|
Bratislava Region
The Bratislava Region (, ; (until 1919); ) is one of the Regions of Slovakia, administrative regions of Slovakia. Its capital is Bratislava. The region was first established in 1923 and its present borders exist from 1996. It is the smallest of the eight regions of Slovakia as well as the most urbanized, most developed and most productive by GDP per capita. Geography The region is located in the south-western part of Slovakia and has an area of 2,053 km2 and a population of 622,706 (2009). The region is split by the Little Carpathians which start in Bratislava and continue north-eastwards; these mountains separate two lowlands, the Záhorie lowland in the west and the fertile Danubian Lowland in the east, which grows mainly wheat and maize. Major rivers in the region are the Morava (river), Morava River, the Danube and the Little Danube; the last of these, together with the Danube, encircle the Žitný ostrov in the south-east. There are three protected landscape areas in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of Slovakia
Since 1949 (except 1990–1996), Slovakia has been divided into a number of (singular ; usually translated as "Regions" with capital R). Their number, borders and functions have been changed several times. There are eight regions of Slovakia and they correspond to the European Union, EU's Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics, NUTS 3 level of local administrative units. Each kraj consists of (counties or districts), which are further divided into (municipalities). There are 79 Districts of Slovakia, districts. List After a period without kraje and without any equivalent (1990–1996), the kraje were reintroduced in 1996. As for administrative division, Slovakia has been subdivided into 8 kraje since 24 July 1996: Since 2002, Slovakia is divided into 8 (self-governing regions), which are called by the Constitution (Higher Territorial Units), abbr. VÚC. The territory and borders of the self-governing regions are identical with the territory and borders of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunajské Luhy Protected Landscape Area
Dunajské luhy Protected Landscape Area (; verbatim: Danube Floodplains PLA) is one of the youngest of the 14 protected landscape areas in Slovakia. The Landscape Area consists of five separate parts in the Danube Lowland, stretching from Bratislava in the north west, following the Danube and the borders between Slovakia and Hungary to a river island called ''Veľkolélsky ostrov'' in Komárno District. The biggest part is Žitný ostrov, the largest river island in Europe. The area is situated in three regions – Bratislava, Trnava Region, Trnava and Nitra Region, Nitra. Altogether, it protects 122.84 km2 (47.43 mi2) of floodplains, wetlands and numerous water bodies, such as lakes, oxbow lakes, ponds, and streams. Dunajské luhy PLA contains diverse flora and fauna, including Endemism, endemic species, living in riparian zones. Geography The first part (farthest north) starts south of the Slovnaft oil refinery in south east Bratislava Bratislava (German: ''P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Moravia
Great Moravia (; , ''Meghálī Moravía''; ; ; , ), or simply Moravia, was the first major state that was predominantly West Slavic to emerge in the area of Central Europe, possibly including territories which are today part of the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Austria, Germany, Poland, Romania, Croatia, Serbia, Ukraine and Slovenia. The formations preceding it in these territories were Samo's tribal union (631–658) and the Pannonian Avar state (567 – after 822). Its core territory is the region now called Moravia in the eastern part of the Czech Republic alongside the Morava River, which gave its name to the kingdom. The kingdom saw the rise of the first ever Slavic literary culture in the Old Church Slavonic language as well as the expansion of Christianity, first via missionaries from East Francia, and later after the arrival of Saints Cyril and Methodius in 863 and the creation of the Glagolitic alphabet, the first alphabet dedicated to a Slavic language. Glagol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principality Of Nitra
The Principality of Nitra (; ), also known as the Duchy of Nitra, was a West Slavic polity encompassing a group of settlements that developed in the 9th century around Nitra, in present-day Slovakia. Its history remains uncertain because of a lack of contemporary sources. The territory's status is subject to scholarly debate: some modern historians describe it as an independent polity that was annexed either around 833 or 870 by the Principality of Moravia, while others say that it was under the influence of the neighbouring West Slavs from Moravia from its inception. Background Modern-day Slovakia was dominated for centuries by Germanic peoples, including the Quadi and the Longobards, who were there until the middle of the 6th century. A new material culture characterized by handmade pottery, cremation burials and small, square, sunken huts that typically featured a corner stone oven appeared in the plains along the Middle Danube around that time. The new culture, with its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerulata
Gerulata was a Roman military camp located near today's Rusovce, a borough of Bratislava, Slovakia. It was part of the Roman province of Pannonia and was built in the 2nd century as a part of the frontier defence system. It was abandoned in the 4th century, when Roman legions withdrew from Pannonia. Today there is a museum, which is part of the Bratislava City Museum. Archaeologists have unearthed its remnants and their discoveries are on exhibition in the hall of the museum, which is open in summer and can be found behind the Catholic Church of St Mary Magdalene in the town. Beyond the remains of the Roman forum, fragments of structures and gravestones, bronze, iron, ceramic and stone pieces are on show in a museum showing daily life. The best preserved object is a quadrilateral building 30 metres long and 30 metres wide, with 2.4 metre thick walls. In July 2021, Gerulata was added to the UNESCO's World Heritage List as part of the Western segment of the Danubian Limes o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bratislava Castle
Bratislava Castle (, ; ; ) is the main castle of Bratislava, the capital of Slovakia. The massive rectangular building with four corner towers stands on an isolated rocky hill of the Little Carpathians, directly above the Danube river, in the middle of Bratislava. Because of its size and location, it has been a dominant feature of the city for centuries. The location provides excellent views of Bratislava, Austria and, in clear weather, parts of Hungary. Many legends are connected with the history of the castle. Castle site The following are at the castle site: Castle building The castle building includes four towers (one on each corner) and a courtyard with an deep water well. The largest and tallest tower is the Crown Tower, on the southwest corner. The tower dates from the 13th century and for approximately 200 years, beginning in the mid-1500s, housed the crown jewels of Hungary. The exterior walls and inside corridors contain fragments of old Gothic and Renais ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
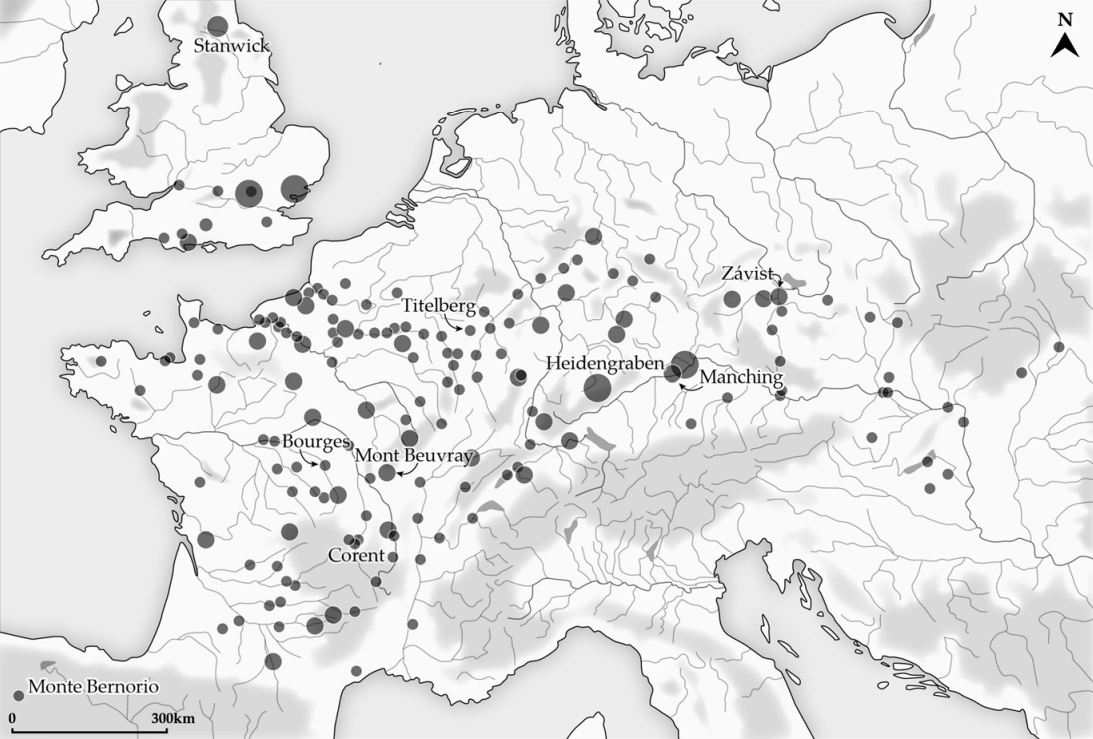
Oppidum
An ''oppidum'' (: ''oppida'') is a large fortified Iron Age Europe, Iron Age settlement or town. ''Oppida'' are primarily associated with the Celts, Celtic late La Tène culture, emerging during the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, spread across Europe, stretching from British Iron Age, Britain and Iberia in the west to the edge of the Great Hungarian Plain, Hungarian Plain in the east. These settlements continued to be used until the Romans conquered Southern and Western Europe. Many subsequently became Roman-era towns and cities, whilst others were abandoned. In regions north of the rivers Danube and Rhine, such as most of Germania, where the populations remained independent from Rome, ''oppida'' continued to be used into the 1st century AD. Definition is a Latin word meaning 'defended (fortified) administrative centre or town', originally used in reference to non-Roman towns as well as provincial towns under Roman control. The word is derived from the earlier Latin , 'encl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the History of agriculture, introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of sedentism, settlement. The term 'Neolithic' was coined by John Lubbock, 1st Baron Avebury, Sir John Lubbock in 1865 as a refinement of the three-age system. The Neolithic began about 12,000 years ago, when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East and Mesopotamia, and later in other parts of the world. It lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BCE), marked by the development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Pottery Culture
The Linear Pottery culture (LBK) is a major archaeological horizon of the European Neolithic period, flourishing . Derived from the German ''Linearbandkeramik'', it is also known as the Linear Band Ware, Linear Ware, Linear Ceramics or Incised Ware culture, falling within the Danubian I culture of V. Gordon Childe. Most cultural evidence has been found on the middle Danube, the upper and middle Elbe, and the upper and middle Rhine. It represents a major event in the initial spread of agriculture in Europe. The pottery consists of simple cups, bowls, vases, jugs without handles and, in a later phase, with pierced lugs, bases, and necks.Hibben, page 121. Important sites include Vráble and Nitra in Slovakia; Bylany in the Czech Republic; Langweiler and Zwenkau (Eythra) in Germany; Brunn am Gebirge in Austria; Elsloo, Sittard, Köln-Lindenthal, Aldenhoven, Flomborn, and Rixheim on the Rhine; Lautereck and Hienheim on the upper Danube; and Rössen and Sond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Austria
Lower Austria ( , , abbreviated LA or NÖ) is one of the nine states of Austria, located in the northeastern corner of the country. Major cities are Amstetten, Lower Austria, Amstetten, Krems an der Donau, Wiener Neustadt and Sankt Pölten, which has been the capital city, capital of Lower Austria since 1986, replacing Vienna, which became a separate state in 1921. With a land area of and a population of 1.7 million people, Lower Austria is the largest and second-most-populous state in Austria (after Vienna). Geography With a land area of situated east of Upper Austria, Lower Austria is the country's largest state. Lower Austria derives its name from its downriver location on the river Enns (river), Enns, which flows from the west to the east. Lower Austria has an international border, long, with the Czech Republic (South Bohemian Region, South Bohemia and South Moravian Region, South Moravia) and Slovakia (Bratislava Region, Bratislava and Trnava Regions). The state has the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Austria, most populous city and state. Austria is bordered by Germany to the northwest, the Czech Republic to the north, Slovakia to the northeast, Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the west. The country occupies an area of and has Austrians, a population of around 9 million. The area of today's Austria has been inhabited since at least the Paleolithic, Paleolithic period. Around 400 BC, it was inhabited by the Celts and then annexed by the Roman Empire, Romans in the late 1st century BC. Christianization in the region began in the 4th and 5th centuries, during the late Western Roman Empire, Roman period, followed by the arrival of numerous Germanic tribes during the Migration Period. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgenland
Burgenland (; ; ; Bavarian language, Austro-Bavarian: ''Burgnland''; Slovene language, Slovene: ''Gradiščanska''; ) is the easternmost and least populous Bundesland (Austria), state of Austria. It consists of two statutory city (Austria), statutory cities and seven rural districts, with a total of 171 municipalities. It is long from north to south but much narrower from west to east ( wide at Sieggraben). The region is part of the Centrope Project. The name of Burgenland was invented/coined in 1922, after its territories became part of Austria. The population of Burgenland as of 1 January 2024 is 301,951. Burgenland's capital is Eisenstadt. History The territory of present-day Burgenland was successively part of the Roman Empire, the Hun Empire, the Kingdom of the Ostrogoths, the Italy, Italian Kingdom of Odoacer, the Kingdom of the Lombards, the Avar Khaganate, the Frankish Empire, Dominion Aba belonging to the Aba (family); Aba – Koszegi, the Kingdom of Hungary, the Habsburg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |