|
Bovine Submaxillary Mucin Coatings
300px, BSM can be derived from any bovine source. , right Bovine submaxillary mucin (BSM) coatings are a surface treatment provided to biomaterials intended to reduce the growth of disadvantageous bacteria and fungi such as '' S. epidermidis'', ''E. coli'', and ''Candida albicans''. BSM is a substance extracted from the fresh salivary glands of cows. It exhibits unique physical properties, such as high molecular weight and amphiphilicity, that allow it to be used for many biomedical applications. Each species possesses mucin-secreting submaxillary glands. Currently, eight different mucins have been identified for humans."Polymeric Biomaterials, Revised and Expanded." Google Books. Ed. Severian Dumitriu. N.p., n.d. Web. 5 May 2013. However, it is the mucin from bovine and porcine sources that have been used in several biomaterial applications. The most common use of BSM is in coatings for implanted materials. In such applications, the adsorption characteristics of BSM are integ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacas En Nicaragua
''Vacas'' (English: ''Cows'') is a 1991 Spanish film, written and directed by Julio Médem. The film stars Carmelo Gómez, Emma Suárez, Ana Torrent, and Karra Elejalde. An eerie family saga set in rural Basque Country, the cryptic film follows the intertwined story of three generations of two families from 1875 to 1936. It was Médem's first film and for it he won the 1993 Goya Award as Best New Director. Plot Fighting in the trenches of Biscay in 1875 during the Third Carlist War, Carmelo Mendiluze, an army sergeant, learns from a young errand boy named Ilegorri that Manuel Iriguíbel, his neighbor from his native village, has joined their exhausted battalion. Eager for news of his child's birth, Carmelo befriends the inexperienced soldier whose reputation as an expert aizcolari (competition log cutter) cannot conceal his apprehension and fear of armed combat. Panicking under fire, Manuel drops to the ground and smears himself with blood gushing hot from the neck of hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
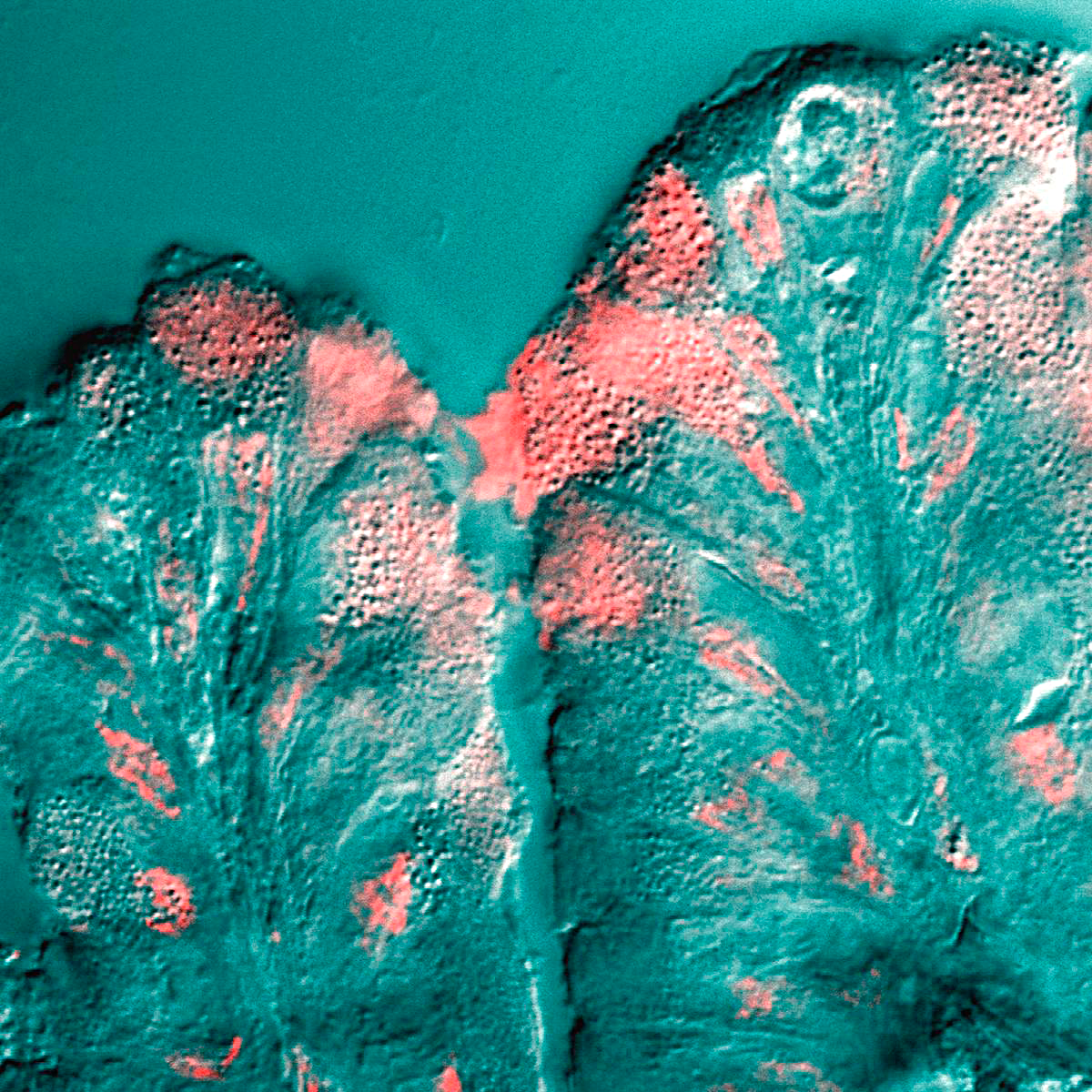
Mucus
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both Serous fluid, serous and mucous cells. It is a viscous colloid containing inorganic ions, inorganic salts, antimicrobial enzymes (such as lysozymes), Antibody, immunoglobulins (especially Immunoglobulin A, IgA), and glycoproteins such as lactoferrin and mucins, which are produced by goblet cells in the mucous membranes and submucosal glands. Mucus covers the Epithelium, epithelial cells that interact with outside environment, serves to protect the linings of the respiratory system, respiratory, Digestion#Digestive system, digestive, and Genitourinary system, urogenital systems, and structures in the Visual system, visual and auditory systems from pathogenic Fungus, fungi, bacteria and viruses. Most of the mucus in the body is produced in the gastrointestinal tract. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Modification Of Biomaterials With Proteins
Biomaterials are materials that are used in contact with biological systems. Biocompatibility and applicability of surface modification with current uses of metallic, polymeric and ceramic biomaterials allow alteration of properties to enhance performance in a biological environment while retaining bulk properties of the desired device. Surface modification involves the fundamentals of physicochemical interactions between the biomaterial and the physiological environment at the molecular, cellular and tissue levels (reduce bacterial adhesion, promote cell adhesion). Currently, there are various methods of characterization and surface modification of biomaterials and useful applications of fundamental concepts in several biomedical solutions. Function The function of surface modification is to change the physical and chemical properties of surfaces to improve the functionality of the original material. Protein surface modification of various types biomaterials (ceramics, polymers, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug Delivery
Drug delivery involves various methods and technologies designed to transport pharmaceutical compounds to their target sites helping therapeutic effect. It involves principles related to drug preparation, route of administration, site-specific targeting, metabolism, and toxicity all aimed to optimize efficacy and safety, while improving patient convenience and compliance. A key goal of drug delivery is to modify a drug's pharmacokinetics and specificity by combining it with different excipients, drug carriers, and medical devices designed to control its distribution and activity in the body. Enhancing bioavailability and prolonging duration of action are essential strategies for improving therapeutic outcomes, particularly in chronic disease management. Additionally, some research emphasizes on improving safety for the individuals administering the medication. For example, microneedle patches have been developed for vaccines and drug delivery to minimize the risk of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogel
A hydrogel is a Phase (matter), biphasic material, a mixture of Porosity, porous and Permeation, permeable solids and at least 10% of water or other interstitial fluid. The solid phase is a water Solubility, insoluble three dimensional network of polymers, having absorbed a large amount of water or biological fluids. Hydrogels have several applications, especially in the biomedical area, such as in hydrogel dressing. Many hydrogels are synthetic, but some are derived from natural materials. The term "hydrogel" was coined in 1894. Chemistry Classification The crosslinks which bond the polymers of a hydrogel fall under two general categories: physical hydrogels and chemical hydrogels. Chemical hydrogels have Covalent bond, covalent cross-linking bonds, whereas physical hydrogels have non-covalent bonds. Chemical hydrogels can result in strong reversible or irreversible gels due to the covalent bonding. Chemical hydrogels that contain reversible covalent cross-linking bonds, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BSM Adhesion
BSM may refer to: Education * Benilde-St. Margaret's, a Catholic, co-educational college prep school in Saint Louis Park, Minnesota, USA * Black-Scholes-Merton formula, a formula to calculate option prices * Black Student Movement, at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, US * Bloomingdale School of Music, Manhattan, New York City, New York, US * British School of Motoring, a British driving school *Budapest Semesters in Mathematics, program for North American students, Budapest, Hungary Military * Band Sergeant Major, a warrant officer appointment in the British Army * Battery Sergeant Major, a warrant officer appointment in some Commonwealth artillery corps *Bronze Star Medal Organizations * Bangladesh Society of Microbiologists *Big Scary Monsters Recording Company, a record label based in the UK * Brick Squad Monopoly, a subsidiary of the 1017 Brick Squad Record label * Blue Star Mothers Science and technology *Bag Source Message, corresponding to an airline bag tag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adhesion
Adhesion is the tendency of dissimilar particles or interface (matter), surfaces to cling to one another. (Cohesion (chemistry), Cohesion refers to the tendency of similar or identical particles and surfaces to cling to one another.) The forces that cause adhesion and cohesion can be divided into several types. The intermolecular forces responsible for the function of various kinds of stickers and sticky tape fall into the categories of chemical adhesion, dispersive adhesion, and diffusive adhesion. In addition to the cumulative magnitudes of these intermolecular forces, there are also certain emergent mechanical effects. Surface energy Surface energy is conventionally defined as the work (physics), work that is required to build an area of a particular surface. Another way to view the surface energy is to relate it to the work required to cleave a bulk sample, creating two surfaces. If the new surfaces are identical, the surface energy γ of each surface is equal to h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the chemical property of a molecule (called a hydrophobe) that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water. In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water. Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, thus, prefer other neutral molecules and nonpolar solvents. Because water molecules are polar, hydrophobes do not dissolve well among them. Hydrophobic molecules in water often cluster together, forming micelles. Water on hydrophobic surfaces will exhibit a high contact angle. Examples of hydrophobic molecules include the alkanes, oils, fats, and greasy substances in general. Hydrophobic materials are used for oil removal from water, the management of oil spills, and chemical separation processes to remove non-polar substances from polar compounds. The term ''hydrophobic''—which comes from the Ancient Greek (), "having a fear of water", constructed Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon. revised and augmented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (H-bond) is a specific type of molecular interaction that exhibits partial covalent character and cannot be described as a purely electrostatic force. It occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom, Covalent bond, covalently bonded to a more Electronegativity, electronegative donor atom or group (Dn), interacts with another electronegative atom bearing a lone pair of electrons—the hydrogen bond acceptor (Ac). Unlike simple Dipole–dipole attraction, dipole–dipole interactions, hydrogen bonding arises from charge transfer (nB → σ*AH), Atomic orbital, orbital interactions, and quantum mechanical Delocalized electron, delocalization, making it a resonance-assisted interaction rather than a mere electrostatic attraction. The general notation for hydrogen bonding is Dn−H···Ac, where the solid line represents a polar covalent bond, and the dotted or dashed line indicates the hydrogen bond. The most frequent donor and acceptor atoms are nitrogen (N), oxyg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrostatics
Electrostatics is a branch of physics that studies slow-moving or stationary electric charges. Since classical antiquity, classical times, it has been known that some materials, such as amber, attract lightweight particles after triboelectric effect, rubbing. The Greek language, Greek word (), meaning 'amber', was thus the Root (linguistics), root of the word ''electricity''. Electrostatic phenomena arise from the forces that electric charges exert on each other. Such forces are described by Coulomb's law. There are many examples of electrostatic phenomena, from those as simple as the attraction of plastic wrap to one's hand after it is removed from a package, to the apparently spontaneous explosion of grain silos, the damage of electronic components during manufacturing, and photocopier and laser printing, laser printer operation. The electrostatic model accurately predicts electrical phenomena in "classical" cases where the velocities are low and the system is macroscopic so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covalent Bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding. For many molecules, the sharing of electrons allows each atom to attain the equivalent of a full valence shell, corresponding to a stable electronic configuration. In organic chemistry, covalent bonding is much more common than ionic bonding. Covalent bonding also includes many kinds of interactions, including σ-bonding, π-bonding, metal-to-metal bonding, agostic interactions, bent bonds, three-center two-electron bonds and three-center four-electron bonds. The term "covalence" was introduced by Irving Langmuir in 1919, with Nevil Sidgwick using "co-valent link" in the 1920s. Merriam-Webster dates the specific phrase ''covalent bond'' to 1939, recognizing its first known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |