|
Bouteloua Radicosa
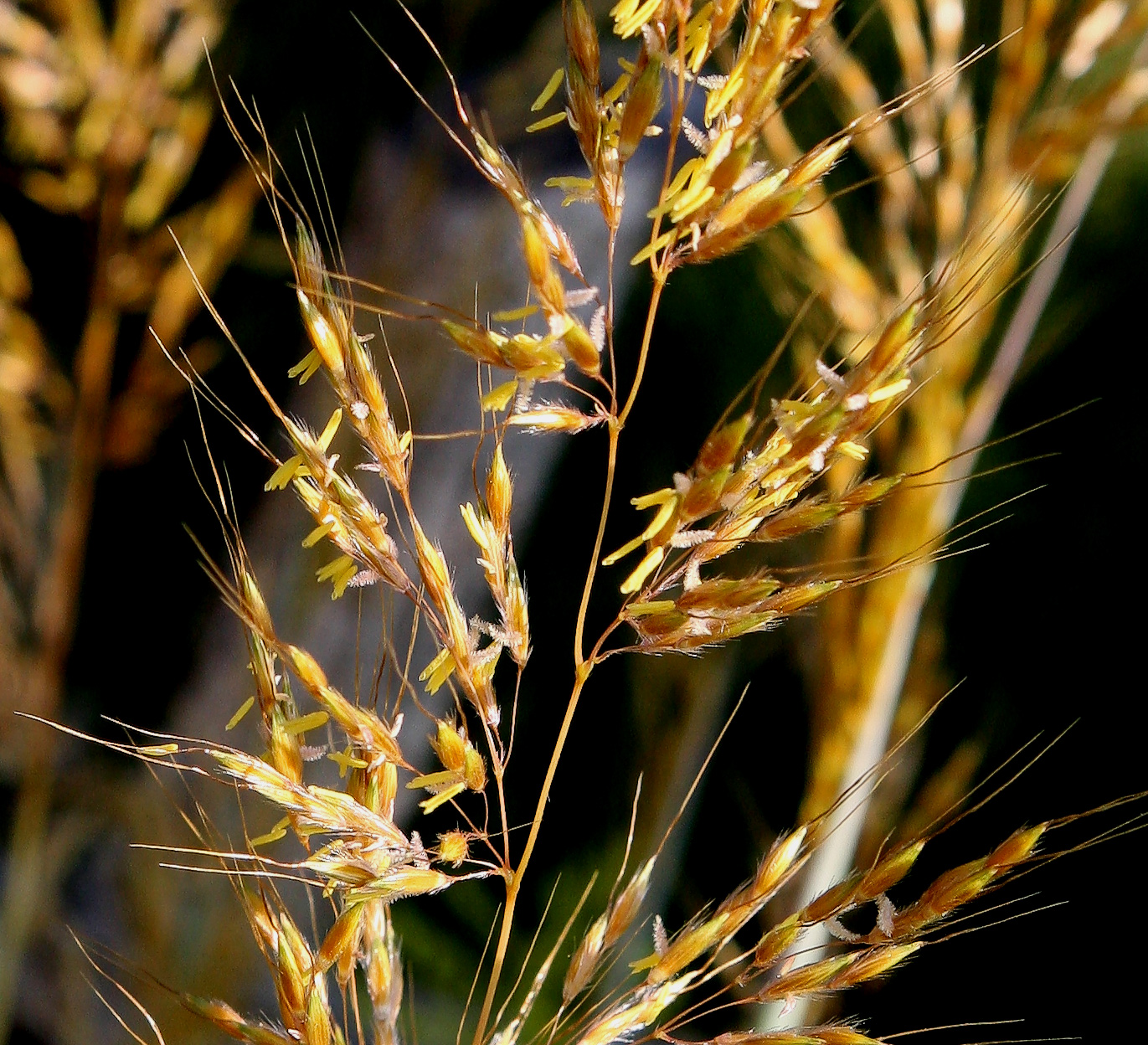
''Bouteloua radicosa'', colloquially known as purple grama, is a grass species in the grama genus native to the southwestern United States and northern Mexico. Description Purple grama is a perennial grass that grows to tall, with a dense rhizomatous base. It bears inflorescences in panicles that are long and usually have seven to twelve branches. Branches are to long and bear eight to eleven spikelets. Each spikelet bears two florets This glossary of botanical terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to botany and plants in general. Terms of plant morphology are included here as well as at the more specific Glossary of plant morphology and Glossary .... The lower floret has a three awned lemma. ''B. radicosa'' may hybridize with '' Bouteloua repens'' and '' Bouteloua williamsii'', which could contribute to its apparent diversity. Distribution Purple grama is found between and prefers desert grasslands or dry rocky slopes. It is present ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Griffiths (botanist)
David Griffiths (1867–1935) was an early 20th century American agronomist and botanist who was a specialist on fungi and on spermatophytes, seed-producing plants, especially cacti. Biography David Griffiths grew up in Dakota Territory after his family emigrated there from his birthplace of Aberystwyth, Wales. He attended South Dakota Agricultural College, receiving both a B.A. (1892) and an MSc (1893) from that institution. For a few years after leaving college, he taught high school science classes. In 1898, he began doctoral studies at Columbia University, focusing on fungi and publishing on such agriculturally important fungal diseases as powdery mildew, ergots, and Smut (fungus), smuts. After gaining his Ph.D. degree in 1900, he became a professor of botany at the University of Arizona Experiment Station, where he studied desert plants. A year later, he moved to the Bureau of Plant Industry of the United States Department of Agriculture, where he would spend a decade and a ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
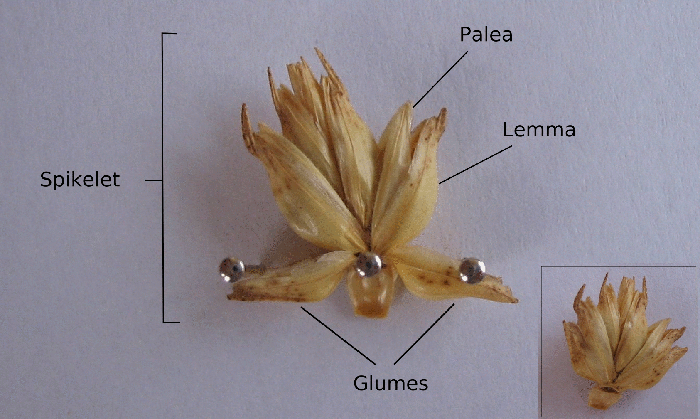
Lemma (botany)
A spikelet, in botany, describes the typical arrangement of the inflorescences of grasses, sedges and some other monocots. Each spikelet has one or more florets. The spikelets are further grouped into panicles or spikes. The part of the spikelet that bears the florets is called the rachilla. In grasses In Poaceae, the grass family, a spikelet consists of two (or sometimes fewer) bracts at the base, called glumes, followed by one or more florets. A floret consists of the flower surrounded by two bracts, one external (the lemma) and one internal (the palea). The perianth is reduced to two scales, called lodicules, that expand and contract to spread the lemma and palea; these are generally interpreted to be modified sepals. The flowers are usually hermaphroditic — maize being an important exception — and mainly anemophilous or wind-pollinated, although insects occasionally play a role. Lemma Lemma is a phytomorphological term referring to a part of the spikelet. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grasses Of The United States
Poaceae ( ), also called Gramineae ( ), is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos, the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns and pasture. The latter are commonly referred to collectively as grass. With around 780 genera and around 12,000 species, the Poaceae is the fifth-largest plant family, following the Asteraceae, Orchidaceae, Fabaceae and Rubiaceae. The Poaceae are the most economically important plant family, including staple foods from domesticated cereal crops such as maize, wheat, rice, oats, barley, and millet for people and as feed for meat-producing animals. They provide, through direct human consumption, just over one-half (51%) of all dietary energy; rice provides 20%, wheat supplies 20%, maize (corn) 5.5%, and other grains 6%. Some members of the Poaceae are used as building materials (bamboo, thatch, and straw); others can provide a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grasses Of Mexico
Poaceae ( ), also called Gramineae ( ), is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos, the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns and pasture. The latter are commonly referred to collectively as grass. With around 780 genera and around 12,000 species, the Poaceae is the fifth-largest :plant families, plant family, following the Asteraceae, Orchidaceae, Fabaceae and Rubiaceae. The Poaceae are the most economically important plant family, including staple foods from domesticated cereal crops such as maize, wheat, rice, oats, barley, and millet for people and as forage, feed for livestock, meat-producing animals. They provide, through direct human consumption, just over one-half (51%) of all dietary energy; rice provides 20%, wheat supplies 20%, maize (corn) 5.5%, and other grains 6%. Some members of the Poaceae are used as building materials (bamboo, thatch, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasive Species
An invasive species is an introduced species that harms its new environment. Invasive species adversely affect habitats and bioregions, causing ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage. The term can also be used for native species that become harmful to their native environment after human alterations to its food web. Since the 20th century, invasive species have become serious economic, social, and environmental threats worldwide. Invasion of long-established ecosystems by organisms is a natural phenomenon, but human-facilitated introductions have greatly increased the rate, scale, and geographic range of invasion. For millennia, humans have served as both accidental and deliberate dispersal agents, beginning with their earliest migrations, accelerating in the Age of Discovery, and accelerating again with the spread of international trade. Notable invasive plant species include the kudzu vine, giant hogweed (''Heracleum mantegazzianum''), Japanese knotw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bouteloua Williamsii
''Bouteloua'' is a genus of plants in the grass family Poaceae. Members of the genus are commonly known as grama grass. Description ''Bouteloua'' includes both annual and perennial grasses, which frequently form stolons. Species have an inflorescence of 1 to 80 racemes or spikes positioned alternately on the culm (stem). The rachis (stem) of the spike is flattened. The spikelets are positioned along one side of the spike. Each spikelet contains one fertile floret, and usually one sterile floret. Taxonomy The genus was first described by Mariano Lagasca in 1805. It was named for Claudio and Esteban Boutelou, 19th-century Spanish botanists. David Griffiths produced a 1912 monograph on the genus. Species Species of ''Bouteloua'' include: * ''Bouteloua alamosana'' Vasey – Mesoamerica * ''Bouteloua americana'' (L.) Scribn. – American grama – southern Mexico, Central America, West Indies, northern South America * ''Bouteloua annua'' Swallen – Baja California Sur, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bouteloua Repens
''Bouteloua repens'', colloquially known as slender grama, is a grass species in the grama genus native to the southwestern United States and northern Mexico. Description Slender grama is a perennial grass that appears similar to '' Bouteloua chondrosioides''. Leaves grow to tall. Its flowers are borne in inflorescences at the tip of culms in groups of four to twelve. The central lobe has an extended awn. The glumes are hairless. The orange or yellow anthers are in length. It does not form rhizomes. It is exceptionally resistant to cattle grazing. Distribution Slender grama prefers dry rocky slopes below , but will also tolerate most open areas of mixed soil types and can be found up . It is present in much of Arizona, as well as into Texas, New Mexico, and Mexico. It is also found in the Caribbean, and Central America as far south as Colombia and Venezuela Venezuela, officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a country on the northern coast of South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Awn (botany)
An awn is a hairy or bristle-like growth on a plant. On the seeds of grasses such as barley or rye, they form foxtails which assist seed dispersal by being barbed and so sticking to passing animals. Also, the awns may twist or curl as they are wetted and dry out and this action can make fallen seeds walk until they fall into a crevice into which they then burrow. Besides grasses, other families of plants which have awns include Asteraceae such as sunflowers and Geraniaceae such as geraniums. In the latter, the awns help disperse the seeds by developing a tension which then catapults the seeds when the seed head ripens and dries out. Description In grasses, awns typically extend from the lemmas of the florets. This often makes the hairy appearance of the grass synflorescence. Awns may be long (several centimeters) or short, straight or curved, single or multiple per floret. Some biological genera are named after their awns, such as the three-awns (''Aristida''). In s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bouteloua
''Bouteloua'' is a genus of plants in the grass family Poaceae. Members of the genus are commonly known as grama grass. Description ''Bouteloua'' includes both annual and perennial grasses, which frequently form stolons. Species have an inflorescence of 1 to 80 racemes or spikes positioned alternately on the culm (stem). The rachis (stem) of the spike is flattened. The spikelets are positioned along one side of the spike. Each spikelet contains one fertile floret, and usually one sterile floret. Taxonomy The genus was first described by Mariano Lagasca in 1805. It was named for Claudio and Esteban Boutelou, 19th-century Spanish botanists. David Griffiths produced a 1912 monograph on the genus. Species Species of ''Bouteloua'' include: * '' Bouteloua alamosana'' Vasey – Mesoamerica * '' Bouteloua americana'' (L.) Scribn. – American grama – southern Mexico, Central America, West Indies, northern South America * '' Bouteloua annua'' Swallen – Baja Californi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floret
This glossary of botanical terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to botany and plants in general. Terms of plant morphology are included here as well as at the more specific Glossary of plant morphology and Glossary of leaf morphology. For other related terms, see Glossary of phytopathology, Glossary of lichen terms, and List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names. A B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spikelet
A spikelet, in botany, describes the typical arrangement of the inflorescences of grasses, sedges and some other monocots. Each spikelet has one or more florets. The spikelets are further grouped into panicles or spikes. The part of the spikelet that bears the florets is called the rachilla. In grasses In Poaceae, the grass family, a spikelet consists of two (or sometimes fewer) bracts at the base, called glumes, followed by one or more florets. A floret consists of the flower surrounded by two bracts, one external (the lemma) and one internal (the palea). The perianth is reduced to two scales, called lodicules, that expand and contract to spread the lemma and palea; these are generally interpreted to be modified sepals. The flowers are usually hermaphroditic — maize being an important exception — and mainly anemophilous or wind-pollinated, although insects occasionally play a role. Lemma Lemma is a phytomorphological term referring to a part of the spikelet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |