|
Bracketing Paradox
In linguistic morphology, the bracketing paradox concerns morphologically complex words which have more than one analysis, or '' bracketing'', e.g., one for phonology and one for semantics, and the two are not compatible, or brackets do not align. English examples Comparatives such as ''unhappier'' One type of a bracketing paradox found in English is exemplified by words like ''unhappier'' or ''uneasier''. Pesetsky, D. 1985. "Morphology and logical form." ''Linguistic Inquiry'' 16:193–246. The synthetic comparative suffix ''-er'' generally occurs with monosyllabic adjectives and a small class of disyllabic adjectives with the primary (and only) stress on the first syllable. Other adjectives take the analytic comparative ''more''. Thus, we have ''older'' and ''grumpier'', but ''more correct'' and ''more restrictive''. From a phonological perspective, this suggests that a word like ''uneasier'' must be formed by combining the suffix ''er'' with the adjective ''easy'', since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Morphology (linguistics)
In linguistics, morphology is the study of words, including the principles by which they are formed, and how they relate to one another within a language. Most approaches to morphology investigate the structure of words in terms of morphemes, which are the smallest units in a language with some independent meaning. Morphemes include roots that can exist as words by themselves, but also categories such as affixes that can only appear as part of a larger word. For example, in English the root ''catch'' and the suffix ''-ing'' are both morphemes; ''catch'' may appear as its own word, or it may be combined with ''-ing'' to form the new word ''catching''. Morphology also analyzes how words behave as parts of speech, and how they may be inflected to express grammatical categories including number, tense, and aspect. Concepts such as productivity are concerned with how speakers create words in specific contexts, which evolves over the history of a language. The basic fields of ling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Meaning (linguistics)
Semantics is the study of linguistic Meaning (philosophy), meaning. It examines what meaning is, how words get their meaning, and how the meaning of a complex expression depends on its parts. Part of this process involves the distinction between sense and reference. Sense is given by the ideas and concepts associated with an expression while reference is the object to which an expression points. Semantics contrasts with syntax, which studies the rules that dictate how to create grammatically correct sentences, and pragmatics, which investigates how people use language in communication. Lexical semantics is the branch of semantics that studies word meaning. It examines whether words have one or several meanings and in what lexical relations they stand to one another. Phrasal semantics studies the meaning of sentences by exploring the phenomenon of compositionality or how new meanings can be created by arranging words. Formal semantics (natural language), Formal semantics relies o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
List Of Paradoxes
This list includes well known paradoxes, grouped thematically. The grouping is approximate, as paradoxes may fit into more than one category. This list collects only scenarios that have been called a paradox by at least one source and have their own article in this encyclopedia. These paradoxes may be due to fallacious reasoning (falsidical), or an unintuitive solution (Veridical paradox, veridical). The term ''paradox'' is often used to describe a counter-intuitive result. However, some of these paradoxes qualify to fit into the mainstream viewpoint of a paradox, which is a self-contradictory result gained even while properly applying accepted ways of reasoning. These paradoxes, often called ''antinomy,'' point out genuine problems in our understanding of the ideas of truth and Definite description, description. Logic * : The supposition that, "if one of two simultaneous assumptions leads to a contradiction, the other assumption is also disproved" leads to paradoxical conseq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Navajo Language
Navajo or Navaho ( ; Navajo: or ) is a Southern Athabaskan languages, Southern Athabaskan language of the Na-Dene languages, Na-Dené family, through which it is related to languages spoken across the western areas of North America. Navajo is spoken primarily in the Southwestern United States, especially in the Navajo Nation. It is one of the most widely spoken Indigenous languages of the Americas#Northern America, Native American languages and is the most widely spoken north of the Mexico–United States border, with almost 170,000 Americans speaking Navajo at home as of 2011. The language has struggled to keep a healthy speaker base, although this problem has been alleviated to some extent by extensive education programs in the Navajo Nation. In World War II, speakers of the Navajo language joined the military and developed a code for sending secret messages. These Code talker#Navajo, code talkers' messages are widely credited with saving many lives and winning some of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Operator (linguistics)
In generative grammar, the technical term operator denotes a type of expression that enters into an a-bar movement dependency.Chomsky, Noam. (1981) Lectures on Government and Binding, Foris, Dordrecht.Haegeman, Liliane (1994) Introduction to Government and Binding Theory. Blackwell.Koopman, H., & Sportiche, D. (1982). Variables and the Bijection Principle. ''The Linguistic Review, 2'', 139-60. One often says that the operator "binds a variable". Cinque, Guglielmo (1991) Types of A-Bar Dependencies. MIT Press. Operators are often determiners, such as interrogatives ('which', 'who', 'when', etc.), or quantifiers ('every', 'some', 'most', 'no'), but adverbs such as sentential negation ('not') have also been treated as operators.Zanuttini, R. (1997) Negation and Clausal Structure: A Comparative Study of Romance Languages, Oxford University Press. It is also common within generative grammar to hypothesise phonetically empty operators whenever a clause type or construction exhibits sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
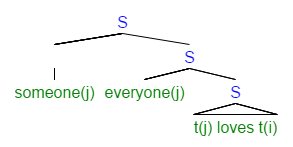 |
Logical Form (linguistics)
In generative grammar and related approaches, the logical form (LF) of a linguistic expression is the variant of its syntactic structure which undergoes formal semantics (linguistics), semantic interpretation. It is distinguished from ''phonetic form'', the structure which corresponds to a sentence's pronunciation. These separate mental representation, representations are postulated in order to explain the ways in which an expression's meaning can be partially independent of its pronunciation, e.g. scope (formal semantics)#Scope ambiguity, scope ambiguities. LF is the cornerstone of the classic generative view of the syntax-semantics interface. However, it is not used in Lexical Functional Grammar and Head-Driven Phrase Structure Grammar, as well as some modern variants of the generative approach. Syntax interfacing with semantics The notion of Logical Form was originally invented for the purpose of determining Quantifier (linguistics), quantifier scope. As the theory around t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Compound Word
In linguistics, a compound is a lexeme (less precisely, a word or Sign language, sign) that consists of more than one Word stem, stem. Compounding, composition or nominal composition is the process of word formation that creates compound lexemes. Compounding occurs when two or more words or signs are joined to make a longer word or sign. Consequently, a compound is a unit composed of more than one stem, forming words or signs. If the joining of the words or signs is orthographically represented with a hyphen, the result is a hyphenated compound (e.g., ''must-have'', ''hunter-gatherer)''. If they are joined without an intervening space, it is a closed compound (e.g., ''footpath'', ''blackbird''). If they are joined with a space (e.g. ''school bus, high school, lowest common denominator''), then the result – at least in English – may be an open compound. The meaning of the compound may be similar to or different from the meaning of its components in isolation. The component stem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Richard Sproat
Richard Sproat is a computational linguist currently working for Sakana AI as a research scientist. Prior to joining Sakana AI, Sproat worked for Google between 2012 and 2024 on text normalization and speech recognition. Linguistics Sproat graduated from Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1985, under the supervision of Kenneth L. Hale. His PhD thesis is one of the earliest work that derives morphosyntactically complex forms from the module which produces the phonological form that realizes these morpho-syntactic expressions, one of the core ideas in Distributed Morphology. One of Sproat's main contributions to computational linguistics is in the field of text normalization, where his work with colleagues in 2001, ''Normalization of non-standard words'', was considered a seminal work in formalizing this component of speech synthesis Speech synthesis is the artificial production of human speech. A computer system used for this purpose is called a speech synthesizer, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Stress (phonology)
In linguistics, and particularly phonology, stress or accent is the relative emphasis or prominence given to a certain syllable in a word or to a certain word in a phrase or sentence. That emphasis is typically caused by such properties as increased loudness and vowel length, full articulation of the vowel, and changes in tone. The terms ''stress'' and ''accent'' are often used synonymously in that context but are sometimes distinguished. For example, when emphasis is produced through pitch alone, it is called ''pitch accent A pitch-accent language is a type of language that, when spoken, has certain syllables in words or morphemes that are prominent, as indicated by a distinct contrasting pitch (music), pitch (tone (linguistics), linguistic tone) rather than by vol ...'', and when produced through length alone, it is called ''quantitative accent''. When caused by a combination of various intensified properties, it is called ''stress accent'' or ''dynamic accent''; Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Word
A word is a basic element of language that carries semantics, meaning, can be used on its own, and is uninterruptible. Despite the fact that language speakers often have an intuitive grasp of what a word is, there is no consensus among linguistics, linguists on its definition and numerous attempts to find specific criteria of the concept remain controversial. Different standards have been proposed, depending on the theoretical background and descriptive context; these do not converge on a single definition. Some specific definitions of the term "word" are employed to convey its different meanings at different levels of description, for example based on phonology, phonological, grammar, grammatical or orthography, orthographic basis. Others suggest that the concept is simply a convention used in everyday situations. The concept of "word" is distinguished from that of a morpheme, which is the smallest unit of language that has a meaning, even if it cannot stand on its own. Words a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Adjective
An adjective (abbreviations, abbreviated ) is a word that describes or defines a noun or noun phrase. Its semantic role is to change information given by the noun. Traditionally, adjectives are considered one of the main part of speech, parts of speech of the English language, although historically they were classed together with Noun, nouns. Nowadays, certain words that usually had been classified as adjectives, including ''the'', ''this'', ''my'', etc., typically are classed separately, as Determiner (class), determiners. Examples: * That's a ''funny'' idea. (Prepositive attributive) * That idea is ''funny''. (Predicate (grammar), Predicative) * * The ''good'', the ''bad'', and the ''funny''. (Substantive adjective, Substantive) * Clara Oswald, completely ''fictional'', died three times. (Apposition, Appositive) Etymology ''Adjective'' comes from Latin ', a calque of (whence also English ''epithet''). In the grammatical tradition of Latin and Greek, because adjectives were I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Suffix
In linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case endings, which indicate the grammatical case of nouns and adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs. Suffixes can carry grammatical information (inflectional endings) or lexical information ( derivational/lexical suffixes)''.'' Inflection changes the grammatical properties of a word within its syntactic category. Derivational suffixes fall into two categories: class-changing derivation and class-maintaining derivation. Particularly in the study of Semitic languages, suffixes are called affirmatives, as they can alter the form of the words. In Indo-European studies, a distinction is made between suffixes and endings (see Proto-Indo-European root). A word-final segment that is somewhere between a free morpheme and a bound morpheme is known as a suffixoidKremer, Marion. 1997. ''Person reference and gender in translation: a contrastive investigation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |