|
British 18 Inch Torpedo
There have been a number of 18-inch (45cm) torpedoes in service with the Royal Navy of the United Kingdom. These have been used on ships of the Royal Navy and aircraft of both the Fleet Air Arm and Royal Air Force, while Royal Navy surface ships and submarines use 21-inch torpedoes. The British 18-inch torpedoes were in diameter, beginning with the "Fiume" Whitehead torpedo of 1890. Fiume Mark I Purchased from Whitehead with the first delivery in 1890, and a second delivery in 1891. The weapon utilized compressed air propulsion, and was prolific for its time, having been exported to multiple other navies across the world. The decision to adopt the 18-inch torpedo caliber was made by the Admiralty in 1889, with the Fiume Mark I being the first weapon of the type, soon thereafter followed by the RGF Mark I. In 1890, Whitehead established a torpedo factory in Weymouth, chiefly for the export market - but also in order to directly supply the Royal Navy with locally-manufact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, such a device was called an automotive, automobile, locomotive, or fish torpedo; colloquially, a ''fish''. The term ''torpedo'' originally applied to a variety of devices, most of which would today be called mines. From about 1900, ''torpedo'' has been used strictly to designate a self-propelled underwater explosive device. While the 19th-century battleship had evolved primarily with a view to engagements between armored warships with large-caliber guns, the invention and refinement of torpedoes from the 1860s onwards allowed small torpedo boats and other lighter surface vessels, submarines/submersibles, even improvised fishing boats or frogmen, and later light aircraft, to destroy large ships without the need of large guns, though somet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elswick Ordnance Company
The Elswick Ordnance Company (sometimes referred to as Elswick Ordnance Works, but usually as "EOC") was a British armaments manufacturing company of the late 19th and early 20th century History Originally created in 1859 to separate William Armstrong's armaments business from his other business interests, to avoid a conflict of interest as Armstrong was then Engineer of Rifled Ordnance for the War Office and the company's main customer was the British Government. Armstrong held no financial interest in the company until 1864 when he left Government service, and Elswick Ordnance was re-united with the main Armstrong businesses to form Sir W.G. Armstrong & Company. EOC was then the armaments branch of W.G. Armstrong & Company and later of Armstrong Whitworth. EOC's main customer in its early years was the British Government, but the Government abandoned "Armstrong guns" in the mid-1860s due to dissatisfaction with Armstrong's breech mechanism, and instead built its own rifled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackburn Ripon Mk
Blackburn () is an industrial town and the administrative centre of the Blackburn with Darwen borough in Lancashire, England. The town is north of the West Pennine Moors on the southern edge of the River Ribble, Ribble Valley, east of Preston, Lancashire, Preston and north-northwest of Manchester. Blackburn is at the centre of the wider unitary authority area along with the town of Darwen. It is the second largest town (after Blackpool) in Lancashire. At the United Kingdom Census 2011, 2011 census, Blackburn had a population of List of urban areas in England by population, 117,963, whilst the wider borough of Blackburn with Darwen had a population of List of English districts by population, 150,030. Blackburn had a population of 117,963 in 2011, with 30.8% being people of ethnic backgrounds other than white British. A former mill town, Blackburn has been the site of textile production since the mid-13th century, when wool was woven in people's houses in the domestic sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribal Class Destroyer (1905)
The Tribal or F class was a class of destroyers built for the Royal Navy. Twelve ships were built between 1905 and 1908 and all saw service during World War I, where they saw action in the North Sea and English Channel as part of the 6th Flotilla and Dover Patrols. Design The preceding River- or E-class destroyers of 1903 had made on the provided by triple expansion steam engines and coal-fired boilers, although was powered by steam turbines.Chesneau and Kolesnik 1979, p. 99. In November 1904, the First Sea Lord "Jackie" Fisher proposed that the next class of destroyers should make at least and should use oil-fired boilers and steam turbines as a means of achieving this.Friedman 2009, pp. 106–107. This resulted in a larger ship to provide the required doubling of installed power over their predecessors, but also pushed the design to the limits of capability of contemporary technology. As a result, the Tribals were severely compromised and a somewhat retrograde step aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River-class Destroyer (1903)
The River-class destroyer (re-designated in 1913 as the E class) was a class of torpedo boat destroyer built for the Royal Navy in the first few years of the 20th century, and which saw extensive service in World War I. These 37 vessels (33 formally ordered under three annual construction programmes, plus another three built on speculation and then purchased by the Admiralty, and a final unit building in Italy for the Portuguese Navy and purchased in 1915) were all constructed to disparate builders' designs, just like the preceding classes. The class introduced new features to destroyer design, placing a greater emphasis on seakeeping and endurance and less on a high maximum speed in good weather. All the ships were named after British, Irish and Portuguese rivers, and as such were the first Royal Navy destroyer class to be named systematically. Genesis The concept for the River class began in December 1900, with a request from Commander John Michael de Robeck, then the sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinitrotoluene
Troponin T (shortened TnT or TropT) is a part of the troponin complex, which are proteins integral to the contraction of skeletal and heart muscles. They are expressed in skeletal and cardiac myocytes. Troponin T binds to tropomyosin and helps position it on actin, and together with the rest of the troponin complex, modulates contraction of striated muscle. The cardiac subtype of troponin T is especially useful in the laboratory diagnosis of heart attack because it is released into the blood-stream when damage to heart muscle occurs. It was discovered by the German physician Hugo A. Katus at the University of Heidelberg, who also developed the troponin T assay. Subtypes * Slow skeletal troponin T1, TNNT1 (19q13.4, ) * Cardiac troponin T2, TNNT2 (1q32, ) * Fast skeletal troponin T3, TNNT3 (11p15.5, ) Reference values The 99th percentile cutoff for cardiac troponin T (cTnT) is 0.01 ng/mL. The reference range for the high sensitivity troponin T is a normal 52 ng/L. Backgr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bincleaves Groyne
Bincleaves Groyne is a breakwater located off the southern area of Weymouth, England. It is the second largest of four breakwaters which create Portland Harbour Portland Harbour is beside the Isle of Portland, Dorset, on the south coast of England. Construction of the harbour began in 1849; when completed in 1872, its surface area made it the largest human-made harbour in the world, and it remains .... It is separated from the Northeastern Breakwater by the North Ship Channel. A landing stage is situated on the southern side of the breakwater near the Western Ledges. Bincleaves Groyne features the C Pier Head Battery on the southern tip. The arm is an Admiralty extension to the earlier breakwater built by the Great Western Railway and known as the Bincleaves Groyne. The head is 100 ft in diameter. The battery was opened in 1901 and was armed with two 12-pounder quick-firing (QF) guns for anti-torpedo craft defence. By the First World War the 12-pounder guns had be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, such a device was called an automotive, automobile, locomotive, or fish torpedo; colloquially, a ''fish''. The term ''torpedo'' originally applied to a variety of devices, most of which would today be called mines. From about 1900, ''torpedo'' has been used strictly to designate a self-propelled underwater explosive device. While the 19th-century battleship had evolved primarily with a view to engagements between armored warships with large-caliber guns, the invention and refinement of torpedoes from the 1860s onwards allowed small torpedo boats and other lighter surface vessels, submarines/submersibles, even improvised fishing boats or frogmen, and later light aircraft, to destroy large ships without the need of large guns, though somet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woolwich
Woolwich () is a town in South London, southeast London, England, within the Royal Borough of Greenwich. The district's location on the River Thames led to its status as an important naval, military and industrial area; a role that was maintained throughout the 16th to 20th centuries. After several decades of economic hardship and social deprivation, the area now has several large-scale urban renewal projects. Geography Woolwich is situated from Charing Cross. It has a long frontage to the south bank of the River Thames. From the riverside it rises up quickly along the northern slopes of Shooter's Hill towards the common, at and the ancient London–Dover Road, at . The Woolwich (parish), ancient parish of Woolwich, more or less the present-day Wards and electoral divisions of the United Kingdom, wards Woolwich Riverside and Woolwich Common, comprises . This included North Woolwich, which is now part of the London Borough of Newham. The ancient parishes of Plumstead and E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Gun Factory
The Royal Arsenal, Woolwich is an establishment on the south bank of the River Thames in Woolwich in south-east London, England, that was used for the manufacture of armaments and ammunition, proofing, and explosives research for the British armed forces. It was originally known as the Woolwich Warren, having begun on land previously used as a domestic warren in the grounds of a mid-16th century Tudor house, Tower Place. Much of the initial history of the site is linked with that of the Office of Ordnance, which purchased the Warren in the late 17th century in order to expand an earlier base at Gun Wharf in Woolwich Dockyard. Over the next two centuries, as operations grew and innovations were pursued, the site expanded massively. At the time of the First World War the Arsenal covered and employed close to 80,000 people. Thereafter its operations were scaled down. It finally closed as a factory in 1967 and the Ministry of Defence moved out in 1994. Today the area, so long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
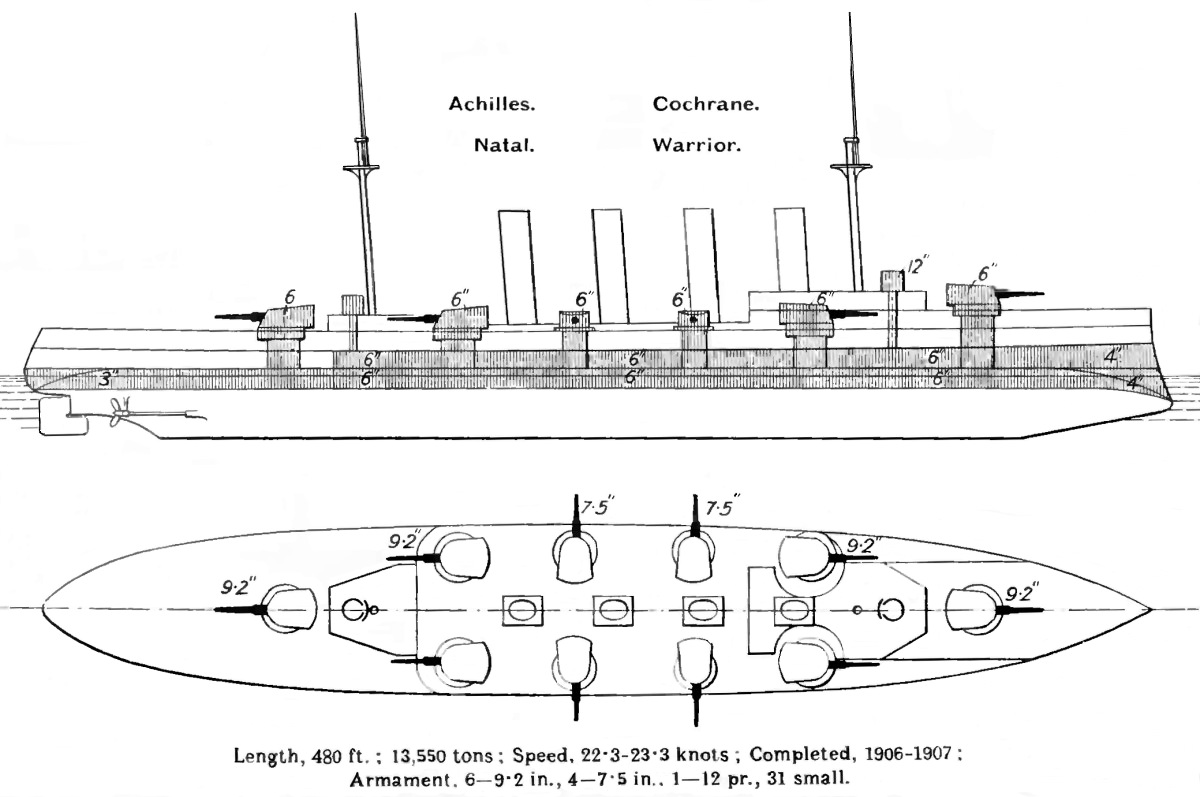
HMS Cochrane (1905)
HMS ''Cochrane'' was a armoured cruiser built for the Royal Navy in the first decade of the 20th century. She served in the 2nd Cruiser Squadron during the First World War under Rear-Admiral Herbert Heath, taking part in the Battle of Jutland in 1916. She was based in Murmansk in mid-1918 during the Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War. She became stranded in the River Mersey on 14 November 1918 and broke in two. The wreck was broken up in place by June 1919. Description Christened by Winifred Cochrane, Countess of Dundonald, ''Cochrane'' displaced as built and fully loaded, with a length of , a beam of and a draft of . She was powered by a pair of four-cylinder triple-expansion steam engines, each driving one propeller shafts, which developed a total of and gave a maximum speed of .Roberts, p. 34 The engines were powered by 19 Yarrow water-tube boilers and six cylindrical boilers. The ship carried enough coal and fuel oil to give her a range of at a speed of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |