|
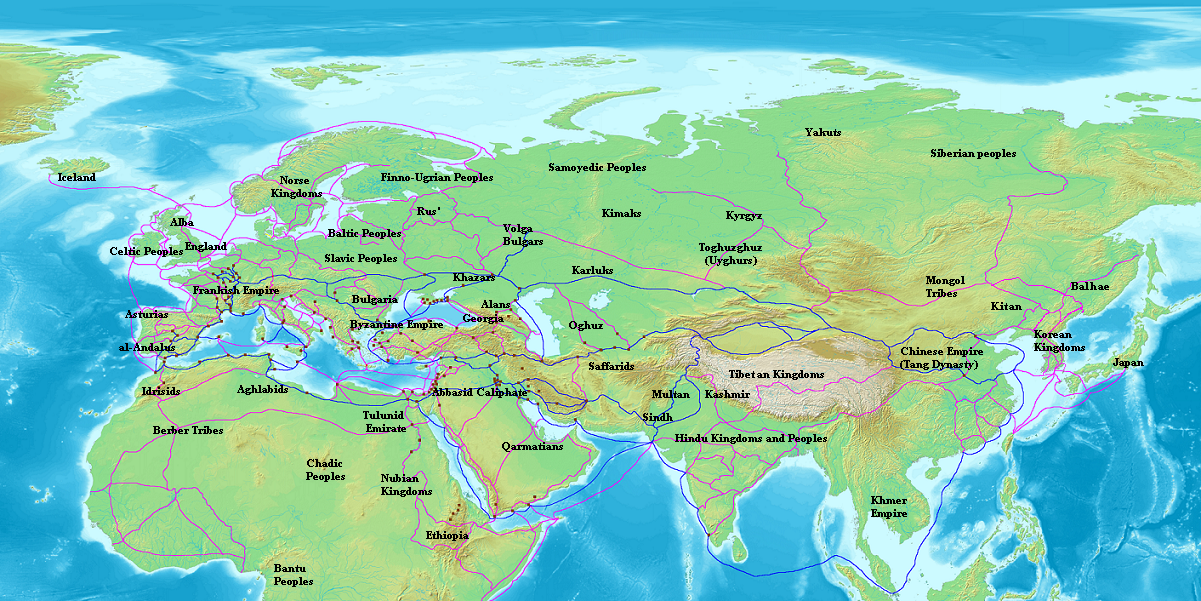
Book Of Roads And Kingdoms (ibn Khordadbeh)
The ''Book of Roads and Kingdoms'' () is a 9th-century geography text written by the Persian geographer Ibn Khordadbeh. It maps and describes the major trade routes of the time within the Muslim world, and discusses distant trading regions such as Japan, Korea, and China. It was written around 870 CE, during the reign of Al-Muʿtamid of the Abbasid Caliphate, while its author was Director of Posts and Police for the Abbasid province of Jibal in modern-day Iran Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort .... The work uses much of the Persian administrative terms, gives considerable attention to pre-Islamic Iranian history, and uses the "native Iranian cosmological division system of the world". These all show "the existence of Iranian sources at the core of the work". pp. 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radhanites
The Radhanites or Radanites (; ) were early medieval Jewish merchants, active in the trade between Christendom and the Muslim world during roughly the 8th to the 10th centuries. Many trade routes previously established under the Roman Empire continued to function during that period, largely through their efforts. Their trade network covered much of Europe, North Africa, the Middle East, Central Asia, and parts of India and China. Only a limited number of primary sources use the term, and it remains unclear whether they referred to a specific guild, to a clan, or generically to Jewish merchants in the trans-Eurasian trade network. Name Several etymologies have been suggested for the word "Radhanite". Many scholars, including Barbier de Meynard and Moshe Gil, believe it refers to a district in Mesopotamia called " the land of Radhan" in Arabic and Hebrew texts of the period. Another hypothesis suggests that the name might be derived from the city of Ray (Rhages) in northern Ira ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jibal
Jibāl (), also al-Jabal (), was the name given by the Arabs to a region and province located in western Iran, under the Umayyad and Abbasid Caliphates. Its name means "the Mountains", being the plural of ''jabal'' ("mountain, hill"), highlighting the region's mountainous nature in the Zagros. Between the 12th and 14th centuries, the name Jibal was progressively abandoned, and it came to be mistakenly referred to as ''ʿIrāq ʿAjamī'' ("Persian Iraq") to distinguish it from "Arab Iraq" in Mesopotamia. The region never had any precisely defined boundaries, but was held to be bounded by the Maranjab Desert in the east, by Fars and Khuzistan in the south, by Iraq in the south-west and west, by Adharbayjan in the north-west and by the Alborz Mountains in the north, making it roughly coterminous with the ancient country of Media. Under the Abbasid Caliphate, Jibal formed a separate province, with its capital usually at Rayy, until the Abbasids lost control in the early 10th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iranian Literature
Iranian literature, or Iranic literature, refers to the literature, literary traditions of the Iranian languages, developed predominantly in Iran and other regions in the Middle East and the Caucasus, eastern Anatolia, Asia Minor, and parts of western Central Asia and northwestern South Asia. These include works attested from as early as the 6th century BC. Modern Iranian literatures include Persian literature, Ossetian literature, Kurdish literature, Pashto literature and poetry, Pashto literature, and Balochi literature, among others. Classical and medieval eras Avestan The earliest surviving literary works in an Iranian language are that of the religious texts of the Avesta, written in Avestan, an Iranian languages#Old Iranian, Old Iranian sacred language. The oldest part of these are the Gathas (, , "hymn"), that are a collection of hymns believed to be composed by Zoroaster, the reformer of the ancient Iranian religion and the founder of Zoroastrianism, dating to the 6t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographical Works Of The Medieval Islamic World
Geography (from Ancient Greek ; combining 'Earth' and 'write', literally 'Earth writing') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. Geography has been called "a bridge between natural science and social science disciplines." Origins of many of the concepts in geography can be traced to Greek Eratosthenes of Cyrene, who may have coined the term "geographia" (). The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as the title of a book by Greek scholar Claudius Ptolemy (100 – 170 AD). This work created the so-called "Ptolemaic tradition" of geography, which included "Ptolemaic cartographic theory." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9th-century Arabic-language Books
The 9th century was a period from 801 (represented by the Roman numerals DCCCI) through 900 (CM) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Carolingian Renaissance and the Viking raids occurred within this period. In the Middle East, the House of Wisdom was founded in Abbasid Baghdad, attracting many scholars to the city. The field of algebra was founded by the Muslim polymath al-Khwarizmi. The most famous Islamic scholar Ahmad ibn Hanbal was tortured and imprisoned by Abbasid official Ahmad ibn Abi Du'ad during the reign of Abbasid caliph al-Mu'tasim and caliph al-Wathiq. In Southeast Asia, the height of the Mataram Kingdom happened in this century, while Burma would see the establishment of the major kingdom of Pagan. Tang China started the century with the effective rule under Emperor Xianzong and ended the century with the Huang Chao rebellions. In America, the Maya experienced widespread political collapse in the central Maya region, resulting in internecine warfar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Asiatique
The ''Journal asiatique'' (; full earlier title ''Journal Asiatique ou Recueil de Mémoires, d'Extraits et de Notices relatifs à l'Histoire, à la Philosophie, aux Langues et à la Littérature des Peuples Orientaux'') is a biannual peer-reviewed academic journal established in 1822 by the Société Asiatique covering Asian studies. It publishes articles in French and several other European languages. Cited texts are presented in their original languages. Each issue also includes news of the Société Asiatique and its members, obituaries of notable Orientalists, critical reviews, and books received. The journal is published by Peeters Publishers on behalf of the Société Asiatique and the editor-in-chief is Jean-Marie Durand. It is one of the oldest continuous French publications. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: Bibliographie linguistique/Linguistic Bibliography, ATLA Religion Database, Index to the Study of Religions Online, Index ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Barbier De Meynard
Charles Adrien Casimir Barbier de Meynard (; 6 February 1826 – 31 March 1908), born at sea on a ship from Constantinople to Marseille, was a nineteenth-century French historian and orientalist. Biography His studies focused on the early history of Islam and the Caliphate. Among his other works, he completed Julius von Mohl's translation of Ferdowsi's '' Shahnama'', with the French title ''Livre des Rois''. This was the first European translation of the pivotal work made available to a wide audience. Barbier de Meynard also translated numerous works by al-Masudi, ibn Khordadbeh and other Caliphate-era historians. He studied the history of Zoroastrianism, editing the ''Dictionnaire Géographique de la Perse'', and wrote about the then-nascent Baháʼí Faith. He was involved in the editing of the 19th-century edition of Crusader sources in Arabic with French translations, the Recueil des Historiens des Croisades. Barbier de Meynard was elected a foreign member of the Royal Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language that developed in early medieval England and has since become a English as a lingua franca, global lingua franca. The namesake of the language is the Angles (tribe), Angles, one of the Germanic peoples that Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, migrated to Britain after its End of Roman rule in Britain, Roman occupiers left. English is the list of languages by total number of speakers, most spoken language in the world, primarily due to the global influences of the former British Empire (succeeded by the Commonwealth of Nations) and the United States. English is the list of languages by number of native speakers, third-most spoken native language, after Mandarin Chinese and Spanish language, Spanish; it is also the most widely learned second language in the world, with more second-language speakers than native speakers. English is either the official language or one of the official languages in list of countries and territories where English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Iran
The history of Iran (also known as Name of Iran, Persia) is intertwined with Greater Iran, which is a socio-cultural region encompassing all of the areas that have witnessed significant settlement or influence exerted by the Iranian peoples and the Iranian languages chiefly the Persians and the Persian language. Central to this region is the Iranian plateau, now largely covered by Iran, modern Iran. The most pronounced impact of Iranian history can be seen stretching from Anatolia in the west to the Indus Valley in the east, including the Levant, Mesopotamia, the Caucasus, and parts of Central Asia. To varying degrees, it also overlaps or mingles with the histories of many other major civilizations, such as History of India, India, History of China, China, History of Greece, Greece, Ancient Rome, Rome, and History of Egypt, Egypt. Iran is home to one of the world's oldest continuous major civilizations, with historical and urban settlements dating back to 4000 BC. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the northeast, Afghanistan to the east, Pakistan to the southeast, and the Gulf of Oman and the Persian Gulf to the south. With a Ethnicities in Iran, multi-ethnic population of over 92 million in an area of , Iran ranks 17th globally in both List of countries and dependencies by area, geographic size and List of countries and dependencies by population, population. It is the List of Asian countries by area, sixth-largest country entirely in Asia and one of the world's List of mountains in Iran, most mountainous countries. Officially an Islamic republic, Iran is divided into Regions of Iran, five regions with Provinces of Iran, 31 provinces. Tehran is the nation's Capital city, capital, List of cities in Iran by province, largest city and financial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caliphate
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of the entire Muslim world (''ummah''). Historically, the caliphates were polities based on Islam which developed into multi-ethnic trans-national empires. During the medieval period, three major caliphates succeeded each other: the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661), the Umayyad Caliphate (661–750), and the Abbasid Caliphate (750–1517). In the fourth major caliphate, the Ottoman Caliphate, the rulers of the Ottoman Empire claimed caliphal authority from 1517 until the Ottoman caliphate was Abolition of the Caliphate, formally abolished as part of the Atatürk's reforms, 1924 secularisation of Turkey. An attempt to preserve the title was tried, with the Sharifian Caliphate, but this caliphate fell quickly after its conquest by the Sultanate o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibn Khordadbeh
Abu'l-Qasim Ubaydallah ibn Abdallah ibn Khordadbeh (; 820/825–913), commonly known as Ibn Khordadbeh (also spelled Ibn Khurradadhbih; ), was a high-ranking bureaucrat and geographer of Persian descent in the Abbasid Caliphate. He is the author of the earliest surviving Arabic book of administrative geography. Biography Ibn Khordadbeh was the son of Abdallah ibn Khordadbeh, who had governed the northern Iranian region of Tabaristan under the Abbasid caliph al-Mamun (), and in 816/17 conquered the neighbouring region of Daylam, as well as repelled the Bavandid '' ispahbadh'' (ruler) Shahriyar I () from the highlands of Tabaristan. Ibn Khordadbeh's grandfather was Khordadbeh, a former Zoroastrian who was convinced by the Barmakids to convert to Islam. He may have been the same person as Khordadbeh al-Razi, who had provided Abu'l-Hasan al-Mada'ini (died 843) the details regarding the flight of the last Sasanian emperor Yazdegerd III during the Arab conquest of Iran. Ib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |