|
Bring Your Own Device
Bring your own device (BYOD ) (also called bring your own technology (BYOT), bring your own phone (BYOP), and bring your own personal computer (BYOPC)) refers to being allowed to use one's personally owned device, rather than being required to use an officially provided device. There are two major contexts in which this term is used. One is in the mobile phone industry, where it refers to carriers allowing customers to activate their existing phone (or other cellular device) on the network, rather than being forced to buy a new device from the carrier. The other, and the main focus of this article, is in the workplace, where it refers to a policy of permitting employees to bring personally owned devices (laptops, tablets, smartphones, etc.) to work, and to use those devices to access privileged company information and applications. This phenomenon is commonly referred to as IT consumerization. BYOD is making significant inroads in the business world, with about 80% of employees ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumerization
Consumerization is the reorientation of product and service designs to focus on (and marketing, market to) the end user as an individual consumer, in contrast with an earlier era of only organization-oriented offerings (designed solely for business-to-business or business-to-government sales). Technologies whose first commercialization was at the inter-organization level thus have potential for later consumerization. The emergence of the individual consumer as the primary driver of product and service design is most commonly associated with the information technology, IT industry, as large business and government organizations dominated the early decades of computer usage and development. Thus the microcomputer revolution, in which electronic computing moved from exclusively enterprise and government use to include personal computer, personal computing, is a cardinal example of consumerization. But many technology-based products, such as calculators and mobile phones, have also had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cisco
Cisco Systems, Inc. (using the trademark Cisco) is an American multinational digital communications technology conglomerate corporation headquartered in San Jose, California. Cisco develops, manufactures, and sells networking hardware, software, telecommunications equipment and other high-technology services and products. Cisco specializes in specific tech markets, such as the Internet of things (IoT), domain security, videoconferencing, and energy management with products including Webex, OpenDNS, Jabber, Duo Security, Silicon One, and Jasper. Cisco Systems was founded in December 1984 by Leonard Bosack and Sandy Lerner, two Stanford University computer scientists who had been instrumental in connecting computers at Stanford. They pioneered the concept of a local area network (LAN) being used to connect distant computers over a multiprotocol router system. The company went public in 1990 and, by the end of the dot-com bubble in 2000, had a market capitali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
One-to-one Computing
In the context of education, one-to-one computing (sometimes abbreviated as "1:1") refers to academic institutions, such as schools or colleges, that allow each enrolled student to use an electronic device in order to access the Internet, digital course materials, and digital textbooks. The concept has been actively explored and sporadically implemented since the late 1990s. One-to-one computing used to be contrasted with a policy of "bring your own device" (BYOD), which encourages or requires students to use their own laptops, smartphones or other electronic devices in class. The distinction between BYOD and school-issued devices became blurred when many schools started recommending devices for parents to buy (examples for both iPads and Chromebooks being used 1:1 in schools, but being paid for by parents exist, there may be similar evidence for other devices). The term 1:1 computing in education is now redefined to a situation where students have access to a device per individua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobile Security
Mobile security, or mobile device security, is the protection of smartphones, tablets, and laptops from threats associated with wireless computing. It has become increasingly important in mobile computing. The Information security, security of personal and business information now stored on smartphones is of particular concern. Increasingly, users and businesses use smartphones not only to communicate, but also to plan and organize their work and private life. Within companies, these technologies are causing profound changes in the organization of information systems and have therefore become the source of new risks. Indeed, smartphones collect and compile an increasing amount of sensitive information to which access must be controlled to protect the Information privacy, privacy of the User (computing), user and the intellectual property of the company. The majority of attacks are aimed at smartphones. These attacks take advantage of vulnerabilities discovered in smartphones that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bring Your Own Operating System
Bring your own operating system (BYOOS) or Bring Your Own Image (BYOI) relates to the practice of providing PC computers, usually without internally installed disks, so users can bring their own operating system (commonly on USB pen drives) and use the supplied hardware with the operating system of their choice. BYOOS has been made possible thanks to the ability to create USB pen drives and other external storage devices with 'live' operating system images containing all the necessary drivers to allow boot up and operation on any compatible computer. Bootable versions of Linux were available by 1993. In 2012, Microsoft Windows 8 Enterprise Edition followed, by introducing Windows To Go functionality to allow the operating system to boot and run from mass storage devices such as USB flash drives, thus enabling BYOOS in the Windows family of operating system similar to that of a Linux live CD/DVD. By allowing users to bring their own operating system there are significant cost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bring Your Own Encryption
Bring your own encryption (BYOE), also known as bring your own key (BYOK), is a cloud computing security model that allows cloud service customers to use their own encryption software and manage their own encryption keys. BYOE enables cloud service customers to utilize a virtual instance of their encryption software alongside their cloud-hosted business applications to encrypt their data. In this model, hosted business applications are configured to process all data through the encryption software. This software then writes the ciphertext version of the data to the cloud service provider's physical data store and decrypts ciphertext data upon retrieval requests. This approach provides enterprises with control over their keys and the ability to generate their own master key using internal hardware security modules (HSM), which are then transmitted to the cloud provider's HSM. When the data is no longer needed, such as when users discontinue the cloud service, the keys can be delet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stipend
A stipend is a regular fixed sum of money paid for services or to defray expenses, such as for scholarship, internship, or apprenticeship. It is often distinct from an income or a salary because it does not necessarily represent payment for work performed; instead it represents a payment that enables somebody to be exempt partly or wholly from waged or salaried employment in order to undertake a role that is normally unpaid or voluntary, or which cannot be measured in terms of a task (e.g. members of the clergy). A paid judge in an English or Welsh magistrates' court (England and Wales), magistrates' court was formerly termed a "stipendiary magistrate", as distinct from the unpaid "lay magistrates". In 2000, these were respectively renamed "district judge (magistrates courts), district judge" and "Magistrate (England and Wales), magistrate". Stipends are usually lower than would be expected as a permanent salary for similar work. This is because the stipend is complemented by other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
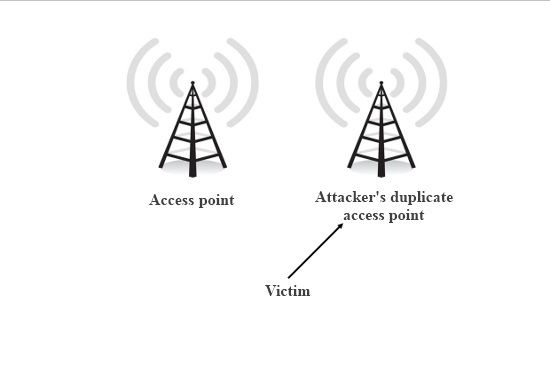
Wireless LAN
A wireless LAN (WLAN) is a wireless computer network that links two or more devices using wireless communication to form a local area network (LAN) within a limited area such as a home, school, computer laboratory, campus, or office building. This gives users the ability to move around within the area and remain connected to the network. Through a Gateway (telecommunications), gateway, a WLAN can also provide a connection to the wider Internet. Wireless LANs based on the IEEE 802.11 standards are the most widely used computer networks in the world. These are commonly called Wi-Fi, which is a trademark belonging to the Wi-Fi Alliance. They are used for home and small office networks that link together laptop computers, printer (computing), printers, smartphones, Web TVs and gaming devices through a Wireless router, wireless network router, which in turn may link them to the Internet. Hotspot (Wi-Fi), Hotspots provided by routers at restaurants, coffee shops, hotels, libraries, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tethering
Tethering or phone-as-modem (PAM) is the sharing of a mobile device's cellular data connection with other connected computers. It effectively turns the transmitting device into a modem to allow others to use its cellular network as a gateway for Internet access. The sharing can be done wirelessly over wireless LAN (Wi-Fi), Bluetooth, IrDA or by physical connection using a cable like USB. If tethering is done over Wi-Fi, the feature may be branded as a personal hotspot or mobile hotspot, and the transmitting mobile device would also act as a portable wireless access point (AP) which may also be protected using a password. Tethering over Bluetooth may use the Personal Area Networking (PAN) profile between paired devices, or alternatively the Dial-Up Networking (DUN) profile where the receiving device virtually dials the cellular network APN, typically using the number ''*99''#. Mobile devices' OS support Many mobile devices are equipped with software to offer tethered Internet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dropbox (service)
Dropbox is a file hosting service operated by the American company Dropbox, Inc., headquartered in San Francisco, California, that offers cloud storage, file synchronization, personal cloud, and client software. Dropbox was founded in 2007 by MIT students Drew Houston and Arash Ferdowsi as a startup company, with initial funding from seed accelerator Y Combinator. Dropbox has experienced criticism and generated controversy for issues including security breaches and privacy concerns. Concept Dropbox brings files together in one central place by creating a special folder on the user's computer. The contents of these folders are synchronized to Dropbox's servers and to other computers and devices where the user has installed Dropbox, keeping the same files up-to-date on all devices. Dropbox uses a freemium business model, where users are offered a free account with set storage size, with paid subscriptions available that offer more capacity and additional features. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
End Node Problem
The end node problem arises when individual computers are used for sensitive work and/or temporarily become part of a trusted, well-managed network/cloud and then are used for more risky activities and/or join untrusted networks. (Individual computers on the periphery of networks/clouds are called end nodes.) End nodes often are not managed to the trusted network‘s high computer security standards. End nodes often have weak/outdated software, weak security tools, excessive permissions, mis-configurations, questionable content and apps, and covert exploitations. Cross contamination and unauthorized release of data from within a computer system becomes the problem. Within the vast cyber-ecosystem, these end nodes often attach transiently to one or more clouds/networks, some trustworthy and others not. A few examples: a corporate desktop browsing the Internet, a corporate laptop checking company webmail via a coffee shop's open Wi-Fi access point, a personal computer used to teleco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |