects freely explored a variety of styles for their buildings, from Egyptian Revival to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoover Building In Perivale (cropped)
Hoover may refer to: Music * Hoover (band), an American post-hardcore band * Hooverphonic, a Belgian band originally named Hoover * Hoover (singer), Willis Hoover, a country and western performer active in 1960s and '70s * Hoover (song), "Hoover" (song), a 2016 song by Swedish rapper Yung Lean * Hoover sound, a heavy bass driven drone sound used in electronic music * Katherine Hoover, Hoover (composer), Katherine Hoover an American contemporary classical music and chamber music composer. People * Hoover (surname) ** Herbert Hoover, 31st president of the United States ** J. Edgar Hoover (1895–1972), first director of the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) * Hoover Orsi (born 1978), Brazilian race car driver * Hoover J. Wright (1928–2003), American football and track and field coach Places in the United States * Hoover, Alabama, the 6th largest city in Alabama * Hoover, Indiana * Hoover, Missouri * Hoover, Oklahoma * Hoover, South Dakota * Hoover, Texas * Hoover Dam, on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoover Building
The Hoover Building is a Listed building, Grade II* listed building of Art Deco architecture designed by Wallis, Gilbert and Partners located in Perivale in the London Borough of Ealing. The site opened in 1933 as the UK headquarters, manufacturing plant and repairs centre for The Hoover Company. The building is now owned by IDM Properties and has been converted into apartments. History The main building was opened in May 1933 by George Kemp, 1st Baron Rochdale, Lord Rochdale as the UK headquarters for The Hoover Company. This was designed by Wallis, Gilbert and Partners - the same firm that designed the Firestone Tyre Factory in Brentford and Victoria Coach Station in Central London. Thomas Wallis said of the Art Deco design: ’A little money spent in the incorporation of some form of decoration, especially colour, is not money wasted. It has a psychological effect on the worker.’ Soon after the main building was built, plans were drawn up for a manufacturing plant. As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
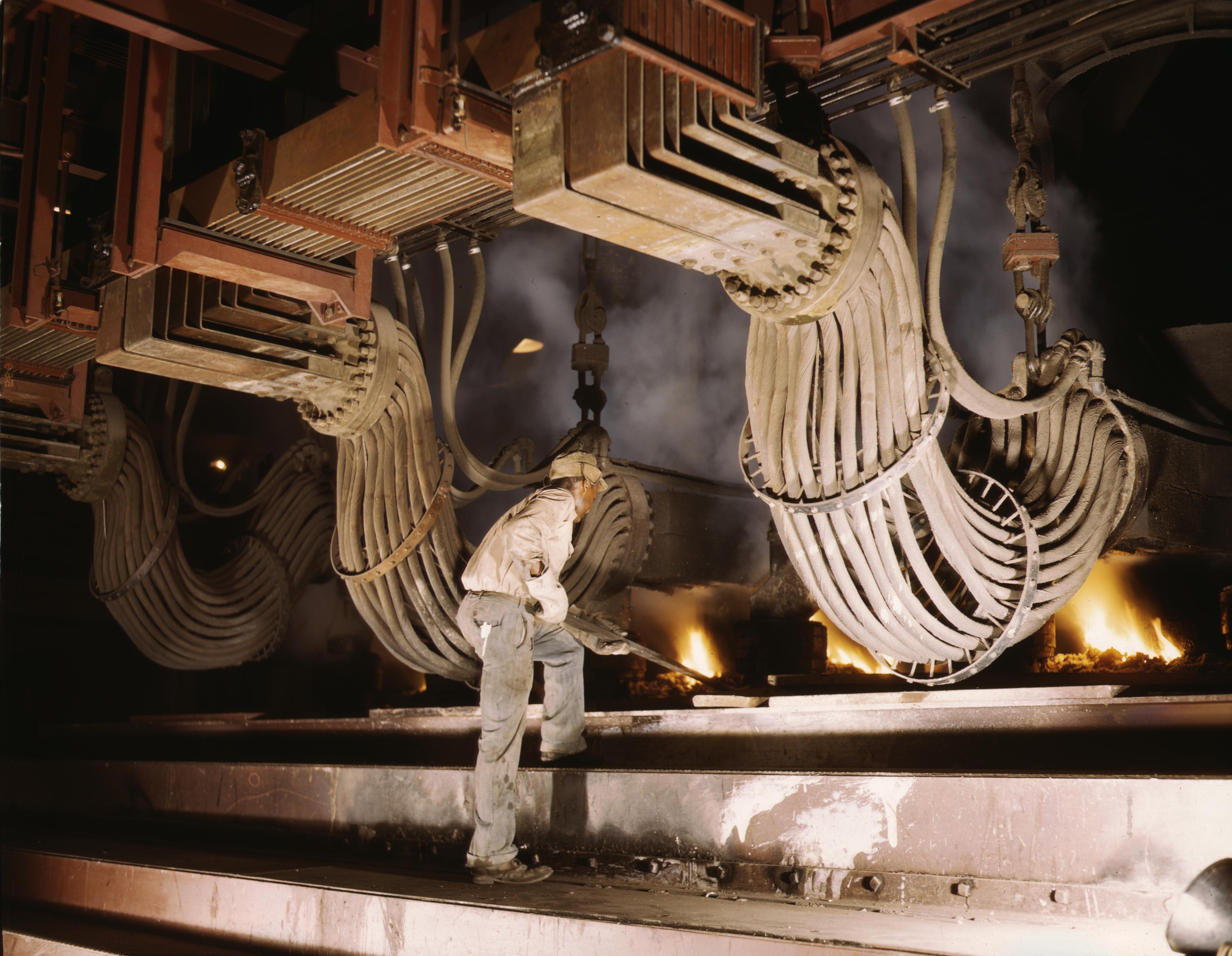
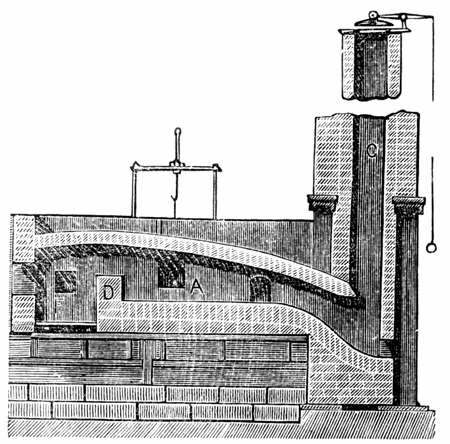
Puddling (metallurgy)
Puddling is the process of converting pig iron to bar (wrought) iron in a coal fired reverberatory furnace. It was developed in England during the 1780s. The molten pig iron was stirred in a reverberatory furnace, in an Redox, oxidizing environment to burn the carbon, resulting in wrought iron. It was one of the most important processes for making the first appreciable volumes of valuable and useful wrought iron, bar iron (malleable wrought iron) without the use of charcoal. Eventually, the furnace would be used to make small quantities of specialty steels. Though it was not the first process to produce bar iron without charcoal, puddling was by far the most successful, and replaced the earlier potting and stamping processes, as well as the much older charcoal finery forge, finery and bloomery processes. This enabled a great expansion of iron production to take place in Great Britain, and shortly afterwards, in North America. That expansion constitutes the beginnings of the Ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Smelting
Smelting is a process of applying heat and a chemical reducing agent to an ore to extract a desired base metal product. It is a form of extractive metallurgy that is used to obtain many metals such as iron, copper, silver, tin, lead and zinc. Smelting uses heat and a chemical reducing agent to decompose the ore, driving off other elements as gases or slag and leaving the metal behind. The reducing agent is commonly a fossil-fuel source of carbon, such as carbon monoxide from incomplete combustion of coke—or, in earlier times, of charcoal. The oxygen in the ore binds to carbon at high temperatures, as the chemical potential energy of the bonds in carbon dioxide () is lower than that of the bonds in the ore. Sulfide ores such as those commonly used to obtain copper, zinc or lead, are roasted before smelting in order to convert the sulfides to oxides, which are more readily reduced to the metal. Roasting heats the ore in the presence of oxygen from air, oxidizing the ore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Farnolls Pritchard
Thomas Farnolls Pritchard (also known as Farnolls Pritchard; baptised 11 May 1723 – 23 December 1777) was an English architect and interior decorator who is best remembered for his design of the first cast-iron bridge in the world. Biography Pritchard was born in Shrewsbury, Shropshire, and baptised in St Julian's Church, Shrewsbury on 11 May 1723. His father was a joiner. Thomas also trained as a joiner, but then developed a professional practice as an architect and interior designer. He specialised in the design of chimney-pieces and other items of interior decoration, and in funerary monuments.Leach, Peter, ‘Pritchard, Thomas Farnolls (''bap''. 1723, ''d''.1798)’, ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, 2004; online edn, May 200 accessed 1 September 2008. Pritchard worked closely with other local architects and craftsmen. William Baker of Audlem, an architect and contractor, used his plans to construct St John's Church, Wolverhampton. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International security, security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It has 194 Member states of UNESCO, member states and 12 associate members, as well as partners in the Non-governmental organization, non-governmental, Intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental and private sector. Headquartered in Paris, France, UNESCO has 53 regional field offices and 199 National Commissions for UNESCO, national commissions. UNESCO was founded in 1945 as the successor to the League of Nations' International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation.English summary). UNESCO's founding mission, which was shaped by the events of World War II, is to advance peace, sustainable development and human rights by facilitating collaboratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of World Heritage Sites In The United Kingdom
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) World Heritage Sites are places of importance to cultural or natural heritage as described in the UNESCO World Heritage Convention, established in 1972. Cultural heritage consists of monuments (such as architectural works, monumental sculptures, or inscriptions), groups of buildings, and sites (including archaeological sites). Natural features (consisting of physical and biological formations), geological and physiographical formations (including habitats of threatened species of animals and plants), and natural sites which are important from the point of view of science, conservation or natural beauty are defined as natural heritage. The United Kingdom ratified the convention on 29 May 1984, making its sites eligible for inclusion on the list. There are 35 World Heritage Sites in the United Kingdom and the British Overseas Territories. Out of these sites, one site is located in both England and Scotla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
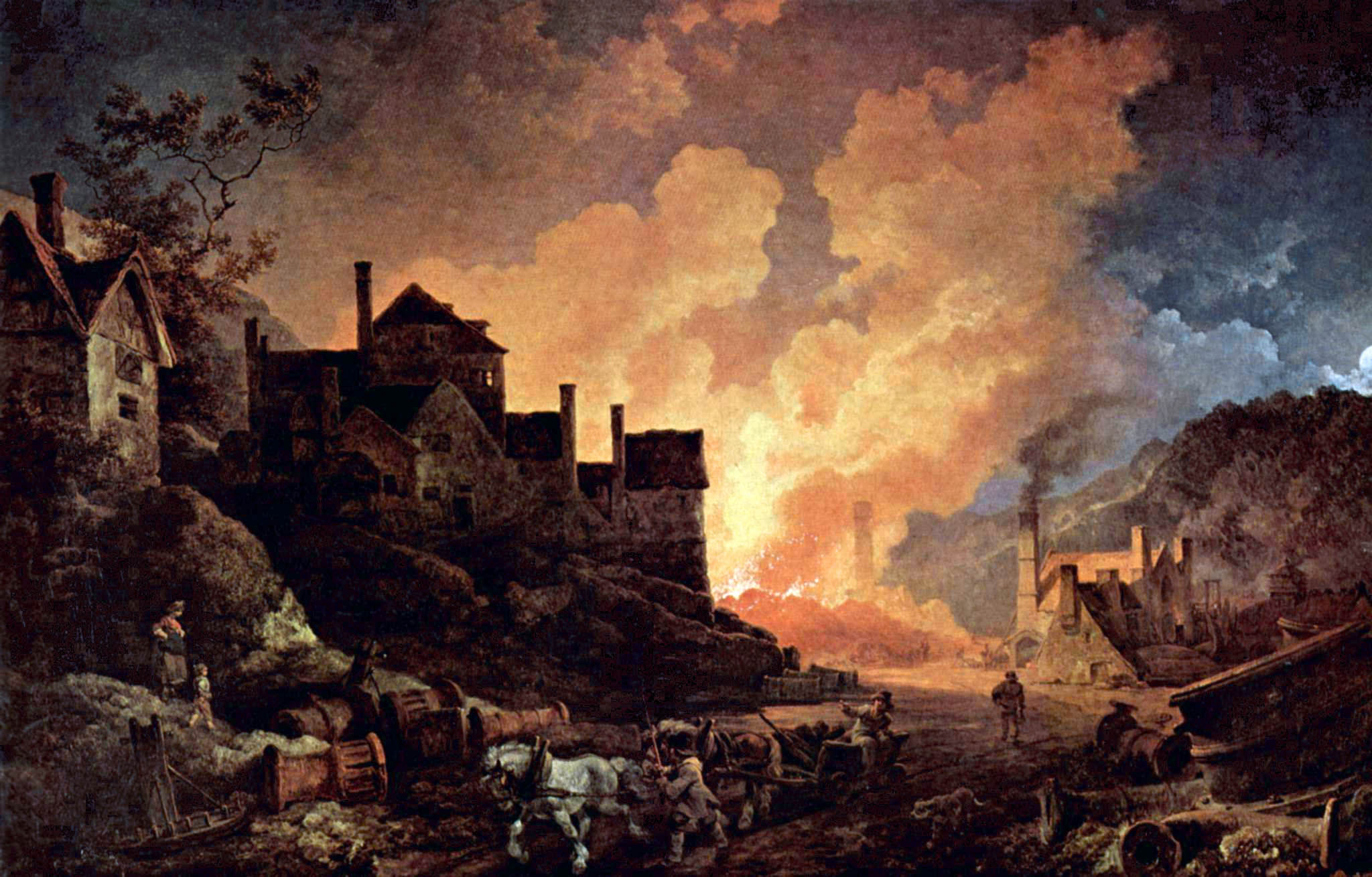
Coalbrookdale By Night
''Coalbrookdale by Night'' is an oil painting by Philip James de Loutherbourg, from 1801. It is held at the Science Museum, in London. History and description The painting depicts the Madeley Wood (or Bedlam) Furnaces, which belonged to the Coalbrookdale Company from 1776 to 1796. The picture has come to symbolize the birth of the Industrial Revolution in the Ironbridge Gorge, Shropshire, England. Loutherbourg undertook tours of England and Wales during 1786 and 1800, observing industrial activity at the time. ''Coalbrookdale by Night'' provides a view of the Bedlam Furnaces in Madeley Dale, downstream along the River Severn The River Severn (, ), at long, is the longest river in Great Britain. It is also the river with the most voluminous flow of water by far in all of England and Wales, with an average flow rate of at Apperley, Gloucestershire. It rises in t ... from the town of Ironbridge itself. Professor Brian Lukacher dubbed the picture as "the best known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip De Loutherbourg
Philip James de Loutherbourg, RA (born Philippe Jacques de Loutherbourg; 31 October 174011 March 1812) was a French-born British painter who became known for his large naval works, his elaborate set designs for London theatres, and his invention of a mechanical theatre called the " Eidophusikon". He also had an interest in faith-healing and the occult, and was a companion of the confidence-trickster Alessandro Cagliostro. Early life Loutherbourg was born in Strasbourg in 1740, the son of an expatriate Polish miniature painter. Intended for the Lutheran ministry, he was educated at the University of Strasbourg. Paris Rejecting a religious calling, Loutherbourg decided to become a painter, and in 1755 placed himself under Charles-André van Loo in Paris, and later under Francesco Giuseppe Casanova. His talent developed rapidly, and he became a figure in the fashionable society of the day. He first exhibited at the Salon of 1763 where his ''Landscape with Figures and Ani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madeley Wood Company
The Madeley Wood Company was formed in 1756 when the Madeley Wood Furnaces, also called Bedlam Furnaces, were built beside the River Severn, one mile west of Blists Hill. Bedlam Furnaces The Madeley Wood Furnaces or Bedlam Furnaces were owned by this company, which held mineral leases in Madeley Parish, enabling it to extract coal and iron ore. The works were taken over by Abraham Darby III of the Coalbrookdale Company in 1776. When the company was reorganised in 1797, the Madeley Wood Works became separate from Coalbrookdale, continuing (in conjunction with the Ketley Ironworks) in the hands of the Reynolds family who had been in partnership with the Darby family at Coalbrookdale since the 1760s. After Joseph Reynolds decided to concentrate on his bank, the Madeley Wood Company works passed to the Anstice family, one of whom had managed it, and their business became another Madeley Wood Company. The name ''Bedlam Furnaces'' may have originated with a painting by John S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Iron Bridge
The Iron Bridge is a cast iron arch bridge that crosses the River Severn in Shropshire, England. Opened in 1781, it was the first major bridge in the world to be made of cast iron. Its success inspired the widespread use of cast iron as a structural material, and today the bridge is celebrated as a symbol of the Industrial Revolution. The geography of the deep Ironbridge Gorge, formed by glacial action during the last ice age, meant that there are industrially useful deposits of coal, iron ore, limestone and fire clay present near the surface where they are readily mined, but also that it was difficult to build a bridge across the river at this location. To cope with the instability of the banks and the need to maintain a navigable channel in the river, a single span iron bridge was proposed by Thomas Farnolls Pritchard. After initial uncertainty about the use of iron, construction took place over two years, with Abraham Darby III responsible for the ironwork. The bridge cro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abraham Darby III
Abraham Darby III (24 April 1750 – 1789) was an English ironmaster and Quaker. He was the third man of that name in several generations of an English Quaker family that played a pivotal role in the Industrial Revolution. Life Abraham Darby was born in Coalbrookdale, Shropshire, in 1750, the eldest son of Abraham Darby the Younger (1711–1763) by his second wife, Abiah Maude, and educated at a school in Worcester kept by a Quaker named James Fell. At age thirteen, Darby inherited his father's shares in the family iron-making businesses in the Severn Valley, and in 1768, aged eighteen, he took over the management of the Coalbrookdale ironworks. He took various measures to improve the conditions of his work force. In times of food shortage he bought up farms to grow food for his workers, he built housing for them, and he offered higher wages than were paid in other local industries, including coal-mining and the potteries. He built the largest cast iron structure of his er ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |