|
Branlebas-class Destroyer
The ''Branlebas'' class was a class of ten destroyers built for the French Navy in the first decade of the 20th century. Eight of the ships survived the World War I, First World War and were ship breaking, scrapped afterwards. Construction and design The ''Branlebas''-class was a development of the previous , and was the final evolution of the ''300-tonne'' type which the French had built since 1899 with their first destroyer ship class, class, the . Like all the ''300-tonne'' destroyers, the ''Branlebas''-class ships had a turtledeck forecastle with a flying deck, raised above the hull, aft.Campbell 1979, pp. 326–327. They were long length between perpendiculars, between perpendiculars, with a Beam (nautical), beam of and a maximum Draft (ship), draught of .''The Engineer'' 21 August 1908, p. 192. Displacement (ship), Displacement was .Couhat 1974, p. 92. Two coal-fired Normand boiler, Normand or Du Temple boilers fed steam at to two 3-cylinder Marine steam engine#Triple or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, maneuverable, long-endurance warship intended to escort larger vessels in a fleet, convoy, or carrier battle group and defend them against a wide range of general threats. They were conceived in 1885 by Fernando Villaamil for the Spanish NavySmith, Charles Edgar: ''A short history of naval and marine engineering.'' Babcock & Wilcox, ltd. at the University Press, 1937, page 263 as a defense against torpedo boats, and by the time of the Russo-Japanese War in 1904, these "torpedo boat destroyers" (TBDs) were "large, swift, and powerfully armed torpedo boats designed to destroy other torpedo boats". Although the term "destroyer" had been used interchangeably with "TBD" and "torpedo boat destroyer" by navies since 1892, the term "torpedo boat destroyer" had been generally shortened to simply "destroyer" by nearly all navies by the First World War. Before World War II, destroyers were light vessels with little endurance for unatte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
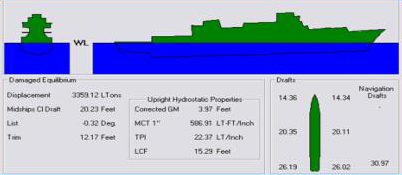
Displacement (ship)
The displacement or displacement tonnage of a ship is its weight. As the term indicates, it is measured indirectly, using Archimedes' principle, by first calculating the volume of water displaced by the ship, then converting that value into weight. Traditionally, various measurement rules have been in use, giving various measures in long tons. Today, tonnes are more commonly used. Ship displacement varies by a vessel's degree of load, from its empty weight as designed (known as "lightweight tonnage") to its maximum load. Numerous specific terms are used to describe varying levels of load and trim, detailed below. Ship displacement should not be confused with measurements of volume or capacity typically used for commercial vessels and measured by tonnage: net tonnage and gross tonnage. Calculation The process of determining a vessel's displacement begins with measuring its draft.George, 2005. p. 5. This is accomplished by means of its "draft marks". A merchant vessel has t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Destroyers Of The French Navy
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, maneuverable, long-endurance warship intended to escort larger vessels in a fleet, convoy, or carrier battle group and defend them against a wide range of general threats. They were conceived in 1885 by Fernando Villaamil for the Spanish NavySmith, Charles Edgar: ''A short history of naval and marine engineering.'' Babcock & Wilcox, ltd. at the University Press, 1937, page 263 as a defense against torpedo boats, and by the time of the Russo-Japanese War in 1904, these "torpedo boat destroyers" (TBDs) were "large, swift, and powerfully armed torpedo boats designed to destroy other torpedo boats". Although the term "destroyer" had been used interchangeably with "TBD" and "torpedo boat destroyer" by navies since 1892, the term "torpedo boat destroyer" had been generally shortened to simply "destroyer" by nearly all navies by the First World War. Before World War II, destroyers were light vessels with little endurance for unattended oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Destroyer Classes
In navy, naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, maneuverable, long-endurance warship intended to escort larger vessels in a Naval fleet, fleet, convoy, or carrier battle group and defend them against a wide range of general threats. They were conceived in 1885 by Fernando Villaamil for the Spanish NavySmith, Charles Edgar: ''A short history of naval and marine engineering.'' Babcock & Wilcox, ltd. at the University Press, 1937, page 263 as a defense against torpedo boats, and by the time of the Russo-Japanese War in 1904, these "torpedo boat destroyers" (TBDs) were "large, swift, and powerfully armed torpedo boats designed to destroy other torpedo boats". Although the term "destroyer" had been used interchangeably with "TBD" and "torpedo boat destroyer" by navies since 1892, the term "torpedo boat destroyer" had been generally shortened to simply "destroyer" by nearly all navies by the First World War. Before World War II, destroyers were light vessels with little endurance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Engineer (UK Magazine)
''The Engineer'' is a London-based monthly magazine and website covering the latest developments and business news in engineering and technology in the UK and internationally. History and description ''The Engineer'' was founded in January 1856. It was established by Edward Charles Healey, an entrepreneur and engineering enthusiast with financial interests in the railways whose friends included Robert Stephenson and Isambard Kingdom Brunel. The journal was created as a technical magazine for engineers. ''The Engineer'' began covering engineering including inventions and patents during a high point of British economic manufacturing power. In the 19th century it also published stock prices of raw materials. Together with the contemporary ''Engineering Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nantes
Nantes (, ; ; or ; ) is a city in the Loire-Atlantique department of France on the Loire, from the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast. The city is the List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, sixth largest in France, with a population of 320,732 in Nantes proper and a metropolitan area of nearly 1 million inhabitants (2020). With Saint-Nazaire, a seaport on the Loire estuary, Nantes forms one of the main north-western French metropolitan agglomerations. It is the administrative seat of the Loire-Atlantique Departments of France, department and the Pays de la Loire Regions of France, region, one of 18 regions of France. Nantes belongs historically and culturally to Brittany, a former Duchy of Brittany, duchy and Province of Brittany, province, and Reunification of Brittany, its omission from the modern administrative region of Brittany is controversial. Nantes was identified during classical antiquity as a port on the Loire. It was the seat of a bishopric at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rouen
Rouen (, ; or ) is a city on the River Seine, in northwestern France. It is in the prefecture of Regions of France, region of Normandy (administrative region), Normandy and the Departments of France, department of Seine-Maritime. Formerly one of the largest and most prosperous cities of medieval Europe, the population of the metropolitan area () is 702,945 (2018). People from Rouen are known as ''Rouennais''. Rouen was the seat of the Exchequer of Normandy during the Middle Ages. It was one of the capitals of the Anglo-Normans, Anglo-Norman and Angevin kings of England, Angevin dynasties, which ruled both England and large parts of modern France from the 11th to the 15th centuries. From the 13th century onwards, the city experienced a remarkable economic boom, thanks in particular to the development of textile factories and river trade. Claimed by both the French and the English during the Hundred Years' War, it was on its soil that Joan of Arc was tried and burned alive on 30 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( ; ; Gascon language, Gascon ; ) is a city on the river Garonne in the Gironde Departments of France, department, southwestern France. A port city, it is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Gironde department. Its inhabitants are called "''Bordelais'' (masculine) or "''Bordelaises'' (feminine). The term "Bordelais" may also refer to the city and its surrounding region. The city of Bordeaux proper had a population of 259,809 in 2020 within its small municipal territory of , but together with its suburbs and exurbs the Bordeaux Functional area (France), metropolitan area had a population of 1,376,375 that same year (Jan. 2020 census), the sixth-most populated in France after Paris, Lyon, Marseille, Lille, and Toulouse. Bordeaux and 27 suburban municipalities form the Bordeaux Métropole, Bordeaux Metropolis, an Indirect election, indirectly elected Métropole, metropolitan authority now in charge of wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyle Et Bacalan
The ''Société Anonyme de Travaux Dyle et Bacalan'' was formed in 1879 by the merger of the Belgian and ''Ateliers and Chantiers de Bacalan'' which had emerged from the bankruptcy of the Arman Brothers shipyard in 1867. The company entered the aviation market during the 1920s and merged with ''Ateliers et Chantiers du Sud-Ouest'' in 1930 to form ''Ateliers et Chantiers du Sud-Ouest et de Bacalan Reunis'', while spinning off its aviation activities as the Société Aérienne Bordelaise The ''Société Aérienne Bordelaise'' (; SAB) was an aircraft manufacturing company based in Bordeaux, France. The predecessor company, ''Dyle et Bacalan, Société de Travaux Dyle et Bacalan'' had been founded in 1879. History The ''Sociét� .... The combined company closed its doors in 1936. Among other endeavors, the company acquired the rights to build the Curitiba-Paranaguá railway line, executing its construction from 1870 to 1875 with the direction of Antonio Ferrucci and later of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oriflamme F Destroyer
The Oriflamme (from Latin ''aurea flamma'', "golden flame"), a pointed, blood-red banner flown from a gilded lance, was the sacred battle standard of the King of France and a symbol of divine intervention on the battlefield from God and Saint Denis in the Middle Ages. The oriflamme originated as the sacred banner of the Abbey of St. Denis, a monastery near Paris. When the oriflamme was raised in battle by the French royalty during the Middle Ages, most notably during the Hundred Years' War, no prisoners were to be taken until it was lowered. Through that tactic, they hoped to strike fear into the hearts of the enemy, especially the nobles, who could usually expect to be taken alive for ransom during such military encounters. In French, the term ''oriflamme'' has come to mean any banner with pointed ends by association with the form of the original. Legendary origin The Oriflamme was mentioned in the 11th-century ballad the ''Chanson de Roland'' (vv. 3093–5) as a royal banne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |