|
British National Corpus
The British National Corpus (BNC) is a 100-million-word text corpus of samples of written and spoken English from a wide range of sources. The corpus covers British English of the late 20th century from a wide variety of genres, with the intention that it be a representative sample of spoken and written British English of that time. It is used in corpus linguistics for analysis of corpora. History The project to create the BNC involved the collaboration of three publishers (with the Oxford University Press as the lead collaborator, Longman and W. & R. Chambers), two universities (the University of Oxford and Lancaster University), and the British Library. The creation of the BNC started in 1991 under the management of the BNC consortium, and the project was finished by 1994. There have been no additions of new samples after 1994, but the BNC underwent slight revisions before the release of the second edition BNC World (2001) and the third edition BNC XML Edition (2007). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Text Corpus
In linguistics and natural language processing, a corpus (: corpora) or text corpus is a dataset, consisting of natively digital and older, digitalized, language resources, either annotated or unannotated. Annotated, they have been used in corpus linguistics for statistical statistical hypothesis testing, hypothesis testing, checking occurrences or validating linguistic rules within a specific language territory. Overview A corpus may contain texts in a single language (''monolingual corpus'') or text data in multiple languages (''multilingual corpus''). In order to make the corpora more useful for doing linguistic research, they are often subjected to a process known as annotation. An example of annotating a corpus is part-of-speech tagging, or ''POS-tagging'', in which information about each word's part of speech (verb, noun, adjective, etc.) is added to the corpus in the form of ''tags''. Another example is indicating the Lemma (morphology), lemma (base) form of each word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchrony And Diachrony
Synchrony and diachrony are two complementary viewpoints in linguistic analysis. A ''synchronic'' approach - from ,("together") + ,("time") - considers a language at a moment in time without taking its history into account. In contrast, a ''diachronic'' - from ,("through, across") + ,("time") - approach, as in historical linguistics, considers the development and evolution of a language through history. For example, the study of Middle English—when the subject is temporally limited to a sufficiently homogeneous form—is synchronic focusing on understanding how a given stage in the history of English functions as a whole. The diachronic approach, by contrast, studies language change by comparing the different stages. This latter approach is what surface analysis often relies on, as a given composition may not have appeared synchronously in history. The terms ''synchrony'' and ''diachrony'' are often associated with historical linguist Ferdinand de Saussure, who considered the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word-sense Disambiguation
Word-sense disambiguation is the process of identifying which sense of a word is meant in a sentence or other segment of context. In human language processing and cognition, it is usually subconscious. Given that natural language requires reflection of neurological reality, as shaped by the abilities provided by the brain's neural networks, computer science has had a long-term challenge in developing the ability in computers to do natural language processing and machine learning. Many techniques have been researched, including dictionary-based methods that use the knowledge encoded in lexical resources, supervised machine learning methods in which a classifier is trained for each distinct word on a corpus of manually sense-annotated examples, and completely unsupervised methods that cluster occurrences of words, thereby inducing word senses. Among these, supervised learning approaches have been the most successful algorithms to date. Accuracy of current algorithms is diffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hidden Markov Model
A hidden Markov model (HMM) is a Markov model in which the observations are dependent on a latent (or ''hidden'') Markov process (referred to as X). An HMM requires that there be an observable process Y whose outcomes depend on the outcomes of X in a known way. Since X cannot be observed directly, the goal is to learn about state of X by observing Y. By definition of being a Markov model, an HMM has an additional requirement that the outcome of Y at time t = t_0 must be "influenced" exclusively by the outcome of X at t = t_0 and that the outcomes of X and Y at t < t_0 must be conditionally independent of at given at time . Estimation of the parameters in an HMM can be performed using maximum likelihood estimation. For linear chain HMMs, the Baum–Welch algorithm can be used to estimate parameters. Hidden Markov models are known for their applications to thermodynamics, statistical mechanics, physics, chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
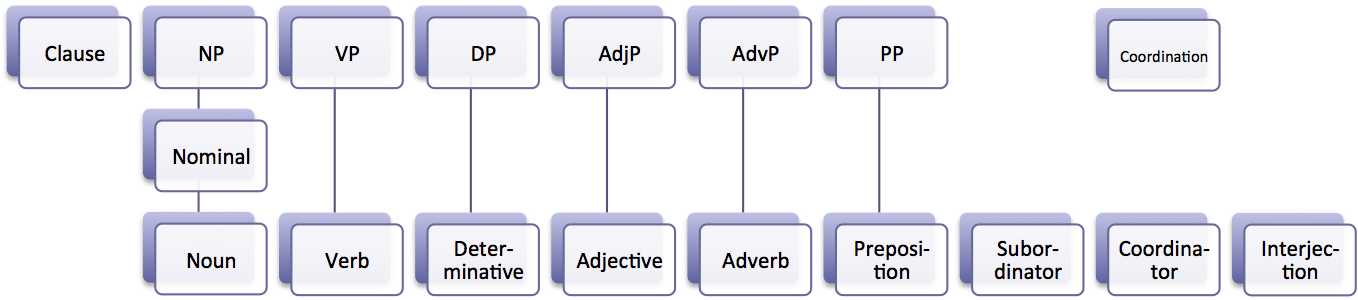
Part Of Speech
In grammar, a part of speech or part-of-speech ( abbreviated as POS or PoS, also known as word class or grammatical category) is a category of words (or, more generally, of lexical items) that have similar grammatical properties. Words that are assigned to the same part of speech generally display similar syntactic behavior (they play similar roles within the grammatical structure of sentences), sometimes similar morphological behavior in that they undergo inflection for similar properties and even similar semantic behavior. Commonly listed English parts of speech are noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, preposition, conjunction, interjection, numeral, article, and determiner. Other terms than ''part of speech''—particularly in modern linguistic classifications, which often make more precise distinctions than the traditional scheme does—include word class, lexical class, and lexical category. Some authors restrict the term ''lexical category'' to refer only to a par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newspapers
A newspaper is a Periodical literature, periodical publication containing written News, information about current events and is often typed in black ink with a white or gray background. Newspapers can cover a wide variety of fields such as politics, business, sports, art, and science. They often include materials such as opinion columns, weather forecasts, reviews of local services, Obituary, obituaries, birth notices, crosswords, editorial cartoons, comic strips, and advice columns. Most newspapers are businesses, and they pay their expenses with a mixture of Subscription business model, subscription revenue, Newsagent's shop, newsstand sales, and advertising revenue. The journalism organizations that publish newspapers are themselves often Metonymy, metonymically called newspapers. Newspapers have traditionally been published Printing, in print (usually on cheap, low-grade paper called newsprint). However, today most newspapers are also Electronic publishing, published on webs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiction
Fiction is any creative work, chiefly any narrative work, portraying character (arts), individuals, events, or setting (narrative), places that are imagination, imaginary or in ways that are imaginary. Fictional portrayals are thus inconsistent with fact, history, or plausibility. In a traditional narrow sense, fiction refers to literature, written narratives in prose often specifically novels, novellas, and short story, short stories. More broadly, however, fiction encompasses imaginary narratives expressed in any Media (communication), medium, including not just writings but also drama, live theatrical performances, films, television programs, radio dramas, comics, role-playing games, and video games. Definition and theory Typically, the fictionality of a work is publicly expressed, so the audience expects a work of fiction to deviate to a greater or lesser degree from the real world, rather than presenting for instance only factually accurate portrayals or character (arts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Writing
Academic writing or scholarly writing refers primarily to nonfiction writing that is produced as part of academic work in accordance with the standards of a particular academic subject or discipline, including: * reports on empirical fieldwork or research in facilities for the natural sciences or social sciences, * monographs in which scholars analyze culture, propose new theories, or develop interpretations from archives, as well as undergraduate versions of all of these. Academic writing typically uses a more formal tone and follows specific conventions. Central to academic writing is its intertextuality, or an engagement with existing scholarly conversations through meticulous citing or referencing of other academic work, which underscores the writer's participation in the broader discourse community. However, the exact style, content, and organization of academic writing can vary depending on the specific genre and publication method. Despite this variation, all academic w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Phonetics Lab
The Phonetics Laboratory is the phonetics laboratory at the University of Oxford, England. It is located at 41 Wellington Square, Oxford Wellington Square is a garden square in central Oxford, England, a continuation northwards of St John Street. In the centre of the square is a small park, Wellington Square Gardens, owned by the University of Oxford. A bicycle route passes in .... The laboratory focusses on experimental tests of linguistic assumptions and empirical linguistics. It provides teaching at the undergraduate and graduate level. Research students in the laboratory are normally reading for a higher degree in Experimental Linguistics, though students from other disciplines touching on the subject of speech are sometimes based in Phonetics. The Phonetics Laboratory was established in 1980. It occupies the basement of 41 Wellington Square, a mid-Victorian brick building, expanded since. It has experimental areas (sound-insulated recording booths), and general exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Library Sound Archive
The British Library Sound Archive, formerly the British Institute of Recorded Sound; also known as the National Sound Archive (NSA), in London, England is among the largest collections of recorded sound in the world, including music, spoken word and ambient recordings. It holds more than six million recordings, including over a million discs and 200,000 tapes. These include commercial record releases (chiefly from the UK), radio broadcasts (many from the BBC Sound Archive), and privately made recordings. Due to the 2023 cyberattack on the British Library, the sound archive's catalogue is currently unavailable. History The history of the Sound Archive can be traced back to 1905, when it was first suggested that the British Museum should have a collection of audio recordings of poets and statesmen. The Gramophone Company started donating metal masters of audio recordings in 1906 (on the basis that records would wear out), with a number of donations being made up until 1933. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conversation
Conversation is interactive communication between two or more people. The development of conversational skills and etiquette is an important part of socialization. The development of conversational skills in a new language is a frequent focus of language teaching and language learning, learning. Conversation analysis is a branch of sociology which studies the structure and organization of human interaction, with a more specific focus on conversational interaction. Definition and characterization No generally accepted definition of conversation exists, beyond the fact that a conversation involves at least two people talking together. Consequently, the term is often defined by what it is not. A ritualized exchange such as a mutual greeting is not a conversation, and an interaction that includes a marked status differential (such as a boss giving orders) is also not a conversation. An interaction with a tightly focused topic or purpose is also generally not considered a conver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demographic
Demography () is the statistics, statistical study of human populations: their size, composition (e.g., ethnic group, age), and how they change through the interplay of fertility (births), mortality (deaths), and migration. Demographic analysis examines and measures the dimensions and Population dynamics, dynamics of populations; it can cover whole societies or groups defined by criteria such as education, nationality, religion, and ethnicity. Educational institutions usually treat demography as a field of sociology, though there are a number of independent demography departments. These methods have primarily been developed to study human populations, but are extended to a variety of areas where researchers want to know how populations of Social actions, social actors can change across time through processes of birth, death, and Human migration, migration. In the context of human biological populations, demographic analysis uses Public records, administrative records to deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |